Abstract
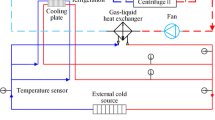
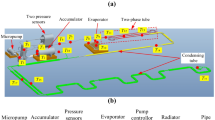
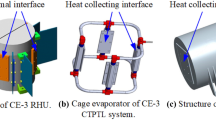
According to the characteristics of science payload, an adaptive design is made for the centrifuge thermal control system of standard experiment rack and the thermal control system is optimized due to the constraints of platform resources. Referring to the operating conditions of in-orbit environment, it compares the advantages and disadvantages of vapor compression refrigeration, the Stirling cycle and thermoelectric cooler. Finally, the two-stage thermal control scheme combined air–liquid heat exchanger with thermoelectric cooler is chose. In consideration of the actual condition in orbit, a ground mirror-image experiment platform is built to carry out the thermal performance experiments of thermal control system under variable working conditions, such as different science payload heat load, different temperature of liquid supply on platform, and voltage change of thermoelectric cooling component. By means of experimental research, it verifies the rationality of the thermal control system and obtains the thermal control parameters status under the in-orbit condition, which improves the safety and reliability of the system. Once the experiment rack is launched with Space Station in the future, the space-ground comparison between the in-orbit equipment and the ground mirror-image experimental platform will provide more data reference for the study of the influence of microgravity.



























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Brendel, L.P.M., Caskey, S.L., Ewert, M.K., Hengeveld, D., Braun, J.E., Groll, E.A.: Review of vapor compression refrigeration in microgravity environments. Int. J. Refrig. 123, 169–179 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2020.10.006
Brinckmann, E.: New facilities and instruments for developmental biology research in space. Adv. Space Biol. Med. 9, 253–280 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1569-2574(03)09010-5
Cai, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, D., Zhao, F.Y.: Thermoelectric cooling technology applied in the field of electronic devices: Updated review on the parametric investigations and model developments. Appl. Therm. Eng. 148, 238–255 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.11.014
Helleseng, K.O., Grønnevik, A., Fossum, K.R., Kittang, A.I., Iversen, T.H.: Utilization of the european modular cultivation system-opportunities and support functions. Int. Astron. Congr. (2012). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.IAC-05-A2.5.01
Kamada, M., Omori, K., Nishitani, K., Hoson, T., Shimazu, T., Ishioka, N.: JAXA space plant research on the ISS with European modular cultivation system. Biol. Sci. Space 21(3), 62–66 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2187/bss.21.62
Liu, F., Yang, Z.P., Yuan, W.X., Ren, K.X.: Research status and development prospect of the chip cooling technologies. Sci. Technol. Eng. 18(23), 163–169 (2018)
Lv, C.D., Wang, H.Q., Li, F.J., Cheng, S.M.: The feasibility of simulation testing under normal gravity of two-phase flow boiling heat transfer under microgravity. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Tech. 25(7), 103–105 (1997). https://doi.org/10.13245/j.hust.1997.07.034
Ma, R., Wu, Y.T., Du, C.X., Chen, X., Zhang, D.L., Ma, C.F.: The performance test of a modified miniature rotary compressor in upright and inverted modes subjected to microgravity. Appl. Therm. Eng. 92, 81–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.09.091
Nnanna, A.G.: Application of refrigeration system in electronics cooing. Appl. Therm. Eng. 26, 18–27 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2005.04.012
Sieiman, A.: Active Thermal Control System Kit for International Standard Payload Rack. SAE Technical Paper. 951459 (1995).
Sung, T.J., Lee, D.H., Kim, H.S., Kim, J.W.: Development of a novel meso-scale vapor compression refrigeration system (mVCRS). Appl. Therm. Eng. 66, 453–463 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.02.037
Trutassanawin, S., Groll, E.A., Garimella, S.V., Cremaschi, L.: Experimental investigation of a miniature-scale refrigeration system for electronics cooling. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 29, 678–687 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCAPT.2006.881762
Wang, Z.C.: Research on the simulation and experimentation of the hybrid heat sink based on thermoelectric cooler and phase change material. Wuhan University of Technology, Hubei (2020)
Wu, Z., Du, R.: Design and experimental study of a miniature vapor compression refrigeration system for electronics cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 31, 385–390 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2010.09.030
Xu, X.H.: Numerical and Experimental Simulations of Dynamic Thermal Management of Small Scale Space Station. Tsinghua University, Beijing (2003)
Zhang, X.R.: Thermal Management of Environment Control and Life Support System of Space Stations. Tsinghua University, Beijing (2002)
Zhang, Y., Dong, S.K., Wang, K., Zhou, Y.L., Sheng, Q., Tan, H.P.: Design, simulation and test of thermal control system of centrifuge for space utilization. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 32(4), 761–772 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-020-09819-7
Zhang, Y., Tong, T.F.: Thermal control scheme study of scientific experiment rack of new manned space station. Procedia Eng. 157, 374–381 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.08.379
Funding
The work presented is funded by the China Manned Space National Science and Technology Major Project—Variable Gravity Rack Centrifuge Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yu Zhang wrote the main manuscript text. Yanlin Zhou and Shikui Dong offered guidance and support. Ke Wang, Qiang Sheng and Caiyun Shao helped to revise manuscript and offered guidance.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhou, Y., Dong, S. et al. Optimization for Thermal Control System of Centrifuge and Operating Status Prediction Experiment in Orbit. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 35, 7 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-023-10033-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-023-10033-4