Abstract
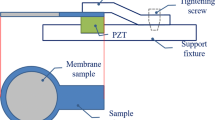
The equilibrium shape of sessile droplets on elastic thin membranes is determined by the balance among three types of surface tensions at the interface, namely vapor-liquid, liquid-solid, and solid-vapor. We studied the cross-sectional contour of the membrane equilibrium state and sessile drops by focusing on the global characteristics of the deformation, both numerically and experimentally. To determine the initial tension, which is required for numerical analysis, we carried out a modal test. A laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) was used to measure the velocity of the membrane vibration on a table isolated from external forces. With the measured the first and second modal frequencies, the initial tension of the membrane was derived using a circular membrane vibration equation by solving a first kind of Bessel function. Furthermore, a high-resolution reflective displacement sensor and micro linear actuator with micrometer accuracy were used to measure the cross-section deformation of the membrane on the sessile drop, and the droplet contact radius in the experimental environment. The membrane sample was assembled on a thin, light aluminum ring with a resonance frequency of about 700 Hz, and three different diameters were employed. Using this technique, we investigated the trend in membrane deformation due to the increase in the weight of the water droplets and the surface tension, which is an intrinsic property of the membrane. In addition, we found that the experimental results related to the contact radius and contour of a water drop agreed with the simulation data well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Nair, I. Sharma and V. Shankar, Planar equilibria of sessile and pendant liquid drops on geometrically non-linear elastic membranes, Physics of Fluids, 30 (2018) 082114.
D. Wu, P. I. Wang, P. Wu, Q. Yang, F. Liu, Y. Han, F. Xu and L. Wang, Determination of contact angle of droplet on convex and concave spherical surfaces, Chemical Physics, 457 (2015) 63–69.
R. D. Schulman and K. Dalnoki-Veress, Liquid droplets on a highly deformable membrane, Physical Review Letters PRL, 115 (2015) 206101.
Critical surface tension and contact angle with water for various polymers, https://www.accudynetest.com/polytable_03.html?sortby=contact_angle.
A. F. Stalder, T. Melchior, M. Muller, D. Sage, T. Blu and M. Unser, Low-Bond axisymmetric drop shape analysis for surface tension and contact angle measurements of sessile drops, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 364 (2010) 72–81.
W. Barthloet, M. Mail, B. Bhushan and K. Koch, Plant surfaces: Structures and functions for biomimetic innovations, Nano-micro Letters, Springer (2017).
R. W. Syle, A. Jagota, C.-Y. Hui and E. R. Dufresne, Elasto-capillarity: Surface tension and the mecahnics of soft solids, Reviews In Advance, 8 (1) (2017) 99–118.
Y.-S. Yu and Y. P. Zhao, Elastic deformation of soft membrane with finite thickness induced by a sessile liquid droplet, Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 339 (2009) 489–494.
S. Errede, Vibration of ideal circular membranes (e.g. Drums) and circular plates, UIUC Physics 406 Acoustical Physics of Music, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
M. Kamper and A. Bekker, Modal analysis of a hyperelastic membrane for the development of a musical instrument, 7th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference IOMAC 17 (2017).
S. S. Rao, Vibration of Continuous System, John Wley & Sons Ltd. (2019).
S. Dash and S. V. Garimella, Droplet evaporation on heated hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces, Physical Review E 9, 042402 (2014).
L. Luo, Z. Jia, H. Yang, Z. Zhang and M. Chen, Evaporation characteristics of droplets on a gradient microhole-patterned surface, J. Mater Sci., 53 (2018) 1447–1454.
R. G. Picknett and R. Bexon, The evaporation of sessile or pendant drops in still air, Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 61 (2) September (1977) ISSN 0021-9797.
C. Pozrikidis, Fluid Dynamics: Theory, Computation, and Numerical Simulation, Third edition.
S. S. Antman, Nonlinear Problems of Elasticity, Springer (2005).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2018R1A2B6006891).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Editor No-cheol Park
Kyoung-Su Park was born in Seoul, Korea, in 1976. He received the B.E. degree in electrical-mechanical engineering from the Yonsei university, Seoul, Korea, in 2000, and the master and Ph.D. degrees in mechanical engineering from the Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea in 2002 and 2006, respectively. In 2006, he joined the Samsung Electronics Corp. and he has worked for about three years. Since September 2008, he has been a Research Professor with the School of Mechanical Engineering at the Yonsei University. And he has become an Associate Professor in mechanical engineering at Gachon University since 2014. His current research interests include the vibration and control issues for cable-driven parallel robot, vibration issues for ultra-high speed maglev and nano-level vibration issues. He has served as executive member for about 10 years in ASMEISPS (Information Storage and Processing System) and he became a Chair of ASME-ISPS Division from July 2016 to August 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, HG., Park, KS. Experimental and numerical analysis on the equilibrium shape of sessile droplets on elastic thin membranes. J Mech Sci Technol 34, 667–673 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-020-0112-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-020-0112-9