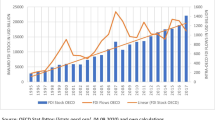
Abstract
As a deficient form of governance, corruption hinders FDI by increasing transaction costs and uncertainty. However, the heterogeneity in findings reported from primary studies has made testing competing hypotheses about the role of corruption on FDI difficult. The paper aims to identify and, if any, measure the authentic empirical effect of corruption on FDI by conducting a meta-regression analysis based upon 616 estimation results from 81 studies. The result suggests a negative authentic empirical effect of corruption on FDI supporting the hypothesis of corruption sands the wheels of foreign direct investment. The marginal effect of corruption changes in direction and magnitude due to the type of FDI (stocks or flows), the corruption index, the estimation technique, the unit, and the time period, used in the primary studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data available upon request.
Code availability
The code available upon request.
References
Abotsi AK, Iyavarakul T (2015) Tolerable level of corruption for foreign direct investment in Africa. Contemp Econ 9(3):249–270
Abotsi AK (2014) Analysis of corruption and foreign direct investment in Africa. Doctoral dissertation, National Institute of Development Administration
Aidt TS (2003) Economic analysis of corruption: a survey. Econ J 113(491):F632–F652
Akinlabi AO, Hamed B, Awoniyi MA (2011) Corruption, foreign direct investment and economic growth in Nigeria: an empirical investigation. J Res Int Bus Manag 1(9):278–292
Al Farooque O, Yarram SR (2013) Evidence on two-way relationships between foreign direct investment inflows and country-level individual governance indicators. Singapore Econ Rev (SER) 58(02):1–26
Alemu AM (2012) Effects of corruption on FDI inflow in Asian economies. Seoul J Econ 25(4):387–412
Ali FA, Fiess N, MacDonald R (2010) Do institutions matter for foreign direct investment? Open Econ Rev 21(2):201–219
Al-Sadig A (2009) The effects of corruption on FDI inflows. Cato J 29:267
Amal M, Tomio BT, Raboch H (2010) Determinants of Foreign direct investment in latin america*/Determinantes de la inversión directa externa en Latinoamérica/ Determinantes do investimento estrangeiro directo na América Latina. Revista De Globalización, Competitividad y Gobernabilidad 4(3):116
Anyanwu JC (2012) Why does foreign direct investment go where it goes?: New evidence from African countries. Ann Econ Financ 13(2):425–462
Asiedu E (2006) Foreign direct investment in Africa: the role of natural resources, market size, government policy, institutions and political instability. World Econ 29(1):63–77
Azam M, Ahmad SA (2013) The effects of corruption on foreign direct investment inflows: some empirical evidence from less developed countries. J Appl Sci Res 9(6):3462–3467
Barassi MR, Zhou Y (2012) The effect of corruption on FDI: a parametric and non-parametric analysis. Eur J Polit Econ 28(3):302–312
Basemera S, Mutenyo J, Hisali E, Bbaale E (2012) Foreign direct investment inflows to East Africa: do institutions matter. J Bus Manag Appl Econ 1(5):49–71
Bayar Y, Alakbarov N (2016) Corruption and foreign direct investment inflows in emerging market economies. Ecoforum J 5(2):303–308
Belgibayeva A, Plekhanov A (2015) Does corruption matter for sources of foreign direct investment?. European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Working Paper No. 176
Belgibayeva A, Plekhanov A (2016) Does corruption matter for sources of foreign direct investment?. Birkbeck College, University of London, Working Paper No. BWPEF 1604
Bellos S, Subasat T (2012a) Corruption and foreign direct investment: a panel gravity model approach. Bull Econ Res 64(4):565–574
Bellos S, Subasat T (2012b) Governance and foreign direct investment: a panel gravity model approach. Int Rev Appl Econ 26(3):303–328
Bénassy-Quéré A, Coupet M, Mayer T (2007) Institutional determinants of foreign direct investment. World Econ 30(5):764–782
Blundell-Wignall A, Roulet C (2017) Foreign direct investment, corruption and the OECD Anti-Bribery Convention”, OECD Working Papers on International Investment, 2017/01
Brada JC, Drabek Z, Perez MF (2012) The Effect of home-country and host-country corruption on foreign direct investment. Rev Dev Econ 16(4):640–663
Busse M, Hefeker C (2007) Political risk, institutions and foreign direct investment. Eur J Polit Econ 23(2):397–415
Castro C, Nunes P (2013) Does corruption inhibit foreign direct investment? Política Revista De Ciencia Política 51(1):61
Coffman C (2015) Institutions, distance, and foreign direct investment. Honors theses. Paper 779.
Cuervo-Cazurra A (2008) Better the devil you don’t know: types of corruption and FDI in transition economies. J Int Manag 14(1):12–27
Daude C, Stein E (2007) The quality of institutions and foreign direct investment. Econ Politics 19(3):317–344
Dauti B (2015) Determinants of foreign direct investment in South East European countries and new member states of European Union countries. Econ Bus Rev Central South-Eastern Eur 17(1):93
De Dominicis L, Florax RJ, De Groot HL (2008) A meta‐analysis on the relationship between income inequality and economic growth. Scott J Polit Econ 55(5):654–682
Doucouliagos H, Ulubaşoğlu MA (2008) Democracy and economic growth: a meta-analysis. Am J Politic Sci 52(1):61–83
Efendic A, Pugh G, Adnett N (2011) Institutions and economic performance: a meta-regression analysis. Eur J Polit Econ 27(3):586–599
Egger P, Winner H (2005) Evidence on corruption as an incentive for foreign direct investment. Eur J Polit Econ 21(4):932–952
Egger P, Winner H (2006) How corruption influences foreign direct investment: a panel data study. Econ Dev Cult Change 54(2):459–486
Epaphra M, Massawe J (2017) The effect of corruption on foreign direct investment: a panel data study. Turk Econ Rev 4(1):19
Fan JP, Morck R, Xu LC, Yeung B (2009) Institutions and foreign direct investment: China versus the rest of the world. World Dev 37(4):852–865
Farazmand H, Moradi M (2014) Determinants of foreign direct investment: does democracy matter? (Determinanty Priamych Zahraničných Investícií: Aký Je Význam Demokracie?). Medzinarodne Vztahy (j Int Relat) 12(4):318–333
Gammoudi M, Cherif M (2016) Capital account openness, political institutions and FDI in MENA region: an empirical investigation. J Econ Develop, 41(2).
Globerman S, Shapiro D (2002) Global foreign direct investment flows: the role of governance infrastructure. World Dev 30(11):1899–1919
Godinez JR, Liu L (2015) Corruption distance and FDI flows into Latin America. Int Bus Rev 24(1):33–42
Gök A (2020) The role of financial development on carbon emissions: a meta regression analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(11):11618–11636
Grosse R, Trevino LJ (2005) New institutional economics and FDI location in Central and Eastern Europe. MIR Manag Int Rev 45:123–145
Habib M, Zurawicki L (2001) Country-level investments and the effect of corruption—some empirical evidence. Int Bus Rev 10(6):687–700
Habib M, Zurawicki L (2002) Corruption and foreign direct investment. J Int Bus Stud 33(2):291–307
Helmy HE (2013) The impact of corruption on FDI: is MENA an exception? Int Rev Appl Econ 27(4):491–514
Hossain S (2016) Foreign direct investment (FDI) and corruption: Is it a major hindrance for encouraging inward FDI? Afr J Bus Manag 10(10):256
Hossain T, Keep W, Peters S (2012) Corruption and foreign direct investment: the moderating effect of bilateral tax treaties. Int J Bus Insights Transf, 4
Hsu YH (2007) Is corruption a grabbing hand? A panel data study of FDI. Graduate institute of political economy. National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan, pp 1–18
Jadhav P (2012) Determinants of foreign direct investment in BRICS economies: analysis of economic, institutional and political factor. Proc Soc Behav Sci 37:5–14
Jayaram A (2004) Corruption and foreign direct investment: A cross-country study. MA dissertation
Karim ZA, Zaidi MAS, Ismail MA, Karim BA (2012) The quality of institutions and foreign direct investment (FDI) in Malaysia. Asian J Account Govern 3:61–69
Ketkar KW, Murtuza A, Ketkar SL (2005) Impact of corruption on foreign direct investment and tax revenues. J Public Budg Account Financ Manag 17(3):313
Kolnes VL (2016) Foreign direct investment and corruption. An econometric analysis of the multidimensional effects of corruption upon FDI inflow. Master's thesis, The University of Bergen
Kurul Z, Yalta AY (2017) Relationship between institutional factors and FDI flows in developing countries: new evidence from dynamic panel estimation. Economies 5(2):17
Lee CH, Cook S, Lee JS, Han B (2016) Comparison of two meta-analysis methods: inverse-variance-weighted average and weighted sum of z-scores. Genom Inform 14(4):173–180
Leff NH (1964) Economic development through bureaucratic corruption. Am Behav Sci 8(3):8–14
Mádr M, Kouba L (2015) Does the political environment affect inflows of foreign direct investment? Evidence from emerging markets. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae Et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis 63(6):2017–2026
Mathur A, Singh K (2013) Foreign direct investment, corruption and democracy. Appl Econ 45(8):991–1002
Melo L, Quinn MA (2015) Oil, foreign direct investment and corruption. Int J Bus Finance Res 9(1):33
Mengistu AA, Adhikary BK (2011) Does good governance matter for FDI inflows? evidence from Asian economies. Asia Pac Bus Rev 17(3):281–299
Mudambi R, Navarra P, Delios A (2013) Government regulation, corruption, and FDI. Asia Pac J Manag 30(2):487–511
Munga J (2012) Corruption, political institutions and foreign direct investments: a disagregated study. Doctoral dissertation, University of Alabama Libraries
Muzurura J (2016) Is public corruption the main cause of low foreign direct investment in Zimbabwe? Br J Econ Finance Manag Sci 13(1):1–18
Navickas V, Navickas M, Kordoš M (2016) Corruption effect on foreign direct investments in European Union countries. Bus Theory Pract 17:299
Niatsetski AY (2011) The effects of host country institutions and corruption on foreign direct investment flows: empirical evidence and robustness of indicators. MA dissertation, Erasmus University
Nugraha I (2013) The impact of corruption and money laundering on foreign direct investment in ASEAN. Jurnal Ekonomi Kuantitatif Terapan 6(2):106–111
Ofori D, Ato-Mensah S, Jinsheng Z (2015) Corruption, foreign direct investment and growth in Ghana: an empirical analysis. Eur J Bus Manag 7(23):1–9
Ohlsson MH (2007) Impact of corruption on FDI a cross-country analysis. MA dissertation, Jönköping International Business School
Okafor G (2015) Locational determinants of US outward fdi into sub-saharan Africa. J Develop Areas 49(1):187–205
Okafor G, Piesse J, Webster A (2015) The motives for inward FDI into Sub-Saharan African countries. J Policy Model 37(5):875–890
Paul S, Portes LSV (2010) Corruption and foreign direct investment. Franklin Bus Law J 33(4):92–97
Qian X, Sandoval-Hernandez J (2016) Corruption distance and foreign direct investment. Emerg Mark Financ Trade 52(2):400–419
Quazi RM (2014) Corruption and foreign direct investment in East Asia and South Asia: an econometric study. Int J Econ Financ Issues 4(2):231
Quazi R, Vemuri V, Soliman M (2014) Impact of corruption on foreign direct investment in Africa. Int Bus Res 7(4):1
Revilla SS, Bayacag PG (2013) Corruption and foreign direct investment in the Philippines. In: Philippine Agricultural and Development Association, Bienial Convention. (Conference Paper)
Romer P (1994) New goods, old theory, and the welfare costs of trade restrictions. J Dev Econ 43(1):5–38
Sarkar H, Hasan MA (2001) Impact of corruption on the efficiency of investment: Evidence from a cross-country analysis. Asia Pac Dev J 8(2):111–116
Sarmidi T, Nor AHSM, Ridzuan S (2015) Environmental stringency, corruption and foreign direct investment (Fdi): lessons from global evidence. Asian Acad Manag J Account Financ (AAMJAF) 11(1):85–96
Schmaljohann M (2013) Enhancing foreign direct investment via transparency? Evaluating the effects of the EITI on FDI (No. 538). Discussion Paper Series, University of Heidelberg, Department of Economics
Senturia JJ (1931) Corruption, political. Encycl Soc Sci 4:448–452
Shleifer A, Vishny RW (1994) Politicians and firms. Q J Econ 109(4):995–1025
Smailbegović L (2015) The impact of corruption on foreign direct investments in transition countries. MA dissertation, University of Sarajevo, School of Economics and Business
Stanley TD (2005) Beyond publication bias. J Econ Surv 19(3):309–345
Stanley TD (2008) Meta-regression methods for detecting and estimating empirical effects in the presence of publication selection. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 70(2):103–127
Stanley TD, Doucouliagos H (2012) Meta-regression analysis in economics and business, vol 5. Routledge
Stanley TD, Doucouliagos H, Giles M, Heckemeyer JH, Johnston RJ, Laroche P, Rosenberger RS (2013) Meta-analysis of economics research reporting guidelines. J Econ Surv 27(2):390–394
Stein E, Daude C (2001) Institutions, integration and the location of foreign direct investment. New horizons for foreign direct investment. OECD Publishing, Paris, pp 101–128
Subasat T, Bellos S (2013) Corruption and foreign direct investment in Latin America: a panel gravity model approach. J Manag Sustain 3(4):151
Tosun MU, Yurdakul MO (2016) An Inquiry on the likely effects of corruption on the foreign direct investments in Turkey. Hacettepe Üniversitesi İktisadi Ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi 34(4):71–96
Touny MA (2016) The interactive effects of corruption and political instability on foreign direct investment: evidence from the Middle East region. Int J Trade Global Mark 9(4):370–385
Udenze O (2014) The effect of corruption on foreign direct investments in developing countries. Park Place Econ 22(1):87–95
Ugur M (2014) Corruption’s direct effects on per-capita income growth: a meta-analysis. J Econ Surv 28(3):472–490
Wah SH (2009) Is corruption endogenous to foreign direct investment in resource-rich developing economies?. Graduate Theses and Dissertations, Iowa State University. 11015
Wei SJ (2000) How taxing is corruption on international investors? Rev Econ Stat 82(1):1–11
Woo JY, Heo U (2009) Corruption and foreign direct investment attractiveness in Asia. Asian Politics Policy 1(2):223–238
Yuan J (2016) How corruption affect foreign direct investment. MA dissertation, Aalborg University, International Business Economic
Zhao JH, Kim SH, Du J (2003) The impact of corruption and transparency on foreign direct investment: an empirical analysis. MIR Manag Int Rev 43:41–62
Zhou Y (2007) An empirical study of the relationship between corruption and FDI: with sample selection error correction. The University of Birmingham Economics Department, Birmingham
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All stages of the paper are done by single author, who is AG
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gök, A. Whether corruption sands or greases the wheels of foreign direct investment: a meta-regression analysis. Int Rev Econ 70, 477–501 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12232-023-00428-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12232-023-00428-5