Abstract
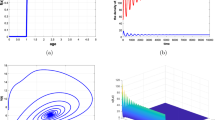
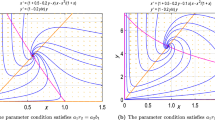
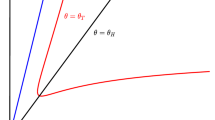
In the present article, we have investigated the impact of the fear effect and non-linear predator harvesting in a prey-predator interaction model with Holling type-II functional response. Fear for predator population enhances the survival probability of prey population, and it can greatly reduce the reproduction of prey population. We have investigated all the biologically feasible equilibrium points and the positivity and boundedness of the system solutions. We have analyzed the local and global stability of the feasible equilibrium points in terms of the model parameters. Analytically we have established that the intrinsic growth rate of the prey population can stabilize the prey-predator interactions by ignoring the existence of periodic behaviors. The model system undergoes through Transcritical, Saddle-Node, Hopf bifurcation by considering the intrinsic growth rate of the prey population as a bifurcation parameter and Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation with respect to the prey intrinsic growth rate and rate of predator harvesting. Numerically we have identified two parametric planes, which are divided into sub-regions associated with different numbers and nature of the equilibrium points by various bifurcation curves. We also found that the system may exhibit bi-stability behavior by producing stable axial and interior equilibrium points. Lastly, the manuscript is concluded with some recommendations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meng, X., Liu, R., Zhang, T.: Adaptive dynamics for a non-autonomous Lotka–Volterra model with size-selective disturbance. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 16, 202–213 (2014)
Morozov, A., Petrovskii, S., Li, B.: Bifurcations and chaos in a predator-prey system with the Allee effect. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 271, 1407–1414 (2004)
Zhang, T., Zang, H.: Delay-induced Turing instability in reaction–diffusion equations. Phys. Rev. E. 90, 052908 (2014)
Panday, P., Pal, N., Samanta, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Stability and bifurcation analysis of a three-species food chain model with fear. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos. 28, 1850009 (2018)
Prasad, K.D., Prasad, B.S.: Qualitative analysis of additional food provided predator-prey system with anti-predator behaviour in prey. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 1765–1793 (2019)
Murray, J.: Mathematical Biology II: Spatial Models and Biomedical Applications, 3rd edn. Springer (2003)
Holmes, E., Lewis, M., Banks, J., Veit, R.: Partial differential equations in ecology: spatial interactions and population dynamics. Ecology 75, 17–29 (1994)
Wang, W., Zhang, Y., Liu, C.: Analysis of a discrete-time predator-prey system with Allee effect. Ecol. Compl. 8, 81–85 (2011)
Yin, C., Cheng, Y., Chen, Y., Stark, B., Zhong, S.: Adaptive fractional-order switching-type control method design for 3D fractional-order nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 82, 39–52 (2015)
Perc, M., Szolnoki, A., Szabo, G.: Cyclical interactions with alliance-specific heterogeneous invasion rates. Phys. Rev. E. 75, 052102 (2007)
Malthus, T.: An Essay on the Principle of Population. J. Johnson, St. Paul’s Church-Yard, London (1978)
Lotka, A.J.: Elements of Physical Biology. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore (1925)
Volterra, V.: Variazione e fluttuazioni del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi. Memorie della Reale Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei. 6, 31–113 (1926)
Holling, C.S.: The components of predation as revealed by a study of small-mammal predation of the European pine sawfly. Can. Entomol. 91, 293–320 (1959)
Hastings, A., Powell, T.: Chaos in three-species food chain. Ecology 72, 896–903 (1991)
Song, Z., Zhen, B., Xu, J.: Species coexistence and chaotic behavior induced by multiple delays in a food chain system. Ecol. Compl. 19, 9–17 (2014)
Debnath, S., Ghosh, U., Sarkar, S.: Global dynamics of a tritrophic food chain model subject to the Allee effects in the prey population with sexually reproductive generalized-type top predator. Comp. Math Methods 1079, e1079 (2019)
Hassell, M.P., Lawton, J.H., Beddington, J.R.: Sigmoid functional responses by invertebrate predators and parasitoids. J. Anim. Ecol. 46, 249–262 (1977)
Ghosh, K., Biswas, S., Samanta, S., Tiwari, P.K., Alshomrani, A.S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Effect of multiple delays in an eco-epidemiological model with strong Allee effect. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos. 27, 175016-1–397 (2017)
Saifuddin, M., Samanta, S., Biswas, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: An eco-epidemiologicalmodel with different competition coefficients and strong-Allee in the prey. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos. 27, 173002-1–237 (2017)
Feng, P., Kang, Y.: Dynamics of a modified Leslie–Gower model with double Allee effects. Nonlinear Dyn. 80, 1051–1062 (2015)
Altendorf, K.B., Laundre, J.W., Gonzalez, C.A.L., Brown, J.S.: Assessing effects of predation risk on foraging behavior of mule deer. J. Mammal. 82, 430–439 (2001)
Creel, S., Christianson, D., Liley, S., Winnie, J.A.: Predation risk affects reproductive physiology and demography of elk. Science 315, 960 (2007)
Creel, S., Christianson, D.: Relationships between direct predation and risk effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 23, 194 (2008)
Zanette, L.Y., White, A.F., Allen, M.C., Clinchy, M.: Perceived predation risk reduces the number of offspring songbirds produce per year. Science 334, 1398–1401 (2011)
Suraci, J.P., Clinchy, M., Dill, L.M., Roberts, D., Zanette, L.Y.: Fear of large carnivores causes a trophic cascade. Nat. Commun. 7, 10698 (2016)
Candolin, U.: Reproduction under predation risk and the trade-off between current and future reproduction in the threespine stickleback. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B: Biol. Sci. 265, 1171–1175 (1998)
Xiao, Y., Chen, L.: Modeling and analysis of a predator-prey model with disease in the prey. Math. Biosci. 171, 59–82 (2001)
Xu, C., Li, Z.: Influence of intraspecific density dependence on a three-species food chain with and without external stochastic disturbances. Ecol. Model. 155, 71–83 (2002)
Ghosh, U., Sarkar, S., Mondal, B.: Study of stability and bifurcation of three species food chain model with non-monotone functional response. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 7(3), 1–24 (2021)
Beddington, J.R.: Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J. Anim. Ecol. 44(1), 331–340 (1975)
Chowdhury, T., Chakraborty, S., Chattopadhyay, J.: Migratory effect of middle predator in a tritrophic food chain model. Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. 33, 1699–1711 (2010)
Wang, X., Zanette, L., Zou, X.: Modelling the fear effect in predator-prey interactions. J. Math. Biol. 73, 1179–1204 (2016)
Clark, C.W.: Mathematical models in the economics of renewable resources. SIAM Rev. 21, 81–99 (1979)
Krishna, S.V., Srinivasu, P.D.N., Kaymackcalan, B.: Conservation of an ecosystem through optimal taxation. Bull. Math. Biol. 60, 569–584 (1998)
Clark, C.W., De Pree, J.D.: A simple linear model for optimal exploitation of renewable resources. J. Appl. Math. Optim. 5, 181–196 (1979)
Clark, C.W.: Mathematical Bieconomic: The Optimal Management of Renewable Resources. Princeton University Press (1976)
Clark, C.W.: Bieconomic Modelling and Fisheries Management. Wiley, New York (1985)
Das, T., Mukherjee, R.N., Chaudhari, K.S.: Bioeconomic harvesting of a prey-predator fishery. J. Biol. Dyn. 3, 447–462 (2009)
Xiao, S., Ruan, S.: Bogdanov-Takens bifurcations in predator-prey systems with constant rate harvesting. Fields Inst. Commun. 21, 493–506 (1999)
Srinivasu, P.D.N.: Bioeconomics of a renewable resource in presence of a predator. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2, 497–506 (2001)
Zhang, N., Chen, F., Su, Q., Wu, T.: Dynamic behaviours of a harvesting Leslie-Gower predator-prey model. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 10(1155), 473–949 (2011)
Dai, G., Tang, M.: Coexistence region and global dynamics of a harvesting predator-prey system. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 58, 193–210 (1998)
Barman, D., Roy, J., Alrabaiah, H., Panja, P., Prasad Mondal, S., Alam, S.: Impact of predator incited fear and prey refuge in a fractional order prey predator model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 142, 110240 (2021)
Sasmal, S.K.: Population dynamics with multiple Allee effects induced by fear factors: a mathematical study on prey-predator interactions. Appl. Math. Model. 64, 1–14 (2018)
La-Salle J.: The stability of Dynamical Systems. SIAM. (1976)
Perko, L.: Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems, vol. 7. Springer, New York (1996)
Kuznetsov, Y.A.: Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory, vol. 112. Springer, New York (1998)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the anonymous referee for a careful checking of the details and for helpful comments that improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendices
1.1 Appendix 1
\(A_1=Eac^2kp^2qr_1r_2-2Eackmpq^2r_1r_2+Eakm^2q^3r_1r_2-Eacknpq^2r_2+Eakmnq^3r_2-ac^2p^2qr_2^2+2acmpq^2r_2^2-am^2q^3r_2^2 ;\, A_2=Ec^2dkp^2qr_1r_2-2Ecdkmpq^2r_1r2+Edkm^2q^3r_1r_2+Eac^2kp^2r_1r_2-4Eackmpqr_1r_2+3Eakm^2q^2r_1r_2-Ecdknpq^2r_2+Edkmnq^3r_2-2Eacknpqr_2+3Eakmnq^2r_2-c^2dp^2qr_2^2+c^2p^2qrr_2^2+2cdmpq^2r_2^2-2cmpq^2rr_2^2-dm^2q^3r_2^2+m^2q^3rr_2^2-ac^2p^2r_2^2+4acmpqr_2^2-3am^2q^2r_2^2 ;\, A_3=-E^2c^2kp^3r_1^2+2E^2ckmp^2qr_1^2-E^2km^2pq^2r_1^2+2E^2cknp^2qr_1-2E^2kmnpq^2r_1+Ec^2dkp^2r_1r_2-4Ecdkmpqr_1r_2+3Edkm^2q^2r_1r_2-E^2kn^2pq^2-2Eackmpr_1r_2+3Eakm^2qr_1r_2+Ec^2p^3r_1r_2-2Ecdknpqr_2-2Ecmp^2qr_1r_2+3Edkmnq^2r_2+Em^2pq^2r_1r_2-Eacknpr_2+3Eakmnqr_2-Ecnp^2qr_2+Emnpq^2r_2-c^2dp^2r_2^2+c^2p^2rr_2^2+4cdmpqr_2^2-4cmpqrr_2^2-3dm^2q^2r_2^2+3m^2q^2rr_2^2+2acmpr_2^2-3am^2qr_2^2 ;\, A_4=2E^2ckmp^2r_1^2-2E^2km^2pqr_1^2+2E^2cknp^2r_1-4E^2kmnpqr_1-2Ecdkmpr_1r_2+3Edkm^2qr_1r_2-2E^2kn^2pq+Eakm^2r_1r_2-Ecdknpr_2-2Ecmp^2r_1r_2+3Edkmnqr_2+2Em^2pqr_1r_2+Eakmnr_2-Ecnp^2r_2+2Emnpqr_2+2cdmpr_2^2-2cmprr_2^2-3dm^2qr_2^2+3m^2qrr_2^2-am^2r_2^2 ;\, A_5=-E^2km^2pr_1^2-2E^2kmnpr_1+Edkm^2r_1r_2-E^2kn^2p+Edkmnr_2+Em^2pr_1r_2+Emnpr_2-dm^2r_2^2+m^2rr_2^2\).
1.2 Appendix 2
\(a_{11}=-\dfrac{1}{(ky_1+1)(qx_1+1)^2}(2akq^2x_1^3y_1+dkq^2x_1^2y_1+4akqx_1^2y_1+2aq^2x_1^3+2dkqx_1y_1+dq^2x_1^2-q^2rx_1^2+2akx_1y_1+4aqx_1^2+kpy_1^2+dky_1+2dqx_1-2q_rx_1+2ax_1+py_1+d-r)\) \(a_{12}=-\dfrac{rx_1k}{(ky_1+1)^2}-\dfrac{px_1}{(qx_1+1)}\) \(a_{13}=-a+\dfrac{py_1q}{(qx_1+1)^3}\) \(a_{14}=-\dfrac{(kq^2rx_1^2+k^2py_1^2+2kqrx_1+2kpy_1+kr+p)}{(qx_1+1)^2(ky_1+1)^2)}\) \(a_{15}=\dfrac{rx_1k^2}{(ky_1+1)^3}\), \(a_{16}=-\dfrac{pq^2y_1}{(qx_1+1)^4}\), \(a_{17}=\dfrac{pq(qx_1+1)}{(qx_1+1)^4}\), \(a_{18}=\dfrac{rk^2}{(ky_1+1)^3}\), \(a_{19}=-\dfrac{rx_1k^3}{(ky_1+1)^4}\), \(a_{21}=-\dfrac{cpy_1}{(qx_1+1)^2}\), \(a_{22}=\dfrac{1}{(qx_1+1)(Er_1+r_2y_1)^2}(E^2cpr_1^2x_1-E^2mqr_1^2x_1+2Ecpr_1r_2x_1y_1-2Emqr_1r_2x_1y_1+cpr_2^2x_1y_1^2-mqr_2^2x_1y_1^2-E^2nqr_1x_1-E^2mr_1^2-2Emr_1r2y_1-mr_2^2y_1^2-E^2nr_1)\) \(a_{23}=-\dfrac{cpy_1q}{(qx_1+1)^3}\) \(a_{24}=\dfrac{cp}{(qx_1+1)^2}\), \(a_{25}=\dfrac{nE^2r_1r_2}{(Er_1+r2y_1)^3}\), \(a_{26}=\dfrac{cpq^2y_1}{(qx_1+1)^4}\), \(a_{27}=-\dfrac{cpq(qx_1+1)}{(qx_1+1)^4}\), \(a_{28}=0\), \(a_{29}=-\dfrac{nE^2r_1r_2^2}{(Er_1+r_2y_1)^4}\), \(B_1=(a_{13}a_{12}^2-a_{14}a_{12}a_{11})u^2+\omega _2(2a_{15}a_{11}-a_{14}a_{12})uv+\omega _2^2a{15}v^2+(a_{18}a_{12}a_{11}^2-a_{19}a_{11}^3+a_{16}a_{12}^3-a_{17}a_{12}^2a_{11})u^3 +\omega _2(2a_{18}a_{11}a_{12}-a_{17}a_{12}^2-3a_{19}a_{11}^2)u^2v+\omega _2^2(a_{18}a_{12}-3a_{19}a_{11})uv^2-\omega _2^3a_{19}v^3\) \(B_2=(a_{23}a_{22}^2-a_{24}a_{22}a_{21})u^2+\omega _2(2a_{25}a_{21}-a_{24}a_{22})uv+\omega _2^2a{25}v^2+(a_{28}a_{22}a_{21}^2-a_{29}a_{21}^3+a_{26}a_{22}^3-a_{27}a_{22}^2a_{21})u^3 +\omega _2(2a_{28}a_{21}a_{22}-a_{27}a_{22}^2-3a_{29}a_{21}^2)u^2v+\omega _2^2(a_{28}a_{22}-3a_{29}a_{21})uv^2-\omega _2^3a_{29}v^3\)
1.3 Appendix 3
\(d_{11}(\psi )=\dfrac{r^{BT}+\psi _1}{ky^*+1)}-d-2ax^*-\dfrac{py^*}{(qx^*+1)^2}, \ d_{12}(\psi )=-\dfrac{(r^{BT}+\psi _1)kx^*}{(ky^*+1)^2}-\dfrac{px^*}{(qx^*+1)}, l_{00}(\psi )=\dfrac{(r^{BT}+\psi _1)x^*}{(ky^*+1)}-dx^*-ax^{*2}-\dfrac{px^*y^*}{(qx^*+1)}, \ l_{20}(\psi )=-a+\dfrac{pqy^*}{(qx^*+1)^3}, l_{11}(\psi )=-\dfrac{(r^{BT}+\psi _1)k}{(ky^*+1)^2}-\dfrac{p}{(qx^*+1)^2}, \ l_{02}(\psi )=\dfrac{(r^{BT}+\psi _1)k^2x^*}{(ky^*+1)^3}, \ d_{21}(\psi )=\dfrac{cpy^*}{(qx^*+1)^2}, m_{00}(\psi )=\dfrac{cpx^*y^*}{qx^*+1}-my^*-\dfrac{n(E^{BT}+\psi _2)y^*}{(r_1(E^{BT}+\psi _2)+r_2y^*)}, \ m_{20}(\psi )=-\dfrac{cpqy^*}{(qx^*+1)^3}, m_{11}(\psi )=\dfrac{cp}{(qx^*+1)^2}, d_{22}(\psi )={nyr_2E^{BT}}{(r_1E^{BT}+r_1\psi _2+r_2y^*)^2}+\dfrac{nr_2\psi _2y*}{(r_1E^{BT}+r_1\psi _2+r_2y^*)^2}\dfrac{cpx^*}{(qx^*+1)}-m-{nE^{BT}}{(r_1E^{BT}+ r_1\psi _2+r_2y^*)} -{n\psi _2}{(r_1E^{BT}+r_1\psi _2+r_2y^*)}, \ m_{02}(\psi )=\dfrac{n(E^{BT}+\psi _2)^2r_1r_2}{((r_1E^{BT}+r_1\psi _2+r_2y^*)^2(r_1(E^{BT}+\psi _2)+r_2y^*))}\)
1.4 Appendix 4
\(e_{02}(\psi )=l_{20}-\dfrac{l_{11}d_{11}}{d_{12}}+\dfrac{l_{02}d_{11}^2}{d_{12}^2}\), \(e_{11}(\psi )=\dfrac{l_{11}}{d_{12}}-\dfrac{2d_{11}l_{02}}{d_{12}^2}\), \(e_{02}(\psi )=\dfrac{l_{02}}{d_{11}^2}\), \(n_{00}(\psi )=d_{11}l_{00}+d_{12}m_{00}\), \(n_{10}(\psi )=d_{12}d_{21}-d_{11}d_{22}\), \(n_{01}(\psi )=d_{11}+d_{22}\), \(n_{20}(\psi )=d_{11}l_{20}-\dfrac{l_{11}d_{11}^2}{d_{12}}+\dfrac{l_{02}d_{11}^3}{d_{12}^2}+d_{12}m_{20}-d_{11}m_{11}+\frac{m_{02}d_{11}^2}{d_{12}}\), \(n_{11}(\psi )=m_{11}+\dfrac{l_{11}d_{11}}{d_{12}}-\dfrac{2d_{11}^2l_{02}}{d_{12}^2}-\dfrac{2d_{11}m_{02}}{d_{12}}\), \(n_{02}(\psi )=\dfrac{d_{11}l_{02}}{d_{12}^2}+\dfrac{m_{02}}{d_{12}}\)
1.5 Appendix 5
\(f_{00}(\psi )=n_{00}(\psi )-l_{00}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )+l_{00}^2(\psi )(n_{02}(\psi )-d_{02}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi ))-2l_{00}(\psi )d_{02}(\psi )(n_{00}(\psi )-l_{00}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi ))+...=n_{00}(\psi )-l_{00}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )+l_{00}^2d_{02}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )+l_{00}^2(\psi )n_{02}(\psi )+... f_{10}(\psi )=n_{10}(\psi )+l_{00}(\psi )d_{11}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )-l_{00}(\psi )n_{11}(\psi )+d_{11}(\psi )(n_{00}(\psi )-l_{00}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )) -2l_{00}(\psi )d_{02}(\psi )n_{10}(\psi )+...=n_{10}(\psi )+d_{11}(\psi )n_{00}(\psi )-l_{00}(\psi )n_{11}(\psi )-2l_{00}(\psi )d_{02}(\psi )n_{10}(\psi )+..., f_{01}(\psi )=n_{01}(\psi )-l_{00}(\psi )d_{11}(\psi )+2l_{00}(\psi )d_{02}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )-2l_{00}(\psi )n_{02}(\psi )+2d_{02}(\psi )n_{00}(\psi )+..., g_{20}(\psi )=n_{20}(\psi )+d_{11}(\psi )n_{10}(\psi )-n_{01}(\psi )d_{20}(\psi )+..., f_{11}(\psi )=-d_{11}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )+n_{11}(\psi )+2d_{20}(\psi )+d_{11}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )+2d_{02}(\psi )n_{10}(\psi )+..., =n_{11}(\psi )+2d_{20}(\psi )+2d_{02}(\psi )n_{10}(\psi )+..., f_{02}(\psi )=n_{02}(\psi )-d_{02}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )+d_{11}(\psi )+2d_{02}(\psi )n_{01}(\psi )+....\)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majumdar, P., Debnath, S., Mondal, B. et al. Complex dynamics of a prey-predator interaction model with Holling type-II functional response incorporating the effect of fear on prey and non-linear predator harvesting. Rend. Circ. Mat. Palermo, II. Ser 72, 1017–1048 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12215-021-00701-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12215-021-00701-y
Keywords
- Fear effect
- Holling type-II functional response
- Stability
- Harvesting
- Transcritical bifurcation
- Saddle-node bifurcation
- Hopf bifurcation
- Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation