Abstract
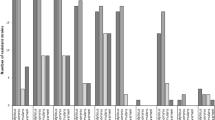
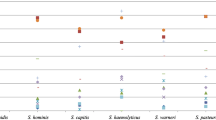
The virulence factors, antibiotic resistance patterns, and the associated genetic elements have been investigated in Staphylococcus species. A total of 100 strains has been isolated from clinical samples in the Microbiology Laboratory of Hesperia Hospital, Modena, Italy, and identified as Staphylococcus aureus (65), Staphylococcus epidermidis (24), Staphylococcus hominis (3), Staphylococcus saprophyticus (3), and Staphylococcus warneri (5). All the strains were analyzed to determine phenotypic and genotypic characters, notably the virulence factors, the antibiotics susceptibility, and the genetic determinants. The highest percentage of resistance in Staphylococcus spp. was found for erythromycin and benzylpenicillin (87% and 85%, respectively). All S. aureus, two S. epidermidis (8.3%), and one S. saprophyticus (33.3%) strains were resistant to oxacillin. The methicillin resistance gene (mecA) was detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification in 65 S. aureus strains and in 3 coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) (8.6%). With regard to the virulence characteristics, all the S. aureus were positive to all virulence tests, except for slime test. Among the CoNS isolates, 19 (79.1%) S. epidermidis and one (33.3%) S. saprophyticus strains resulted positive for the slime test only. The results obtained are useful for a more in-depth understanding of the function and contribution of S. aureus and CoNS antibiotic resistance and virulence factors to staphylococcal infections. In particular, the production of slime is very important for CoNS, a virulence factor frequently found in infections caused by these strains. Further investigations on the genetic relatedness among strains of different sources will be useful for epidemiological and monitoring purposes and will enable us to develop new strategies to counteract the diffusion of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and CoNS strains not only in clinical field, but also in other related environments.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
References
Ahmad-Mansour N, Loubet P, Pouget C, Dunyach-Remy C, Sotto A, Lavigne JP, Molle V (2021) Staphylococcus aureus toxins: an update on their pathogenic properties and potential treatments. Toxins (Basel) 13:677. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13100677
Algammal AM, Hetta HF, Elkelish A, Alkhalifah DHH, Hozzein WN, Batiha GE, El Nahhas N, Mabrok MA (2020) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): one health perspective approach to the bacterium epidemiology, virulence factors, antibiotic-resistance, and zoonotic impact. Infect Drug Resist 13:3255–3265. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S272733
Argemi X, Matelska D, Ginalski K, Riegel P, Hansmann Y, Bloom J, Pestel-Caron M, Dahyot S, Lebeurre J, Prévost G (2018) Comparative genomic analysis of Staphylococcus lugdunensis shows a closed pan-genome and multiple barriers to horizontal gene transfer. BMC Genomics 19:621. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-4978-1
Argemi X, Hansmann Y, Prola K, Prevost G (2019) Coagulase-negative staphylococci pathogenomics. Int J Mol Sci 20:1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051215
Baldassarri L, Simpson WA, Donelli G, Christensen GD (1993) Variable fixation of staphylococcal slime by different histochemical fixatives. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 12:866–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02000411
Becker K, Both A, Weißelberg S, Heilmann C, Rohde H (2020) Emergence of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 18:349–366. https://doi.org/10.1080/14787210.2020.1730813
Booth MC, Pence LM, Mahasreshti P, Callegan MC, Gilmore MS (2001) Clonal associations among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from various sites of infection. Infect Immun 69:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.69.1.345-352.2001.Erratum.In:InfectImmun69:1976
Burlak C, Hammer CH, Robinson MA, Whitney AR, McGavin MJ, Kreiswirth BN, Deleo FR (2007) Global analysis of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus exoproteins reveals molecules produced in vitro and during infection. Cell Microbiol 9:1172–1190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00858.x
Cadieux B, Vijayakumaran V, Bernards MA, McGavin MJ, Heinrichs DE (2014) Role of lipase from community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain USA300 in hydrolyzing triglycerides into growth-inhibitory free fatty acids. J Bacteriol 196:4044–4056. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.02044-14
Campbell SJ, Deshmukh HS, Nelson CL, Bae IG, Stryjewski ME, Federspiel JJ, Tonthat GT, Rude TH, Barriere SL, Corey R, Fowler VG Jr (2008) Genotypic characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a multinational trial of complicated skin and skin structure infections. J Clin Microbiol 46:678–684. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01822-07
Cherifi S, Byl B, Deplano A, Nagant C, Nonhoff C, Denis O, Hallin M (2014) Genetic characteristics and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from patients with catheter-related bloodstream infections and from colonized healthcare workers in a Belgian hospital. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 4:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-0711-13-20
Choi SM, Kim SH, Kim HJ, Lee DG, Choi JH, Yoo JH, Kang JH, Shin WS, Kang MW (2003) Multiplex PCR for the detection of genes encoding aminoglycoside modifying enzymes and methicillin resistance among Staphylococcus species. J Korean Med Sci 18:631–636. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2003.18.5.631
Costa SS, Sobkowiak B, Parreira R, Edgeworth JD, Viveiros M, Clark TG, Couto I (2019) Genetic diversity of norA, coding for a main efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus. Front Genet 9:710. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00710
European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing EUCAST (2023) Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters version 13.1. http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints
Fey PD, Olson ME (2010) Current concepts in biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Future Microbiol 5:917–933. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.10.56
França A, Gaio V, Lopes N, Melo LDR (2021) Virulence Factors in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Pathogens 10:170. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10020170
Fredheim EG, Klingenberg C, Rohde H, Frankenberger S, Gaustad P, Flaegstad T, Sollid JE (2009) Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus haemolyticus. J Clin Microbiol 47:1172–1180. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01891-08
García-Malinis AJ, Milagro A, Torres Sopena L, Gilaberte Y (2021) Staphylococcus lugdunensis skin infection: report of 16 cases. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed) 112:261–265. English, Spanish. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ad.2019.05.017
Heilmann C, Ziebuhr W, Becker K (2019) Are coagulase-negative staphylococci virulent? Clin Microbiol Infect 25:1071–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2018.11.012
Iseppi R, Sabia C, Bondi M, Mariani M, Messi P (2020) Virulence factors, drug resistance and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas species isolated from healthcare water systems. Curr Microbiol 77:1737–1745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01990-9
Jessen O, Faber V, Rosendal K, Eriksen KR (1959) Some properties of Staphylococcus aureus, possibly related to pathogenicity. Part 1. A study of 446 strains from different types of human infection. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 47:316–326
Jiang N, Li J, Feßler AT, Wang Y, Schwarz S, Wu C (2019) Novel pseudo-staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec element (φSCCmecT55) in MRSA ST9. J Antimicrob Chemother 74:819–820. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dky457
Khan S, Marasa BS, Sung K, Nawaz M (2021) Genotypic characterization of clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from Pakistan. Pathogens 10:918. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10080918
Khodabux RMJ, Mariappan S, Sekar U (2023) Spectrum of virulence factors in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and prevalence of SCCmec types in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a tertiary care center. J Lab Physicians 15:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1764483
Lachica RV, Genigeorgis C, Hoeprich PD (1971) Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl Microbiol 21:585–587. https://doi.org/10.1128/am.21.4.585-587.1971
Lakhundi S, Zhang K (2018) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: molecular characterization, evolution, and epidemiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 31:e00020-e118. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00020-18
Larsson DGJ, Flach CF (2022) Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat Rev Microbiol 20:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-021-00649-x
Makris G, Wright JD, Ingham E, Holland KT (2004) The hyaluronate lyase of Staphylococcus aureus - a virulence factor? Microbiology (reading) 150:2005–2013. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.26942-0
Marincola G, Liong O, Schoen C, Abouelfetouh A, Hamdy A, Wencker FDR, Marciniak T, Becker K, Köck R, Ziebuhr W (2021) Antimicrobial resistance profiles of coagulase-negative staphylococci in community-based healthy individuals in Germany. Front Public Health 9:684456. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.684456
Matos JE, Harmon RJ, Langlois BE (1995) Lecithinase reaction of Staphylococcus aureus strains of different origin on Baird-Parker medium. Lett Appl Microbiol 21:334–335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.1995.tb01073
Metwally LA, Hashem AA, ElAzab SZ, El Islam HN, Mansour MK (2017) Biofilm production and antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus epidermidis in catheter related bloodstream infections. Egypt J Med Microbiol 26:73–80. https://doi.org/10.12816/0046254
Michalik M, Samet A, Podbielska-Kubera A, Savini V, Międzobrodzki J, Kosecka-Strojek M (2020) Coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) as a significant etiological factor of laryngological infections: a review. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 19:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12941-020-00367-x
Motallebi M, Jabalameli F, Asadollahi K, Taherikalani M, Emaneini M (2016) Spreading of genes encoding enterotoxins, haemolysins, adhesin and biofilm among methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains with staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type III. A isolated from burn patients. Microb Pathog 97:34–37
Nashev D, Toshkova K, Salasia SIO, Hassan AA, Lämmler C, Zschöck M (2004) Distribution of virulence genes of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from stable nasal carriers. FEMS Microbiol Lett 233:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2004.01.032
Nayak N, Satpathy G (2000) Slime production as a virulence factor in Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from bacterial keratitis. Indian J Med Res 111:6–10
Peck KR, Baek JY, Song JH, Ko KS (2009) Comparison of genotypes and enterotoxin genes between Staphylococcus aureus isolates from blood and nasal colonizers in a Korean hospital. J Korean Med Sci 24:585–591. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2009.24.4.585
Petrillo F, Pignataro D, Di Lella FM, Reibaldi M, Fallico M, Castellino N, Parisi G, Trotta MC, D’Amico M, Santella B, Folliero V, Della Rocca MT, Rinaldi M, Franci G, Avitabile T, Galdiero M, Boccia G (2021) Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns and resistance trends of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci strains isolated from ocular infections. Antibiotics (Basel) 10:527. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10050527
Preda M, Mihai MM, Popa LI, Dițu LM, Holban AM, Manolescu LSC, Popa GL, Muntean AA, Gheorghe I, Chifiriuc CM, Popa MI (2021) Phenotypic and genotypic virulence features of staphylococcal strains isolated from difficult-to-treat skin and soft tissue infections. PLoS ONE 16:e0246478. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0246478
Rosenstein R, Götz F (2013) What distinguishes highly pathogenic staphylococci from medium- and non-pathogenic? Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 358:33–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2012_286
Shallcross LJ, Fragaszy E, Johnson AM, Hayward AC (2013) The role of the panton-valentine leucocidin toxin in staphylococcal disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 13:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70238-4
Sharma S, Mohler J, Mahajan SD, Schwartz SA, Bruggemann L, Aalinkeel R (2023) Microbial biofilm: a review on formation, infection, antibiotic resistance, control measures, and innovative treatment. Microorganisms 11:1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061614
Taylor TA, Unakal CG (2023) Staphylococcus aureus infection. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441868/. PMID: 28722898
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland TL, Fowler VG Jr (2015) Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 28:603–661. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00134-14
Zhan XY, Zhu QY (2018) Evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: evidence of positive selection in a penicillin-binding protein (PBP) 2a coding gene mecA. Infect GeNet Evol 59:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2018.01.018
Zhao H, Xu S, Yang H, He C, Xu X, Hu F, Shu W, Gong F, Zhang C, Liu Q (2019) Molecular typing and variations in amount of tst gene expression of TSST-1-producing clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Front Microbiol 10:1388. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, C.S.; methodology, N.P, R.I., and C.C.; validation, P.M., C.S., and A.D.C.; formal analysis, N.P, C.C., and R.I.; investigation, N.P, C.C., and R.I.; resources, C.S., A.D.C., and P.M.; data curation, S.G., C.C., and R.I.; writing—original draft preparation, C.S., R.I., A.D.C., and P.M.; writing—review and editing, A.D.C., C.C., and S.G.; visualization, C.S., R.I., A.D.C., and P.M.; supervision, C.S.; project administration, P.M. and C.S.; funding acquisition, P.M., C.S., and A.D.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pedretti, N., Iseppi, R., Condò, C. et al. Characterization of virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from clinical samples. Folia Microbiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-024-01148-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-024-01148-1