Abstract
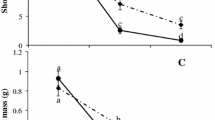
Pistia stratiotes is one of the worst weeds in the world, and it adversely affects the environment and biodiversity. A large gap remains in the quantitative knowledge about the growth, biomass and life cycle of this invasive macrophyte under natural conditions in Egypt. Therefore, this study aims to determine the monthly variation in P. stratiotes population dynamics in the South Nile Delta (Egypt) to identify the potential weak stages in the species’ life cycle and thereby suggest the best time to begin control of this invasive species. Sampling was performed monthly from May 2013 to February 2014 at three sites along the Al-Sero Drain; three randomly distributed quadrats (each of 0.5 × 0.5 m) were used at each site. Generally, the Al-Sero Drain is characterized by having alkaline, brackish and moderately eutrophic waters. The shoot systems started to grow in May, reached their maximum biomass of 320.7 g DM m−2 in September and then decreased and reached their lowest value in February. The root biomass increased from 2.3 g DM m−2 in May to 26.6 g DM m−2 in August and decreased to a minimum of 4.9 g DM m−2 in February. The relative growth rate of the plant was highest during the summer, whereas the lowest relative growth rate occurred in the winter. In conclusion, to suppress or eradicate this macrophyte from a drain, the harvest should be performed in May, when the biomass is low, and the offshoot production is just beginning (before the formation of large mature individuals).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo AA, Briski E, Briski E, Kalaci O, Hernandez MEP, Ghabooli S, Beric B, Chan FT, Zhan A, Fifield E, Leadley TA, Maclsaac HJ (2011) Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) and water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) in the Great Lakes: playing with fire? Aquat Invas 6:91
Anonymous (2012) Water lettuce Pistia stratiotes: fact sheet. The State of Queensland, Department of Employment, Economic Development and Innovation, Queensland
APHA (American Public Health Association) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Attionu RH (1976) Some effects of water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes, L.) on its habitat. Hydrobiologia 50:245–254
Bazzaz FA, Grace J (1997) Plant resource allocation. Academic Press, London
Boulos L (2005) Flora of Egypt: Vol. 4 (Monocotyledons). Al-Hadara Publishing, Cairo
Carvalho LB, Souza MC, Bianco MS, Bianco S (2011) Estimate of the leaf area of aquatic weeds: Pistia stratiotes. Planta Daninha 29:65–68
Center TD, Spencer NR (1981) The phenology and growth of water hyacinth Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms in an eutrophic north-central Florida lake. Aquat Bot 10:1–32
Center TD, Van TK (1989) Alteration of water hyacinth Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms leaf dynamics and phytochemistry by insect damage and plant density. Aquat Bot 35:181–195
Chadwick MJ, Obeid M (1966) A comparative study of the growth of Eichhornia crassipes Solms. and Pistia stratiotes L. in water-culture. J Ecol 54:563–575
Chapman D, Coetzee J, Hill M, Hussner A, Netherland M, Pescott O, Stiers I, van Valkenburg J, Tanner R (2017) Pistia stratiotes L. EPPO Bull 47:537–543
Coelho FF, Deboni L, Lopes FS (2000) Density-dependent morphological plasticity in Salvinia auriculata aublet. Aquat Bot 66:273–280
Coelho FF, Deboni L, Lopes FS (2005) Density-dependent reproductive and vegetative allocation in the aquatic plant Pistia stratiotes (Araceae). Rev Biol Trop 53:369–376
Coetzee JA, Hill MP, Byrne MJ, Bownes A (2011) A review of the biological control programmes on Eichhornia crassipes (C.Mart.) Solms (Pontederiaceae), Salvinia molesta D.S.Mitch. (Salviniaceae), Pistia stratiotes L. (Araceae), Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdc. (Haloragaceae) and Azolla filiculoides Lam. (Azollaceae) in South Africa. Afr Entomol 19:451–468
den Hollander NG, Schenk IW, Diouf S, Kropff MJ, Pieterse AH (1999) Survival strategy of Pistia stratiotes L. in the Djoudj National Park in Senegal. Hydrobiologia 415:21–27
Dewald LB, Lounibos LP (1990) Seasonal growth of Pistia stratiotes L. in South Florida. Aquat Bot 36:263–275
du Toit RF (1985) Unexpected growth of Pistia stratiotes in Sanyati Gorge, Lake. Kariba. J Limnol Soc Southern Africa 11:51–53
Eid EM (2017) Verification of a numerical growth model of Pistia stratiotes L. using field data from tropical and subtropical sites. J Freshw Ecol 32:391–403
Eid EM, Shaltout KH (2017a) Population dynamics of Eichhornia crassipes (C. Mart.) Solms in the Nile Delta, Egypt. Plant Spec Biol 32:279–291
Eid EM, Shaltout KH (2017b) Growth dynamics of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): a modelling approach. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 28:169–181
Eid EM, Galal TM, Dakhil MA, Hassan LM (2016) Modeling the growth dynamics of Pistia stratiotes L. populations along the water courses of south Nile Delta, Egypt. Rend Fis Acc Lincei 27:375–382
Galal TM, Farahat EA (2015) The invasive macrophyte Pistia stratiotes L. as a bioindicator for water pollution in Lake Mariut, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 187:701
Galal T, Shaltout K, Hassan L (2012) The Egyptian northern lakes: habitat diversity, vegetation and economic importance. LAP Lambert Academic, Saarbrücken
Galal TM, Eid EM, Dakhil MA, Hassan LM (2018) Bioaccumulation and rhizofiltration potential of Pistia stratiotes L. for mitigating water pollution in the Egyptian wetlands. Int J Phytorem 20:440–447
GISD (Global Invasive Species Database) (2018) Species profile: Pistia stratiotes. http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/speciesname/Pistia+stratiotes. Accessed 30 Sep 2018
Gopal B (1987) Water hyacinth (Aquatic plant studies 1). Elsevier, Amsterdam
Hall JB, Okali DUU (1974) Phenology and productivity of Pistia stratiotes L. on the Volta Lake, Ghana. J Appl Ecol 11:709–725
Haller WT, Sutton DL, Barlow WC (1974) Effects of salinity on growth of several aquatic macrophytes. Ecology 55:891–894
Henry-Silva GG, Camargo AFM, Pezzato MM (2008) Growth of free-floating aquatic macrophytes in different concentrations of nutrients. Hydrobiologia 610:153–160
Hoffmann WA, Poorter H (2002) Avoiding bias in calculations of relative growth rate. Ann Bot 80:37–42
Holm LG, Plucknett DL, Pancho JV, Herberger JP (1991) The world’s worst weeds: distribution and biology. Krieger, Malabar
Khedr AA, Serag MS (1998) Environmental influences on the distribution and abundance of waterlettuce (Pistia stratiotes L.) in Egypt. Limnologica 28:387–393
Lallana VH (1989) Reproductive aspects of water lettuce Pistia stratiotes L. in lentic environment of the middle Parana River, Argentina. Iheringia Serie Bot 39:37–54
Luther H (1983) On life forms, and above-ground and underground biomass of aquatic macrophytes. Acta Bot Fenn 123:1–23
Madsen JD (1991) Resource allocation at the individual plant level. Aquat Bot 41:67–86
NASA-POWER (2018) Climatology resource for agroclimatology. NASA Prediction of Worldwide Energy http://power.larc.nasa.gov/cgi-bin/cgiwrap/solar/agro.cgi. Accessed 28 Sep 2018
Odum HT (1957) Trophic structure and productivity of Silver Springs, Florida. Ecol Monogr 27:55–112
Pettet A, Pettet J (1970) Biological control of Pistia stratiotes L. in Western State, Nigeria. Nature 226:282
Rao PN, Reddy AS (1984) Studies on the population biology of water lettuce: Pistia stratiotes L. Hydrobiologia 119:15–19
Reddy KR, DeBusk WF (1984) Growth characteristics of aquatic macrophytes cultured in nutrient-enriched water: I. water hyacinth, water lettuce, and pennywort. Econ Bot 38:229–239
Šajna N, Haler M, Škornik S, Kaligarič M (2007) Survival and expansion of Pistia stratiotes L. in a thermal stream in Slovenia. Aquat Bot 87:75–79
Sand-Jensen K (1989) Environmental variables and their effect on photosynthesis of aquatic plant communities. Aquat Bot 34:5–25
Shaltout KH, Galal TM, El-Komi TM (2014) Biomass, nutrients and nutritive value of Persicaria salicifolia Willd. in the water courses of Nile Delta, Egypt. Rendiconti Fisiche Accademia Lincei 25:167–179
Shaltout KH, Eid EM, El-Komi TM (2016a) Phytomass and nutrient value of Potamogeton crispus L. in the water courses of Nile Delta, Egypt. Rendiconti Fisiche Accademia Lincei 27:251–259
Shaltout KH, Galal TM, El-Komi TM (2016b) Phenology, biomass and nutrients of Imperata cylindrica and Desmostachya bipinnata along the water courses in Nile Delta, Egypt. Rendiconti Fisiche Accademia Lincei 27:215–228
Sharma BM (1984) Ecophysiological studies on water lettuce in a polluted lake. J Aquat Plant Manag 22:17–21
Sharma BM, Sridhar MKC (1981) The productivity of Pistia stratiotes L. in a eutrophic lake. Environ Pollut 24:277–289
Singh BP, Tandon PK (2009) Effect of water pollution on Pistia stratiotes in river Suheli of Dudhwa National Park and River Gomti of Lucknow city. Res Environ Life Sci 2:173–178
Sommaruga R, Crosa D, Mazzeo N (1993) Study on the decomposition of Pistia stratiotes L. (Araceae) in Cisne Reservoir, Uruguay. Int Rev Hydrobiol 78:263–272
Statsoft (2007) Statistica version 7.1. Statsoft Inc, Tulsa
Täckholm V (1974) Students’ flora of Egypt. Cooperative Printing Company, Beirut
ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2012) Canoco reference manual and user’s guide: software for ordination: version 5.0. Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Tucker CS (1983) Culture density and productivity of Pistia stratiotes. J Aquat Plant Manag 21:40–41
UNESCO (1977) Map of the world distribution of arid regions. MAB Technical Notes, Paris
Watson MA (1984) Developmental constraints: effect on population growth and patterns of resource allocation in a clonal plant. Am Nat 123:411–426
Weiner J (2004) Allocation, plasticity and allometry in plants. Perspect Plant Ecol Evol Syst 6:207–215
Xie Y, Wen MZ, Yu D, Li YK (2004) Growth and resource allocation of water hyacinth as affected by gradually increasing nutrient concentrations. Aquat Bot 79:257–266
Xie Y, An S, Wu B, Wang W (2006) Density-dependent root morphology and root distribution in the submerged plant Vallisneria natans. Environ Exp Bot 57:195–200
You WH, Yu D, Liu CH, Xie D, Xiong W (2013) Clonal integration facilitates invasiveness of the alien aquatic plant Myriophyllum aquaticum L. under heterogeneous water availability. Hydrobiologia 718:27–39
Acknowledgements
We thank the anonymous reviewer and the editor for their useful comments on an earlier version. This work was supported by the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University under Grant number R.G.P. 1/94/40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galal, T.M., Dakhil, M.A., Hassan, L.M. et al. Population dynamics of Pistia stratiotes L.. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 30, 367–378 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-019-00800-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-019-00800-0