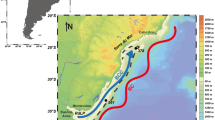
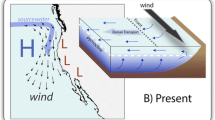
Abstract
To investigate to what extent episodic physical processes regulate nutrient availability and phytoplankton assemblages of the Mahon estuary (Minorca Island), we carried out an intensive field study during 2010–2011. During the study period, environmental conditions spanned from intense stratification to a continuous mixing and from lack of riverine inflow to intense runoff. Our data reveals a sequence of biogeochemical states of the estuary that result from the interplay between runoff, other non-periodic forcings (winds, sea level oscillations), and variations in water renewal. Seasonal runoff was revealed as a major driver of winter circulation and of the influx of inorganic nutrients, in particular nitrate. However, because of the combination between runoff and flushing time, the effects of floodwater events on phytoplankton are short-lived (days). Conversely, during summer, when freshwater influx declines, water renewal relies on pulsed atmospheric forcing that may be of local or remote origin. As depicted from the low nitrate concentrations (<1 μM) and enhanced ammonium (>1 μM), this change in circulation and external loads carries nutrient assimilation within the estuary head and forces the use of remnant nutrients through regenerating pathways to sustain an enhanced phytoplankton biomass at the lower estuary. Episodic variability represented between 52 and 65% of the annual chlorophyll variance. Despite the fact that episodic pulses represented intense departures from base biogeochemical state of the estuary, at time scale larger than weeks, the phytoplankton community composition and dynamics was largely regulated by the integrated effect of these episodes and other environmental drivers associated with seasonality rather than by individual storm events only. Our results suggest that even though the system presents good recovery capacity to individual storm episodes, it may be more vulnerable to increased nutrient fluxes during summer, as well as to changes in episode timing and frequency.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemany, F., S. Deudero, B. Morales-Nin, J.L. López-Jurado, J. Jansà, M. Palmer, and I. Palomera. 2006. Influence of physical environmental factors on the composition and horizontal distribution of summer larval fish assemblages off Mallorca island (Balearic archipelago, Western Mediterranean). Journal of Plankton Research 28: 473–487.
Alpert, P., T. Ben-Gai, A. Baharad, Y. Benjamini, D. Yekutieli, M. Colacino, L. Diodato, C. Ramis, V. Homar, R. Romero, S. Michaelides, and A. Manes. 2002. The paradoxical increase of Mediterranean extreme daily rainfall in spite of decrease in total values. Geophysical Research Letters 29: 1536. doi:10.1029/2001GL013554.
Andersen, P., and J. Throndsen. 2003. Estimating cell numbers. In Manual on harmful marine microalgae, ed. G.M. Hallegraeff, D.M. Anderson, and A.D. Cembella, 99–129. Paris: UNESCO Publishing.
Arin, L., J. Guillén, M. Segura-Noguera, and M. Estrada. 2013. Open sea hydrographic forcing of nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics in a Mediterranean coastal ecosystem. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 133: 116–128.
Basterretxea, G., A. Tovar-Sanchez, A.J. Beck, P. Masqué, H.J. Bokuniewicz, R. Coffey, C.M. Duarte, J. Garcia-Orellana, E. Garcia-Solsona, L. Martinez-Ribes, and R. Vaquer-Sunyer. 2010. Submarine groundwater discharge to the coastal environment of a Mediterranean island (Majorca, Spain): ecosystem and biogeochemical significance. Ecosystems 13: 629–643.
Beardsley, R.C. and L.K. Rosenfeld. 1983. Introduction to the CODE-1 moored array and large-scale data report. In CODE-1: Moored Array and Large-Scale Data Report, ed. L.K. Rosenfeld, Woods Hole Oceanogr. Inst. Tech. Rep. WHOI-83-23, CODE Tech. Rep. 21, 1216, Woods Hole, Massachusetts.
Blauw, A.N., E. Beninca, R.W.P.M. Laane, N. Greenwood, and J. Huisman. 2012. Dancing with the tides: Fluctuations of coastal phytoplankton orchestrated by different oscillatory models of the tidal cycle. PloS One 7: 1–14.
Boldrin, A., S. Carniel, M. Giani, M. Marini, F. Bernardi-Aubry, A. Campanelli, F. Grilli, and A. Russo. 2009. The effects of bora wind on physical and bio-chemical properties of stratified waters in the northern Adriatic. Journal of Geophysical Research 114: C08S92. doi:10.1029/2008JC004837.
Borum, J., and K. Sand-Jensen. 1996. Is total primary production in shallow coastal marine waters stimulated by nitrogen loading? Oikos 76: 406–410.
Chen, Z., C. Hu, F.E. Muller-Karger, and M.E. Luther. 2010. Short-term variability of suspended sediment and phytoplankton in Tampa Bay, Florida: Observations from a coastal oceanographic tower and ocean color satellites. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 89: 62–72.
Cloern, J.E., and A. Jassby. 2010. Patterns and scales of phytoplankton variability in estuarine–coastal ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 33: 230–241.
Cloern, J.E. 1991. Tidal stirring and phytoplankton bloom dynamics in an estuary. Journal of Marine Research 49: 203–221.
Dortch, Q., and T.E. Whitledge. 1992. Does nitrogen or silicon limit phytoplankton production in the Mississippi River plume and nearby regions? Continental Shelf Research 12: 1293–1309.
Doswell, C.A. III, C. Ramis, R. Romero, and S. Alonso. 1998. A diagnostic study for three heavy precipitation episodes in the western Mediterranean region. Weather and Forecasting 13: 102–124.
Dyer, K.R. 1997. Estuaries: A physical introduction. Chichester: Wiley and Sons.
Estrela, T., M. Menendez, M. Dimas, C. Marcuello, G. Rees, G. Cole, K. Weber, J. Grath, J. Leonard, N.B. Oveson, J. Feher, and V. Consulkt. 2001. Sustainable water use in Europe. Part 3: Extreme hydrological events: Floods and droughts. Environmental issue report No 21. Copenhagen: EEA.
Eyre, B.D., and A.J.P. Ferguson. 2006. Impact of a flood event on benthic and pelagic coupling in a sub-tropical east Australian Estuary (Brunswick). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 66: 111–122.
Garcés, E., and J. Camp. 2012. Habitat changes in the Mediterranean Sea and the consequences for harmful algal blooms formation. In Life in the Mediterranean Sea: A look at habitat changes, ed. Noga Stambler , 519–541. New York: Nova Science Publishers Inc.Chapter 19
Garnier, J., A. Sferratore, M. Meybeck, G. Billen, and H. Dürr. 2006. Modelling silica transfer processes in river catchments. In The silicon cycle. Human perturbations and impacts on aquatic systems, ed. V. Ittekkot, D. Unger, C. Humborg, and N. Tac An, 139–162. Washington D.C.: Island Press.Chapter 10
Geyer, W.R. 1997. Influence of wind on dynamics and flushing of shallow estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 44: 713–722.
Gillanders, B.M., and M.J. Kingsford. 2002. Impact of changes in flow of freshwater on estuarine and open coastal habitats and the associated organisms. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review 40: 233–309.
Giorgi, F. 2006. Climate change hot-spots. Geophysical Research Letters. 33: L08707.
Giorgi, F., and P. Lionello. 2008. Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Global and Planetary Change 63: 90–104.
Gobler, C.J., L.A. Cullison, F. Koch, T.M. Harder, and J.W. Krause. 2005. Influence of freshwater flow, ocean exchange, and seasonal cycles on phytoplankton–nutrient dynamics in a temporarily open estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 65: 275–288.
Gonella, J. 1972. A rotary-component method for analysing meteorological and oceanographic vector time series. Deep-Sea Research 19: 833–846.
Grasshoff, K., M. Ehrhardt, and K. Kremling. 1983. Methods of seawater analysis. Weinheim: Verlag-Chemie.
Guadayol, Ò., F. Peters, C. Marrasé, J.M. Gasol, C. Roldán, E. Berdalet, R. Massana, and A. Sabata. 2009. Episodic meteorological and nutrient load events as drivers of coastal ecosystem dynamics: A time series analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 381: 139–151.
Guizien, K., F. Charles, F. Lantoine, and J.J. Naudin. 2007. Nearshore dynamics of nutrients and chlorophyll during Mediterranean-type flash-floods. Aquatic Living Resources 20: 3–14.
Hall, N.S., H.W. Paerl, B.L. Peierls, A.C. Whipple, and K.L. Rossignol. 2013. Effects of climatic variability on phytoplankton biomass and community structure in the eutrophic, microtidal, New River Estuary, North Carolina, USA. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 117: 70–82.
Harding, L.W. Jr. 1994. Long-term trends in the distribution of phytoplankton in Chesapeake Bay: Roles of light, nutrients and streamflow. Marine Ecology Progress Series 104: 267–291.
Hearn, C.J. 1998. Application of the Stommel model to shallow Mediterranean estuaries and their characterization. Journal of Geophysical Research 103: 10391–10404.
Hearn, C.J., and B.J. Robson. 2002. On the effects of wind and tides on the hydrodynamics of a shallow Mediterranean estuary. Continental Shelf Research 22: 2655–2672.
Howarth, R.W. 1988. Nutrient limitation of net primary production in marine ecosystems. Annual Review in Ecology 19: 89–110.
Jordi, A., G. Basterretxea and D.P. Wang. 2009a. Evidence of sediment resuspension by island trapped waves. Geophysical Research Letters 36. doi: L18610
Jordi, A., G. Basterretxea, and S. Anglès. 2009b. Influence of ocean circulation on phytoplankton biomass distribution in the Balearic Sea: Study based on sea-viewing wide field-of-view sensor and altimetry satellite data. Journal of Geophysical Research 114: C11005.
Jordi, A., G. Basterretxea, and D.P. Wang. 2011. Local versus remote wind effects on the coastal circulation of a microtidal bay in the Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Marine Systems 88: 312–322. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2011.05.007.
Largier, J.L., J.T. Hollibaugh, and S.V. Smith. 1997. Seasonally hypersaline estuaries in Mediterranean-climate regions. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 45: 789–797.
Levin, L.A., D.F. Boesch, A. Covich, C. Dahm, C. Erséus, K.C. Ewel, R.T. Kneib, A. Moldenke, M.A. Palmer, and P. Snelgrove. 2001. The function of marine critical transition zones and the importance of sediment biodiversity. Ecosystems 4: 430–451.
Lichter, M., M. Klein, and D. Zviely. 2011. Dynamic morphology of small south-eastern Mediterranean river mouths: A conceptual model. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 36: 547–562.
Lipizer, M., C. De Vittor, C. Falconi, C. Comici, F. Tamberlich, and M. Giani. 2012. Effects of intense physical and biological forcing factors on CNP pools in coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic Sea). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 115: 40–50.
Lorenz, E. N. 1956. Empirical orthogonal functions and statistical weather prediction. Sci. Rep. 1, 49 pp., Mass. Inst. of Technol., Cambridge.
Malej, A., P. Mozetič, V. Malačič, and V. Turk. 1997. Response of summer phytoplankton to episodic meteorological events (Gulf of Trieste, Adriatic Sea). PSZNI Marine Ecology 18: 273–288.
Mallin, M.A., M.H. Posey, M.R. McIver, D.C. Parsons, S.H. Ensign, and T.D. Alphin. 2002. Impacts and recovery from multiple hurricanes in a Piedmont-coastal plain river system. Bioscience 52: 999–1010.
Martínez-Soto, M.C., G. Basterretxea, E. Garcés, S. Anglès, A. Jordi, and A. Tovar-Sánchez. 2015. Species-specific variation in the phosphorus nutritional sources by microphytoplankton in a Mediterranean estuary. Frontiers in Marine Science 2: 54. doi:10.3389/fmars.2015.00054.
Mooers, C. 1973. A technique for analysis of pair complex-valued time series. Deep-Sea Research 20: 1129–1141.
Nakane, T., K. Nakaka, H. Bouman, and T. Platt. 2008. Environmental control of short-term variation in the plankton community of inner Tokyo Bay, Japan. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 78: 796–810.
Nicolau, R., A. Galera-Cunha, and Y. Lucas. 2006. Transfer of nutrients and labile metals from the continent to the sea by a small Mediterranean river. Chemosphere 63: 469–476.
Nielsen, E., and K. Richardson. 1996. Can changes in the fisheries yield in the Kattegat (1950–1992) be linked to changes in primary production? ICES Journal of Marine Science 53: 988–994.
O’Callaghan, J., C. Pattiaratchi, and H. Hamilton. 2007. The response of circulation and salinity in a micro-tidal estuary to sub-tidal oscillations in coastal sea surface. Continental Shelf Research 27: 1947–1965.
Paerl, H.W. 1997. Coastal eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: Importance of atmospheric deposition and groundwater as “new” nitrogen and other nutrient sources. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1154–1165.
Palomera, I. 1992. Spawning of anchovy Engraulis encrasicolus in the Northwestern Mediterranean relative to hydrographic features in the region. Marine Ecology Progress Series. 79: 215–223.
Parsons, T.R., Y. Maita, and C.M. Lalli. 1984. A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Pinckney, J.L., H.W. Paerl, and M.B. Harrington. 1999. Responses of the phytoplankton community growth rate to nutrient pulses in variable estuarine environments. Journal of Phycology 35: 1455–1463.
Pitcher, G.C., A.J. Boyd, D.A. Horstman, and B.A. Mitchell-Innes. 1998. Subsurface dinoflagellate populations, frontal blooms and the formation of red tide in the southern Benguela upwelling system. Marine Ecology Progress Series 172: 253–264.
Rabalais, N.N., R.E. Turner, R.J. Diaz, and D. Justic. 2009. Global change and eutrophication of coastal waters. ICES Journal of Marine Science 66: 1528–1537.
Ramos, A.M., N. Cortesi, and R.M. Trigo. 2014. Circulation weather types and spatial variability of daily precipitation in the Iberian Peninsula. Frontiers in Earth Science 2: 25. doi:10.3389/feart.2014.00025.
Rodellas, V., J. Garcia-Orellana, P. Masqué, and J.S. Font-Muñoz. 2015. The influence of sediment sources on radium-derived estimates of Submarine Groundwater Discharge. Marine Chemistry 171: 107–117.
Romero, E., F. Peters, L. Arin, and J. Guillén. 2014. Decreased seasonality and high variability of coastal plankton dynamics in an urban location of the NW Mediterranean. Journal of Sea Research 88: 130–143.
Romero, R., J.A. Guijarro, C. Ramis, and S. Alonso. 1998. A 30 year (1964-1993) daily rainfall data base for the Spanish Mediterranean regions: First exploratory study. International Journal of Climatology 18: 541–560.
Rudek, J., H.W. Paerl, M.A. Mallin, and P.W. Bates. 1991. Seasonal and hydrological control of phytoplankton nutrient limitation in the lower Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina. Marine Ecology Progress Series 75: 133–142.
Scavia, D., J.C. Field, D.F. Boesch, R.W. Buddemeier, D.R. Cayan, V. Burkett, M. Fogarty, M. Harwell, R. Howarth, C. Mason, D.J. Reed, T.C. Royer, A.H. Sallenger, and J.G. Titus. 2002. Climate change impacts on U.S. coastal and marine ecosystems. Estuaries 25: 149–164.
Siokou-Frangou, I., U. Christaki, M.G. Mazzocchi, M. Montresor, M. Ribera d'Alcalà, D. Vaqué, and A. Zingone. 2010. Plankton in the open Mediterranean Sea: A review. Biogeosciences 7: 1543–1586.
Sferratore, A., J. Garnier, G. Billen, D. Conley, and S. Pinault. 2006. Silica diffuse and point sources in the Seine watershed. Environmental Science and Technology 40: 6630–6635.
Smayda, T.J. 1997. Harmful algal blooms: Their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1137–1153. doi:10.4319/lo.1997.42.5_part_2.1137.
Spatharis, S., G. Tsirtsis, D. Danielidis, T. Do Chi, and D. Mouillot. 2007. Effects of pulsed nutrient inputs on phytoplankton assemblage structure and blooms in an enclosed coastal area. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 73: 807–815.
Stanley, S.M. 1973. An explanation for Cope’s rule. Evolution 27: 1–26.
Thompson, P.A., T.D. O’Brien, H.W. Paerl, B.L. Peierls, P.J. Harrison, and M. Robb. 2015. Precipitation as a driver of phytoplankton ecology in coastal waters: A climatic perspective. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 162: 119–129.
Tomasko, D.A., C. Anastasiou, and C. Kovach. 2006. Dissolved oxygen dynamics in Charlotte Harbor and its contributing watershed, in response to Hurricanes Charley, Frances, and Jeanne impacts and recovery. Estuaries and Coasts 29: 932–938.
Torrence, C., and G.P. Compo. 1998. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 79: 61–78.
Tzoraki, O., and N.P. Nikolaidis. 2007. A generalized framework for modeling the hydrologic and biogeochemical response of a Mediterranean temporary river basin. Journal of Hydrology 346: 112–121.
Ubertini, M., S. Lefebvre, A. Gangnery, K. Grangere, R. Le Gendre, and F. Orvain. 2012. Spatial variability of benthic-pelagic coupling in an estuary ecosystem: Consequences for microphytobenthos resuspension phenomenon. PloS One 7: e44155. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044155.
Valiela, I., P. Peckol, C. D’Avanzo, J. Kremer, D. Hersh, K. Foreman, K. Lajtha, B. Seely, W.R. Geyer, T. Isaji, and R. Crawford. 1998. Ecological effects of major storms on coastal watersheds and coastal waters: Hurricane Bob on Cape Cod. Journal of Coastal Research 14: 218–238.
Yeager, C.L.J., L.W. Harding, and M.E. Mallonee. 2005. Phytoplankton production, biomass and community structure following a summer nutrient pulse in Chesapeake Bay. Aquatic Ecology 39: 135–149.
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the “Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad” MINECO grants EHRE (CTM2009-08270) and GRADIENTS (CTM2012-39476-C02-01). A Jordi’s work was carried out under a Ramón y Cajal contract from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness. We are indebted to “Puertos del Estado” and “Autoritat Portuaria de Balears” for support during sampling and providing data from their archives. We are also grateful to Rafael Quintana, Itziar Álvarez, and Ana Massanet for assistance in fieldwork. Meteorological data were provided by the “Agencia Estatal de Meteorología (AEMET)” and sea level data by the “Puertos del Estado,” and watershed information was obtained from the IDE-Menorca (Consell Insular). We are grateful for the constructive comments of the two anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Dennis Swaney
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basterretxea, G., Jordi, A., Martínez-Soto, M.C. et al. Episodic Biogeochemical Variability in a Low-Flow Mediterranean Estuary. Estuaries and Coasts 40, 1247–1262 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-017-0212-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-017-0212-7