Abstract
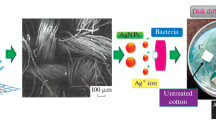
The article presents a comparison of innovative technologies of producing silver nanoparticles directly on fibrous structures using digital printing and screen printing. The research was focused on the antibacterial modification of cotton fabric using an in-situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Moreover, for the first time, the evaluation of two techniques of modification, taking into account the antibacterial effect and the consumption of chemicals, water, and energy in both processes were presented. Silver nanoparticles were prepared by direct reduction of the paste/ink containing silver salt on the fibres using screen and ink-jet printing techniques. The deposition of silver nanoparticles was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy, Raman dispersive spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The durability of the antibacterial effect against washing was estimated by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Both printing techniques allow obtaining cotton fabric with long-lasting antibacterial properties (50 items of washing) against strains of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. However, the digital printing method is more environmentally friendly due to lower water and energy usage and four times lower silver concentration in fabric compared to the conventional, screen-printing method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Montazer and T. Harifi in “Nanofinishing of Textile Materials” (M. Montazer and T. Harifi Eds.), pp.1–17, Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 2018.
H. Schoenberger and T. Schaefer, “Texte 14/03 — Best Available Techniques in Textile Industry”, pp.42–57, Federal Environmental Agency, Berlin, 2003.
K. Fletcher, “Sustainable Fashion and Textiles: Design Journeys”, Routledge, 2014.
C. Cie, “Ink Jet Textile Printing”, British Library, Elsevier, Woodhead Publishing, 2015.
J. Pulit-Prociak and M. Banach, Open Chem., 14, 76 (2016).
F. F. Larese, F. D’Agostin, M. Crosera, G. Adami, N. Renzi, M. Bovenzi, and G. Maina, Toxicology, 255, 33 (2009).
A. B. G. Landsdown, J. Wound Care, 11, 125 (2002).
J. Roszak, A. Smok-Pieniazek, S. Spryszynska, K. Kowalczyk, K. Domeradzka-Gajda, R. Swiercz, J. Grobelny, E. Tomaszewska, K. Ranoszek-Soliwoda, G. Celichowski, M. Cieslak, D. Puchowicz, and M. Stepnik, J. Hazard Mater., 392, 122442 (2020).
M. V. D. Z. Park, A. M. Neigh., J. P. Vermeulen, L. J. J. de la Fonteyne, H. W. Verharen, and J. J. Briedé, Biomaterials, 32, 9810 (2011).
E. A. Melnik, Y. P. Buzulukov, V. F. Demin, V. A. Demin, I. V. Gmoshinski, N. V. Tyshko, and V. A. Tutelyan, Acta Naturae, 5, 107 (2013).
C. Castellini, S. Ruggeri, S. Mattioli, G. Bernardini, L. Macchioni, and E. Moretti, Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med., 60, 143 (2014).
L. Hritcu, M. Stefan, L. Ursu, A. Neagu, M. Mihasan, and L. Tartau, Cent. Eur. J. Biol., 6, 497 (2011).
Y. Liu, W. Guan, G. Ren, and Z. Yang, Toxicol. Lett., 209, 227 (2012).
S. A. Blaster, M. Scheringer, M. MacLeod, and K. Hungerbuhler, Sci. Total Environ., 390, 396 (2008).
H. Saleem and S. J. Zaidi, Materials, 13, 5134 (2020).
H. A. Abu-Qdais, M. A. Abu-Dalo, and Y. Y. Hajeer, Sustainability, 13, 3436 (2021).
L. Pourzahedi, M. Vance, and M. J. Eckelman, Environ. Sci. Technol., 51, 7148 (2017).
M. Pollinim, M. Russo, and A. Licciulli, J. Mat. Sci: Mater. Med., 20, 2361 (2009).
H. J. Lee, S. Y. Yeo, and S. H. Jeong, J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Med., 38, 2199 (2003).
J. Scholza, G. Nocke, F. Hollstein, and A. Weissbach, Surf. Coat. Technol., 192, 252 (2005).
F. Zhang, X. Wu, Y. Chen, and H. Lin, Fiber. Polym., 10, 496 (2009).
E. Matyjas-Zgondek, A. Bacciarelli, E. Rybicki, M. I. Szynkowska, and M. Kołodziejczyk, Fibres Text East Eur., 69, 108 (2008).
P. Lyczkowska, M. Cieslak, J. Grobelny, and I. Kaminska in “Nanoczastki i Nanomaterialy” (J. Gromadzinska and W. Wasowicz Eds.), pp.73–83, Lodz: Zarząd Glowny Polskiego Towarzystwa Toksykologicznego, Lodz, 2013.
Z. Ma, M. Yin, Z. Qi, and X. Ren, Fiber. Polym., 19, 2097 (2018).
R. Begam, M. Joshi, and R. R. Purwar, Fiber. Polym., 23, 148 (2022).
A. Bacciarelli-Ulacha, E. Rybicki, E. Matyjas-Zgondek, A. Pawlaczyk, and M. I. Szynkowska, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 53, 4147 (2014).
Z. G. Gök, A. Demiral, O. Bozkaya, and M. Yiğitoğlu, Polym. Bull., 78, 7241 (2021).
G. Montes-Hernandez, M. Di Girolamo, G. Sarret, S. Bureau, A. Fernandez-Martinez, C. Lelong, and E. E. Vernain, ACS Omega, 6, 1316 (2021).
N. I. Khan, A. G. Maddaus, and E. Song, Biosensors, 8, 7 (2018).
R. M. El-Shishtawy, A. M. Asiri, N. A. M. Abdelwahed, and M. M. Al-Otaibi, Cellulose, 18, 75 (2011).
A. M. El Badawy, K. G. Scheckel, M. Suidan, and T. Tolaymat, Sci. Total Environ., 429, 325 (2012).
B. V. Crist, XPS, “Handbook of the Elements and Native Oxides”, XPS International Inc., 1999.
D. Briggs and M. P. Seah (Eds.), “Practical Surface Analysis: By Auger and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy”, Ap. Auger and Photoelectron Energies, 503, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 1983.
D. Puchowicz, P. Giesz, M. Kozanecki, and M. Cieślak, Talanta, 195, 516 (2019).
K. Kavkler and A. Demsar, Spectrochim Acta Part A, 78, 740 (2011).
C. B. Wang, G. Deo, and I. E. Wachs, J. Phys. Chem. B, 103, 5645 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bacciarelli-Ulacha, A., Matyjas-Zgondek, E., Puchowicz, D. et al. Comparison of Innovative Silver Nanoparticles Finishing Technologies to Obtain Antibacterial Properties of Cotton Fabric. Fibers Polym 23, 2606–2615 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4327-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4327-5