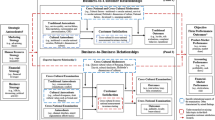
Abstract
Given the increase in technology-based services in the public sector, such as the use of web-based or mobile applications, understanding the levels of customer satisfaction with electronic public services is important for academics and practitioners. Thus, this paper presents an up-to-date systematic literature review (SLR) of customer satisfaction with electronic public services. The authors classified and analysed 129 relevant articles on customer satisfaction in the context of electronic public services published from 2005 to 2022 in numerous Scopus and Google Scholar journals. Afterwards, this present research analysed papers based on their year of publication, the countries where the study was conducted, service types and the antecedents (psychological, technological, social, and behavioural) and consequences of customer satisfaction, including the mediators between antecedents and consequences. Based on the SLR, this paper outlines directions for future research related to a conceptual framework highlighting promising research areas linked to the antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction with electronic public services, as well as the theories and methodologies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ain, N., Vaia, G., DeLone, W. H., & Waheed, M. (2019). Two decades of research on business intelligence system adoption, utilization and success–A systematic literature review. Decision Support Systems, 125, 113113.
Aksnes, D. W., & Sivertsen, G. (2019). A criteria-based assessment of the coverage of Scopus and Web of Science. Journal of Data and Information Science, 4(1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.2478/jdis-2019-0001
Antman, E. M., Lau, J., Kupelnick, B., Mosteller, F., & Chalmers, T. C. (1992). A comparison of results of meta-analyses of randomized control trials and recommendations of clinical experts. Treatments for myocardial infarction. Jama, 268(2), 240–248.
Arca, J. M., De Elizagarate Gutiérrez, V., & Egiguren, I. L. (2017). An approach to market orientation in the basic units of public action. International Review on Public and Nonprofit Marketing, 14(4), 409–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-017-0180-4
Bouzas-Lorenzo, R. (2010). Public sector marketing, political science and the science of public administration: The evolution of a transdisciplinary dialogue. International Review on Public and Nonprofit Marketing, 7(2), 113–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-010-0057-2
Budgen, D., & Brereton, P. (2006). Performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 28th international conference on Software engineering, Shanghai, China. https://doi.org/10.1145/1134285.1134500
Butler, P., & Collins, N. (1995). Marketing public sector services: Concepts and characteristics. Journal of Marketing Management, 11(1–3), 83–96. https://doi.org/10.1080/0267257X.1995.9964331
Carter, L., & Bélanger, F. (2005). The utilization of e-government services: Citizen trust, innovation and acceptance factors*. Information Systems Journal, 15(1), 5–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2575.2005.00183.x
Caruana, A., Ramaseshan, B., & Ewing, M. T. (1998). The market orientation-performance link: Some evidence from the public sector and universities. Journal of Nonprofit & Public Sector Marketing, 6(1), 63–82.
Cervera, A., Mollá, A. & Sánchez, M. (2001). “Antecedents and consequences of market orientation in public organisations”, European Journal of Marketing, Vol. 35 No. 11/12, pp. 1259–1288. https://doi.org/10.1108/EUM0000000006476
Chan, F. K. Y., Thong, J. Y. L., Venkatesh, V., Brown, S. A., Hu, P. J. H., & Tam, K. Y. (2010). Modeling citizen satisfaction with mandatory adoption of an e-government technology. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 11(10), 519–549. https://doi.org/10.17705/1jais.00239
Cook, D. J., Mulrow, C. D., & Haynes, R. B. (1997). Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine, 126(5), 376–380. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-126-5-199703010-00006
Coulter, K. S., & Coulter, R. A. (2002). Determinants of trust in a service provider: The moderating role of length of relationship. Journal of Services Marketing, 16(1), 35–50. https://doi.org/10.1108/08876040210419406
Dash, G., Kiefer, K., & Paul, J. (2021). Marketing-to-Millennials: Marketing 4.0, customer satisfaction and purchase intention. Journal of Business Research, 122, 608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.10.016
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–340. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (1992). Information systems success: The quest for the dependent variable. Information Systems Research, 3(1), 60–95.
DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2003.11045748
Eid, R., Al Zaabi, A., Alzahmi, R., & Elsantil, Y. (2019). Integrating internal branding antecedents, customer and job satisfaction in the public sector. International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 27(5), 1480–1503. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-09-2018-1548
Giese, J. L., & Cote, J. A. (2000). Defining consumer satisfaction. Academy of Marketing Science Review, 1(1), 1–22.
Hati, S. R. H., Balqiah, T. E., Hananto, A., & Yuliati, E. (2021). A decade of systematic literature review on Airbnb: The sharing economy from a multiple stakeholder perspective. Heliyon, 7(10), e08222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08222
Hoehle, H., Scornavacca, E., & Huff, S. (2012). Three decades of research on consumer adoption and utilization of electronic banking channels: A literature analysis. Decision Support Systems, 54(1), 122–132.
Hung, S. Y., Chen, K., & Su, Y. K. (2020). The effect of communication and social motives on e-government services through social media groups. Behaviour and Information Technology, 39(7), 741–757. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2019.1610907
Janita, M. S., & Miranda, F. J. (2018). Quality in e-government services: A proposal of dimensions from the perspective of public sector employees. Telematics and Informatics, 35(2), 457–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2018.01.004
Khan, G. F., Moon, J., Swar, B., Zo, H., & Rho, J. J. (2012). E-government service use intentions in Afghanistan: Technology adoption and the digital divide in a war-torn country. Information Development, 28(4), 281–299. https://doi.org/10.1177/0266666912438879
Khan, S., Umer, R., Umer, S., & Naqvi, S. (2021). Antecedents of trust in using social media for e-government services: An empirical study in Pakistan. Technology in Society, 64,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101400
Kim, G.-S. (2020). The effect of quality management and big data management on customer satisfaction in Korea’s public sector. Sustainability, MDPI, 12(13), 1–13.
Klassen, T. P., Jadad, A. R., & Moher, D. (1998). Guides for reading and interpreting systematic reviews: I. Getting started. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 152(7), 700–704.
Kotler, P., & Lee, N. (2007a). Marketing in the public sector : a roadmap for improved performance. Pearson Education.
Kotler, P., & Lee, N. (2007b). Marketing in the public sector: The final Frontier. Public Manager, 36(1), 12–17.
Laing, A. (2003). Marketing in the public sector: Towards a typology of public services. Marketing Theory, 3(4), 427–445.
Marikyan, D., Papagiannidis, S., & Alamanos, E. (2019). A systematic review of the smart home literature: A user perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 138, 139–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.08.015
McColl-Kennedy, J., & Schneider, U. (2000). Measuring customer satisfaction: Why, what and how. Total Quality Management, 11(7), 883–896. https://doi.org/10.1080/09544120050135434
Nightingale, A. (2009). A guide to systematic literature reviews. Surface Science Reports, 27(9), 381–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpsur.2009.07.005
Oliver, R. L. (2010). Satisfaction: A behavioral perspective on the consumer (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Pavlou, P. A., & Fygenson, M. (2006). Understanding and predicting electronic commerce adoption: An extension of the theory of planned behavior. MIS Quarterly, 30(1), 115–143. https://doi.org/10.2307/25148720
Pikkarainen, T., Pikkarainen, K., Karjaluoto, H., & Pahnila, S. (2004). Consumer acceptance of online banking: An extension of the technology acceptance model. Internet Research, 14(3), 224–235. https://doi.org/10.1108/10662240410542652
Rhee, S.-K., & Rha, J.-Y. (2009). Public service quality and customer satisfaction: Exploring the attributes of service quality in the public sector. The Service Industries Journal, 29(11), 1491–1512. https://doi.org/10.1080/02642060902793441
Sirdeshmukh, D., Singh, J., & Sabol, B. (2002). Consumer Trust, Value, and Loyalty in Relational Exchanges. Journal of Marketing, 66(1), 15–37. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmkg.66.1.15.18449
Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., & Smart, P. (2003). Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British Journal of Management, 14(3), 207–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Upton, J. (2013). Psychosocial Factors. In M. D. Gellman & J. R. Turner (Eds.), Encyclopedia of Behavioral Medicine (pp. 1580–1581). Springer New York.
Walker, R. M., Brewer, G. A., Boyne, G. A., & Avellaneda, C. N. (2011). Market Orientation and Public Service Performance: New Public Management Gone Mad? Public Administration Review, 71(5), 707–717. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6210.2011.02410.x
Walsh, K. (1994). Marketing and Public Sector Management. European Journal of Marketing, 28(3), 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1108/03090569410057308
Warkentin, M., Gefen, D., Pavlou, P. A., & Rose, G. M. (2002). Encouraging citizen adoption of e-government by building trust. Electronic Markets, 12(3), 157–162. https://doi.org/10.1080/101967802320245929
Wu, W.-N. (2021). Does citizens’ 311 system use improve satisfaction with public service encounters?—lessons for citizen relationship management. International Journal of Public Administration, 44(8), 665–673. https://doi.org/10.1080/01900692.2020.1744644
Yan, M., Filieri, R., & Gorton, M. (2021). Continuance intention of online technologies: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Information Management, 58, 102315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2021.102315
Yap, C. S., Ahmad, R., Newaz, F. T., & Mason, C. (2020). Continuous Use and Extended Use of e-government Portals in Malaysia. International Journal of Public Administration. https://doi.org/10.1080/01900692.2020.1759626
Yi, Y., & Nataraajan, R. (2018). Customer satisfaction in Asia. Psychology & Marketing, 35(6), 387–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21093
Zarezadeh, Z. Z., Rastegar, R., & Xiang, Z. (2022). Big data analytics and hotel guest experience: A critical analysis of the literature. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 34(6), 2320–2336. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-10-2021-1293
Zhang, J., Chen, W., Petrovsky, N. and Walker, R.M. (2022). The expectancy-disconfirmation model and citizen satisfaction with public services: A meta-analysis and an agenda for best practice. Public Administration Review, 82, 147–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/puar.13368
Zhao, Y., Wen, L., Feng, X., Li, R., & Lin, X. (2020). How managerial responses to online reviews affect customer satisfaction: An empirical study based on additional reviews. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 57, 102205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102205
Reviewed Articles
Abdulkareem, A. K., Abdulkareem, Z. J., Ishola, A. A., & Akindele, I. T. (2022). Does e-government impact E-participation? The influence of trust in e-government. International Review of Public Administration, 27, 2, 91–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/12294659.2022.2071540
Abdulkareem, A. K., & Ramli, R. M. (2021a). Evaluating the performance of e-government: Does citizens’ access to ICT matter? Pertanika Journal of Tropical Agricultural Science, 29(3), 1507–1534. https://doi.org/10.47836/pjssh.29.3.03
Abdulkareem, A. K., & Ramli, R. M. (2021b). Does trust in e-government influence the performance of e-government? An integration of information system success model and public value theory. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy.
Abudaqa, A. M. M., Hassim, A. A., & Saidun, Z. (2019). Relationship between service usefulness and information awareness toward citizen satisfaction of e-government services in Kuala Lumpur. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 5(2), 118–127.
Akram, M. S., Malik, A., Shareef, M. A., & Goraya, M. A. S. (2019). Exploring the interrelationships between technological predictors and behavioral mediators in online tax filing: The moderating role of perceived risk. Government Information Quarterly, 36(2), 237–251.
Alawneh, A., Al-Refai, H., & Batiha, K. (2013). Measuring user satisfaction from e-government services: Lessons from Jordan. Government Information Quarterly, 30(3), 277–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2013.03.001
Alkraiji, A. I. (2020a). Citizen satisfaction with mandatory e-government services: A conceptual framework and an empirical validation. IEEE Access, 8, 117253–117265. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004541
Alkraiji, A. I. (2020b). An examination of citizen satisfaction with mandatory e-government services: Comparison of two information systems success models. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 15(1), 36–58. https://doi.org/10.1108/TG-01-2020-0015
Alkraiji, A., & Ameen, N. (2021). The impact of service quality, trust and satisfaction on young citizen loyalty towards government e-services. Information Technology & People. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-04-2020-0229
Al Athmay, A. A. A., Fantazy, K., & Kumar, V. (2016). E-government adoption and user’s satisfaction: An empirical investigation. EuroMed Journal of Business, 11(1), 57–83. https://doi.org/10.1108/EMJB-05-2014-0016
Al-Ammary, J., Al-Kaabi, R., Al-Soufi, A., Ali, H., AlRayes, A., & Aljawder, M. (2017). Assessment of e-government services from the supply side to the demand side: Towards better e-services in the Kingdom of Bahrain. International Journal of Economic Research, 14(16), 29–55.
Al-Hujran, O., Al-Debei, M. M., Chatfield, A., & Migdadi, M. (2015). The imperative of influencing citizen attitude toward e-government adoption and use. Computers in Human Behavior, 53, 189–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.06.025
Al-ma’Aitah, M. (2019). Drivers of e-government citizen satisfaction and adoption: The case of Jordan. International Journal of E-Business Research, 15(4), 40–55. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJEBR.2019100103
Al-Soni, S. M. M., & Abu-Shanab, E. A. (2021). Factors influencing users’ satisfaction when using Ehteraz app: The case of Qatar. International Journal of Information Systems and Change Management, 12(4), 365–389.
Al-Sulami, Z. A., & Hashim, H. S. (2018). Measuring the success of e-government systems: Applying the success model of the delone and mclean information system. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 96(22), 7654–7670.
Al-Yafi, K., Hindi, N. M., & Osman, I. H. (2016). A user-centric evaluation of e-government services in the GCC region: Case of state of Qatar. International Journal of Electronic Government Research, 12(4), 15–34. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJEGR.2016100102
Al-Zahrani, M. S. (2020). Integrating IS success model with cybersecurity factors for e-government implementation in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 10(5), 4937–4955. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v10i5.pp4937-4955
Alalwan, J. A. (2013). Continuance intention to use government 2.0 services: The impact of citizens’ satisfaction and involvement. International Journal of Electronic Government Research (IJEGR), 9(3), 58–73.
Albalushi, M. A., Jano, Z., & Devi, I. (2020). Framework of public agency website quality evaluation in the UAE. Journal of Computer Science, 16(12). https://doi.org/10.3844/jcssp.2020.1765.1777
Alfahadi, A. (2021). Evaluating the effect of e-government quality of services on citizens’ satisfaction and in Saudi Arabia within 2030 vision: A conceptual perspective. European Online Journal of Natural and Social Sciences, 10(4), 491–501.
Ali, H., & Al Kabbi, R. (2018). M-government applications: Measurement of users’ satisfaction in the Kingdom of Bahrain. Electronic Government, 14(4), 375–388. https://doi.org/10.1504/EG.2018.095549
Ali, M., Asmi, F., Rahman, M. M., Malik, N., & Ahmad, M. S. (2017). Evaluation of e-service quality through customer satisfaction (a case study of FBR E-taxation). Open Journal of Social Sciences, 5(9), 175–195.
Allam, A. A., AbuAli, A. N., Ghabban, F. M., Ameerbakhsh, O., Alfadli, I. M., & Alraddadi, A. S. (2021). Citizens Satisfaction with e-government Mobile Services and M-Health Application during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Al-Madinah Region. Journal of Service Science and Management, 14(6), 636–650.
Alqaralleh, B. A. Y., Al-Omari, A. H., & Alksasbeh, M. Z. (2020). An integrated conceptual model for m-government acceptance in developing countries: The case study of Jordan. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 14(6), 115–136. https://doi.org/10.3991/IJIM.V14I06.11449
Alruwaie, M., El-Haddadeh, R., & Weerakkody, V. (2020). Citizens’ continuous use of eGovernment services: The role of self-efficacy, outcome expectations and satisfaction. Government Information Quarterly, 37(3), 101485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2020.101485
Altaany, F. H., & Alsoudani, K. A. (2014). Conceptual for User Satisfaction with the e-government in north of Jordan. International Journal of Advanced Computer Research, 4(2), 665.
Andriani, F. D., Napitupulu, T. A., & Haryaningsih, S. (2017). The user acceptance factors of E-filing system in Pontianak. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 95(17), 4265–4272.
Anwar, M., Esichaikul, V., Rehman, M., & Anjum, M. (2016). E-government services evaluation from citizen satisfaction perspective: A case of Afghanistan. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 10(1), 139–167. https://doi.org/10.1108/TG-03-2015-0017
Baharon, B. M., Yap, C. S., Ashar, S. F. E., Hanafi, M. H. H. M., & Hazmi, M. S. R. M. (2017). Citizen satisfaction with e-government portals in Malaysia. International Journal of Business & Information, 12(3), 289–309. https://doi.org/10.6702/ijbi.2017.12.3.3
Belanche, D., Casaló, L. V., & Guinaliu, M. (2012). How to make online public services trustworthy. Electronic Government, an International Journal, 9(3), 291–308.
Bin Musa, O., Abuwdn, F., BintiZolkifly, I. A., & Almasri, A. (2019). Factors affecting Libyan citizens satisfaction with e-government services. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 6(4), 1–23.
Byun, D.-H., & Finnie, G. (2011). Evaluating usability, user satisfaction and intention to revisit for successful e-government websites. Electronic Government, an International Journal, 8(1), 1–19.
Carlos Pinho, J., & Macedo, I. M. (2008). Examining the antecedents and consequences of online satisfaction within the public sector: The case of taxation services. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 2(3), 177–193. https://doi.org/10.1108/17506160810902185
Chan, F. K. Y., Thong, J. Y. L., Brown, S. A., & Venkatesh, V. (2020). Service design and citizen satisfaction with e-government services: A multidimensional perspective. Public Administration Review. https://doi.org/10.1111/puar.13308
Chan, V. H. Y., Chiu, D. K., & Ho, K. K. (2022). Mediating effects on the relationship between perceived service quality and public library app loyalty during the COVID-19 era. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 67, 102960.
Chen, J. V., Jubilado, R. J. M., Capistrano, E. P. S., & Yen, D. C. (2015). Factors affecting online tax filing - An application of the IS Success Model and trust theory. Computers in Human Behavior, 43, 251–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.017
Cheng, T.-H., Chen, S.-C., & Hariguna, T. (2021). The empirical study of usability and credibility on Intention usage of government-to-citizen services. Journal of Applied Data Sciences, 2(2). https://doi.org/10.47738/jads.v2i2.30
Chung, Y. K., Sheu, L. C., & Chien, S. H. L. (2007). A model of users’ satisfaction with Taiwan’s government website. Psychological Reports, 101(2), 395–406. https://doi.org/10.2466/PR0.101.2.395-406
Donie, R. S., Prihantoro, E., & Lestari, F. D. (2019). The effect of usability, quality of information, and interaction services quality on user satisfaction of DEPOK City Government Website Services using WEBQUAL 4.0 method. International Journal of Computer Science and Software Engineering, 8(10), 234–241.
Ebbers, W. E., Jansen, M. G. M., & van Deursen, A. J. A. M. (2016). Impact of the digital divide on e-government: Expanding from channel choice to channel usage. Government Information Quarterly, 33(4), 685–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2016.08.007
Fan, J., & Yang, W. (2015). Study on e-government services quality: The integration of online and offline services. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management, 8(3), 693–718. https://doi.org/10.3926/jiem.1405
Gemoets, L. A., Mahmood, M. A., Adenso-Díaz, B., & Gonzalez, P. (2011). A cross-national comparison of e-government success measures: A theory-based empirical research. International Journal of Electronic Governance, 4(3), 184–208. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEG.2011.043815
Goh, C. Y., Ong, J. W., Tan, S. Z., Goh, G. G. G., & Eze, U. C. (2012). E-service quality and user satisfaction toward e-filing. International Journal on Social Science, Economics and Art, 2(2), 50–54.
Guo, W., Chen, T., & Luo, Q. (2022). Does modified mobile government satisfy elders’ needs? An empirical study of China’s Zhejiang and Jiangxi provinces. Government Information Quarterly, 39(2), 101676.
Gupta, K. P., Bhaskar, P., & Singh, S. (2016). Critical factors influencing e-government adoption in India: An investigation of the citizens’ perspectives. Journal of Information Technology Research (JITR), 9(4), 28–44.
Harfouche, A. (2010). The same wine but in new bottles. Public e-services divide and low citizens’ satisfaction: an example from Lebanon. International Journal of Electronic Government Research (IJEGR), 6(3), 73–105.
Hassan, A., & Abu-Shanab, E. A. (2020). Exploring the factors affecting user satisfaction with metrash2 system. International Journal of Electronic Government Research, 16(1), 18–39. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJEGR.2020010102
Horan, T. A., & Abhichandani, T. (2006). Evaluating user satisfaction in an e-government initiative: Results of structural equation modeling and focus group discussions. Journal of Information Technology Management, 17(4), 33.
Hujran, O. A., Aloudat, A., & Altarawneh, I. (2013). Factors influencing citizen adoption of e-government in developing countries: The case of jordan. International Journal of Technology and Human Interaction, 9(2), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.4018/jthi.2013040101
Idoughi, D., & Abdelhakim, D. (2018). Developing countries e-government services evaluation identifying and testing antecedents of satisfaction Case of Algeria. International Journal of Electronic Government Research, 14(1), 63–85. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJEGR.2018010104
Islam, M. T., Talukder, M. S., Khayer, A. & Islam, A. K. M. N. (2021). Exploring continuance usage intention toward open government data technologies: an integrated approach. VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/VJIKMS-10-2020-0195
Irani, Z., Weerakkody, V., Molnar, A., Lee, H., Hindi, N., & Osman, I. (2014). A user satisfaction study of the NHS Online Prescription Prepayment Certificate. Health Policy and Technology, 3(3), 176–184.
Jiang, X., & Ji, S. (2014). E-government web portal adoption: The effects of service quality. E-Service Journal: A Journal of Electronic Services in the Public and Private Sectors, 9(3), 43–60.
Jun, K.-N., Wang, F., & Wang, D. (2014). E-government use and perceived government transparency and service capacity: Evidence from a Chinese local government. Public Performance & Management Review, 38(1), 125–151.
Kim, S., & Lee, J. (2012). E-participation, transparency, and trust in local government. Public Administration Review, 72(6), 819–828.
Kumar, R., Kumar, R., Sachan, A., & Gupta, P. (2020). An examination of the e-government service value chain. Information Technology and People. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-09-2018-0438
Lai, C. S. K., & Pires, G. (2010). Testing of a model evaluating e-government portal acceptance and satisfaction. Electronic Journal of Information Systems Evaluation, 13(1), 35–46-35–46.
Lee, B.-K., Lee, E. H., & Lee, T. (2022). The effect of e-government website evaluation on user satisfaction and intention to use: the mediating role of warmth and competence judgment on government. Information, Communication & Society, 1–22.
Lee, H. (2021). Does the medium matter? Linking citizens’ use of communication platform for information about urban policies to decision to trust in local government. Sustainability, 13(5), 2723.
Lee, K. C., Kirlidog, M., Lee, S., & Lim, G. G. (2008). User evaluations of tax filing web sites: A comparative study of South Korea and Turkey. Online Information Review.
Li, H. (2021). An empirical research on the construction of a government website public satisfaction index model in China. Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM), 29(5), 112–137.
Li, Y., & Shang, H. (2020). Service quality, perceived value, and citizens’ continuous-use intention regarding e-government: Empirical evidence from China. Information and Management, 57(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2019.103197
Li, W., & Xue, L. (2021). Analyzing the critical factors influencing post-use trust and its impact on citizens’ continuous-use intention of e-government: Evidence from Chinese municipalities. Sustainability, 13(14), 7698.
Li, Y., Wang, H., Zeng, X., Yang, S., & Wei, J. (2020). Effects of interactivity on continuance intention of government microblogging services: An implication on mobile social media. International Journal of Mobile Communications, 18(4), 420–442.
Lu, Z.-H., Wang, C.-L., & Wang, H.-L. (2012). E-government satisfaction in mandatory adoption environment. Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology, 4(20), 4034–4038.
Magoutas, B., & Mentzas, G. (2010). SALT: A semantic adaptive framework for monitoring citizen satisfaction from e-government services. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(6), 4292–4300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.11.071
Malik, B. H., Shuqin, C., Mastoi, A. G., Gul, N., & Gul, H. (2016). Evaluating citizen e-satisfaction from e-government services: A case of Pakistan. European Scientific Journal, 12(5), 346. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2016.v12n5p346
Mandari, H., & Koloseni, D. (2021). Examining the antecedents of continuance usage of Mobile government services in Tanzania. International Journal of Public Administration, 45, 12, 917–929. https://doi.org/10.1080/01900692.2021.1945622
Manolitzas, P., & Yannacopoulos, D. (2013). Citizen satisfaction: A multicriteria satisfaction analysis. International Journal of Public Administration, 36(9), 614–621. https://doi.org/10.1080/01900692.2013.774416
Mbaidin, H. O. (2021). The impact of e-government success factors on citizen satisfaction: The context of UAE. Journal of Hunan University Natural Sciences, 48(12), 8–19.
Mensah, I. K., & Luo, C. (2021). Exploring factors determining chinese college students’ satisfaction with e-government services: The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) approach. Information Resources Management Journal (IRMJ), 34(3), 1–20.
Mishra, S. S., & Geleta, A. T. (2020). Can an e-government system ensure citizens’ satisfaction without service delivery? International Journal of Public Administration, 43(3), 242–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/01900692.2019.1628053
Morgeson, F. V., III. (2011). Comparing determinants of website satisfaction and loyalty across the e-government and e-business domains. Electronic Government, an International Journal, 8(2–3), 164–184.
Morgeson, F. V., III., Vanamburg, D., & Mithas, S. (2011). Misplaced trust? Exploring the structure of the e-government-citizen trust relationship. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 21(2), 257–283. https://doi.org/10.1093/jopart/muq006
Nguyen, T. T., Phan, D. M., Le, A. H., & Nguyen, L. T. N. (2020). The determinants of citizens’ satisfaction of e-government: An empirical study in Vietnam. Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 7(8), 519–531. https://doi.org/10.13106/JAFEB.2020.VOL7.NO8.519
Noor, Z. M., Kasimin, H., Aman, A., & Sahari, N. (2011a). An adoption model of electronic government services in Malaysia: Electronic labor exchange (ELX). Jurnal Pengurusan, 33, 87–97.
Noor, Z. M., Kasimin, H., Aman, A., & Sahari, N. (2011b). Evaluating end-user satisfaction with an e-government service Electronic Labor Exchange (ELX). Jurnal Ekonomi Malaysia, 45(1), 11–20.
Noori, M. (2022). The effect of e-service quality on user satisfaction and loyalty in accessing e-government information. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 6(3), 945–952.
Nour, A. A., et al. (2021). Determining the citizen loyalty factor of COVID-19 website using the trust model. IJITEE (International Journal of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering), 5(4), 145–151.
Obaid, Q. M. S., & Ahmad, M. F. (2021). The linkage between e government and citizens’ satisfaction in UAE. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 25(1), 3118–3130.
Ogunsola, K., & Tiamiyu, M. A. (2021). Predicting customers use of electronic government services in Nigeria. International Journal of Public Administration in the Digital Age (IJPADA), 8(1), 1–21.
Osman, I. H., Anouze, A. L., Irani, Z., Al-Ayoubi, B., Lee, H., Balc, A., & Weerakkody, V. (2014). COBRA framework to evaluate e-government services: A citizen-centric perspective. Government Information Quarterly, 31(2), 243–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2013.10.009
Park, H., & Samijadi, M. F. (2021). Citizens perception of e-government in Korea: Importance-performance analysis on users satisfaction and behavioral intention. Journal of Public Administration and Governance, 11(2), 357381–357381.
Park, M. J., Choi, H., & Rho, J. J. (2016). Citizen patronage behavior of government social media services: Extended perspective of perceived value with the moderating effect of media synchronicity. Information Development, 32(3), 293–312.
Perlman, B. J., Reddick, C. G., & Zheng, Y. (2020). Agency vs. Stewardship theory in local government contracted mobile apps: Analysis of survey data on user satisfaction in China. International Journal of Public Administration in the Digital Age (IJPADA), 7(4), 16–34.
Porumbescu, G. A. (2016). Linking public sector social media and e-government website use to trust in government. Government Information Quarterly, 33(2), 291–304.
Porumbescu, G. A. (2017). Does transparency improve citizens’ perceptions of government performance? Evidence from Seoul, South Korea. Administration & Society, 49(3), 443–468.
Prokop, C., & Tepe, M. (2021). Talk or type? The effect of digital interfaces on citizens' satisfaction with standardized public services. Public Administration.
Qasem, M., & Zolait, A. H. (2016). Determinants of Behavioral Intentions towards Using e-government Services in the Kingdom of Bahrain. International Journal of Computing and Digital Systems, 5(4), 345–355. https://doi.org/10.12785/ijcds/050406
Ramdan, S., Azizan, Y. N. B., & Saadan, K. B. (2014). E-government systems success evaluating under principle islam: A validation of the delone and mclean model of islamic information systems success. Academic Research International, 5(2), 72.
Reddick, C., Zheng, Y., & Perlman, B. (2020). Channel choice in China: Correlates and determinates of satisfaction and use of government service channels in a survey of Chinese cities. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 14(1), 81–100.
Reddick, C. G., & Turner, M. (2012). Channel choice and public service delivery in Canada: Comparing e-government to traditional service delivery. Government Information Quarterly, 29(1), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2011.03.005
Reddick, C. G., & Zheng, Y. (2017). Determinants of citizens’ mobile apps future use in Chinese local governments. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 11(2), 213–235. https://doi.org/10.1108/TG-11-2016-0078
Rey-Moreno, M., Medina-Molina, C., & Barrera-Barrera, R. (2018). Multichannel strategies in public services: Levels of satisfaction and citizens’ preferences. International Review on Public and Nonprofit Marketing, 15(1), 9–24.
Rodrigues, G., Sarabdeen, J., & Balasubramanian, S. (2016). Factors that Influence Consumer Adoption of e-government Services in the UAE: A UTAUT Model Perspective. Journal of Internet Commerce, 15(1), 18–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332861.2015.1121460
Rouibah, K., Qurban, H., Al-Qirim, N., & Tarhini, A. (2018). Understanding mobile government success in an Arab country: Findings from a qualitative study. Issues in Information Systems, 19(2), 185–198.
Sachan, A., Kumar, R., & Kumar, R. (2018). Examining the impact of e-government service process on user satisfaction. Journal of Global Operations and Strategic Sourcing, 11(3), 321–336. https://doi.org/10.1108/JGOSS-11-2017-0048
Saleh, A. A., Alkhuwaylidee, A. R., & Thangiah, M. (2021). Behavioural intention and user satisfaction successful factors determining to achieve government operation excellence. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 19977–19989.
Samsuri, A. S., Hussin, S. M., Badaruddin, M. N. A., Arifin, T. R. T., Zainol, S. S., & Mohamad, Z. Z. (2022). Antecedents of User Satisfaction and Continuance Usage of Mobile Health Applications: A Study on MySejahtera Apps in Malaysia. Asian Journal of Behavioural Sciences, 4(2), 91–105.
Sausi, J. M., Mtebe, J. S., & Mbelwa, J. (2021). Evaluating user satisfaction with the e-payment gateway system in Tanzania. South African Journal of Information Management, 23(1), 1–9.
Shouran, Z. (2021). The specific factors influencing the intention of electronic government services for Libyans. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(10), 5065–5076.
Shuib, L., Yadegaridehkordi, E., & Ainin, S. (2019). Malaysian urban poor adoption of e-government applications and their satisfaction. Cogent Social Sciences, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311886.2019.1565293
Sichone, J., & Mbamba, U. (2021). E-government service quality evaluation on tax operations: A test of users’s satisfaction perception in Tanzania. International Journal of Information, Business and Management, 13(3), 132–144.
Skordoulis, M., Alasonas, P., & Pekka-Economou, V. (2017). E-government services quality and citizens’ satisfaction: A multi-criteria satisfaction analysis of TAXISnet information system in Greece. International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management, 22(1), 82–100. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJPQM.2017.085848
Sorongan, E., & Hidayati, Q. (2020). Integration of eucs variables into delone and mclean models for e-government evaluation: Conceptual models. Register: Jurnal Ilmiah Teknologi Sistem Informasi, 6(1), 32–42. https://doi.org/10.26594/register.v6i1.1608
Sugandini, D., Feriyanto, N., Yuliansyah, Y., Sukwadi, R., & Muafi, M. (2018). Web quality, satisfaction, trust and its effects on government website loyalty. International Journal for Quality Research, 12(4), 885–904.
Teo, T. S. H., Srivastava, S. C., & Jiang, L. (2008). Trust and electronic government success: An empirical study. Journal of Management Information Systems, 25(3), 99–132. https://doi.org/10.2753/MIS0742-1222250303
Thao, N. T. P., Van Anh, N., Huong, L., & Huy, D. T. N. (2021). Measuring citizen’s satisfaction when using e-government online public services: lessons from Vietnam. The Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27(2), 992–1000. https://doi.org/10.47750/cibg.2021.27.02.118
Titiani, F., Riana, D., Budihartanti, C., Rahmatullah, S., & Tutupoly, T. A. (2020). Analysis of user satisfaction on Corona. Jakarta. go. id Website: Use webqual method 4.0. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1641(1), 0–6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1641/1/012015
Tjen, C., Indriani, V., & Wicaksono, P. T. (2019). Prior experience, trust, and is success model: A study on the use of tax e-filing in Indonesia. Journal of the Australasian Tax Teachers Association, 14(1), 240–263.
Tsohou, A., Lee, H., Irani, Z., Weerakkody, V., Osman, I. H., Anouze, A. L., & Medeni, T. (2013). Proposing a reference process model for the citizen-centric evaluation of e-government services. Transforming Government: People, Process and Policy, 7(2), 240–255. https://doi.org/10.1108/17506161311325387
Udo, G. J., Bagchi, K. K., & Kirs, P. J. (2012). Exploring the role of espoused values on e-service adoption: A comparative analysis of the US and Nigerian users. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(5), 1768–1781.
Valaei, N., & Baroto, M. B. (2017). Modelling continuance intention of citizens in government Facebook page: A complementary PLS approach. Computers in Human Behavior, 73, 224–237.
Veeramootoo, N., Nunkoo, R., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2018). What determines success of an e-government service? Validation of an integrative model of e-filing continuance usage. Government Information Quarterly, 35(2), 161–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2018.03.004
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y., Chan, F. K., Hu, P. J. H., & Brown, S. A. (2011). Extending the two-stage information systems continuance model: Incorporating UTAUT predictors and the role of context. Information Systems Journal, 21(6), 527–555.
Venkatesh, V., Chan, F. K. Y., & Thong, J. Y. L. (2012). Designing e-government services: Key service attributes and citizens’ preference structures. Journal of Operations Management, 30(1–2), 116–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2011.10.001
Venkatesh, V., Thong, J. Y. L., Chan, F. K. Y., & Hu, P. J. H. (2016). Managing citizens’ uncertainty in e-government services: The mediating and moderating roles of transparency and trust. Information Systems Research, 27(1), 87–111. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2015.0612
Verdegem, P., & Verleye, G. (2009). User-centered e-government in practice: A comprehensive model for measuring user satisfaction. Government Information Quarterly, 26(3), 487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2009.03.005
Wang, C., & Teo, T. S. H. (2020). Online service quality and perceived value in mobile government success: An empirical study of mobile police in China. International Journal of Information Management, 52, 102076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102076
Wang, C., Teo, T. S. H., Dwivedi, Y., & Janssen, M. (2021). Mobile services use and citizen satisfaction in government: Integrating social benefits and uses and gratifications theory. Information Technology & People, 34(4), 1313–1337. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-02-2020-0097
Wang, Y.-S., & Liao, Y.-W. (2008). Assessing eGovernment systems success: A validation of the DeLone and McLean model of information systems success. Government Information Quarterly, 25(4), 717–733.
Weerakkody, V., Irani, Z., Lee, H., Hindi, N., & Osman, I. (2016). Are U.K. citizens satisfied with e-government services? Identifying and testing antecedents of satisfaction. Information Systems Management, 33(4), 331–343. https://doi.org/10.1080/10580530.2016.1220216
Welch, E. W., Hinnant, C. C., & Moon, M. J. (2005). Linking citizen satisfaction with e-government and trust in government. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 15(3), 371–391.
Widiyanto, N., Sandhyaduhita, P. I., Hidayanto, A. N., & Munajat, Q. (2016). Exploring information quality dimensions of government agency’s information services through social media: A case of the Ministry of Education and Culture in Indonesia. Electronic Government, an International Journal, 12(3), 256–278.
Wirtz, B. W., & Kurtz, O. T. (2016). Local e-government and user satisfaction with city portals – the citizens’ service preference perspective. International Review on Public and Nonprofit Marketing, 13(3), 265–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-015-0149-0
Xiong, L., Wang, H., & Wang, C. (2022). Predicting mobile government service continuance: A two-stage structural equation modeling-artificial neural network approach. Government Information Quarterly, 39(1), 101654.
Yang, Y. (2017). Towards a new digital era: Observing local e-government services adoption in a Chinese municipality. Future Internet, 9(3), 53.
Zhu, Y.-Q., & Alamsyah, N. (2022). Citizen empowerment and satisfaction with smart city app: Findings from Jakarta. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 174, 121304.
Ziaee Azimi, S. A., & Saidi-Mehrabad, M. (2016). The identifying, evaluating and prioritizing the factors affecting customers’ satisfaction with E-service Centers of Iran's police. International Journal of Supply and Operations Management, 3(3), 1466–1485.
Acknowledgements
First Author is funded by Indonesia Endowment Fund for Education (LPDP) for her doctoral study at Faculty of Economy and Business, University of Indonesia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fathya, V.N., Viverita, V., Hati, S.R.H. et al. Customer satisfaction with electronic public services: An 18 years of systematic literature review. Int Rev Public Nonprofit Mark 20, 759–812 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-022-00350-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-022-00350-6