Abstract
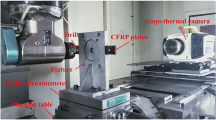
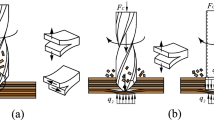
The control of hole exit damage and hole wall quality poses a considerable challenge during the drilling of carbon fiber-reinforced plastic (CFRP). This study aims to study the effect of the cutting edge type on the aforementioned issues. First, a comparative study between hole exit damage caused by a twist drill and a double-point angle drill was conducted to investigate the influences of the chisel, principal, and secondary cutting edges on hole exit damage. The maximum damage ring caused by the double-point angle drill is smaller than that caused by the twist drill because the drop speed of the cutting force in the secondary cutting edge drill during the exit stage of the double-point angle drill is less than that of the twist drill. Then, the double-point angle drill was used to determine the effects of tool wear on thrust force and hole wall damage. Outer corner wear and flank wear were investigated, and hole wall damage mechanisms were discussed. The damage of missing fibers does not worsen with an increase in tool wear, but the damage of fiber pullout becomes more serious due to increased cutting force. Consequently, a double-point angle drill bit is preferable for drilling holes on CFRP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. J. Yoon, D. D. Chen, S. W. Han, N. S. Choi and K. Arakawa, AE analysis of delamination crack propagation in carbon fiber-reinforced polymer materials, J. Mech. Sci. Technal., 29 (1) (2015) 17–21.
S. J. Ha, K. B. Kim, J. K. Yang and M. W. Cho, Influence of cutting temperature on carbon fiber-reinforced plastic composites in high-speed machining, J. Mech. Sci. Technal., 31 (4) (2017) 1861–1867.
R. Stone and K. Krishnamurthy, A neural network thrust force controller to minimize delamination during drilling of graphite-epoxy laminates, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 36 (9) (1996) 985–1003.
C. C. Tsao and H. Hocheng, Parametric study on thrust force of core drill, J. Mater. Processing Tech., 192–193 (2007) 37–40.
X. Qin, B. Wang, G. Wang, H. Li, Y. Jiang and X. Zhang, Delamination analysis of the helical milling of carbon fiber-reinforced plastics by using the artificial neural network model, J. Mech. Sci. Technol, 28 (2) (2014) 713–719.
A. Faraz, D. Biermann and K. Weinert, Cutting edge rounding: An innovative tool wear criterion in drilling CFRP composite laminates, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 49 (15) (2009) 1185–1196.
N. Feito, J. Diaz Alvarez, J. L. Cantero and M. H. Miguelez, Influence of special tool geometry in drilling woven CFRPs materials, Procedia Engineering, 132 (2015) 632–638.
T. J. Grilo, R. M. F. Paulo, C. R. M. Silva and J. P. Davim, Experimental delamination analyses of CFRPs using different drill geometries, Compos. Part B: Eng., 45 (1) (2013) 1344–1350.
I. Singh and N. Bhatnagar, Drilling of uni-directional glass fiber reinforced plastic (UD-GFRP) composite laminates, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 27 (9–10) (2006) 870–876.
M.-B. Lazar and P. Xirouchakis, Experimental analysis of drilling fiber reinforced composites, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 51 (12) (2011) 937–946.
U. Heisel and T. Pfeifroth, Influence of point angle on drill hole quality and machining forces when drilling CFRP, Procedia CIRP, 1 (7) (2012) 471–476.
J. Y. Xu, Q. L. An, X. J. Cai and M. Chen, Drilling machinability evaluation on new developed high-strength T800S/250F CFRP laminates, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Man., 14 (10) (2013) 1687–1696.
A. M. Abrao, J. C. C. Rubio, P. E. Faria and J. P. Davim, The effect of cutting tool geometry on thrust force and delamination when drilling glass fiber reinforced plastic composite, Mater. Des., 29 (2) (2008) 508–513.
S. Rawat and H. Attia, Characterization of the dry high speed drilling process of woven composites using machinability maps approach, CIRP Ann-Manuf. Technol., 58 (1) (2009) 105–108.
S. Rawat and H. Attia, Wear mechanisms and tool life management of WC-Co drills during dry high speed drilling of woven carbon fibre composites, Wear, 267 (5–8) (2009) 1022–1030.
Z. Y. Jia, R. Fu, B. Niu, B. W. Qian, Y. Bai and F. J. Wang, Novel drill structure for damage reduction in drilling CFRP composites, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 110 (2016) 55–65.
F. Wang, B. Qian, Z. Y. Jia, R. Fu and D. Cheng, Secondary cutting edge wear of one-shot drill bit in drilling CFRP and its impact on hole quality, Compos. Struct., 178 (2017) Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/jxompstruct2017.04.024.
K. S. Woon, A. Chaudhari, A. S. Kumar and M. Rahman, The effects of tool degradation on hole straightness in deep hole gundrilling of Inconel-718, Procedia CIRP, 14 (2014) 593–598.
A. Z. Sultan, S. Sharif and D. Kurniawan, Effect of machining parameters on tool wear and hole quality of AISI 316L stainless steel in conventional drilling, Procedia Manufacturing, 2 (2015) 202–207.
J. L. Merino-Perez, E. Merson, S. Ayvar-Soberanis and A. Hodzic, The applicability of Taylor’s model to the drilling of CFRP using uncoated WC-Co tools: The influence of cutting speed on tool wear, International Journal of Machining and Machinability of Materials, 16 (2) (2014) 95–112.
S. Gaugel, P. Sripathy, A. Haeger, D. Meinhard, T. Bernthaler, F. Lissek, M. Kaufeld, V. Knoblauch and G. Schneider, A comparative study on tool wear and laminate damage in drilling of carbon-fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP), Compos. Struct., 155 (2016) 173–183.
A. Celik, I. Lazoglu, A. Kara and F. Kara, Wear on SiAlON ceramic tools in drilling of aerospace grade CFRP composites, Wear, 338 (2015) 11–21.
G. Poulachon, J. Outeiro, C. Ramirez, V. Andre and G. Abrivard, Hole surface topography and tool wear in CFRP drilling, Procedia CIRP, 45 (2016) 35–38.
S. Rawat and H. Attia, Wear mechanisms and tool life management of WC-Co drills during dry high speed drilling of woven carbon fibre composites, Wear, 267 (5) (2009) 1022–1030.
Y. Karpata and O. Bahtiyar, Comparative analysis of PCD drill designs during drilling of CFRP laminates, Procedia CIRP, 31 (2015) 316–321.
Y. Karpat, B. Deger and O. Bahtiyar, Experimental evaluation of polycrystalline diamond tool geometries while drilling carbon fiber-reinforced plastics, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 71 (5–8) (2014) 1295–1307.
C. C. Tsao and H. Hocheng, Effects of exit back-up on delamination in drilling composite materials using a saw-drill and a core drill, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 45 (11) (2005) 1261–1270.
Z. Qi, K. Zhang, Y. Li, S. Liu and H. Cheng, Critical thrust force predicting modeling for delamination-free drilling of metal-FRP stacks, Compos. Struct., 107 (1) (2014) 604–609.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Recommended by Editor Hyung Wook Park
Pengnan Li obtained his Ph.D. in mechanical design and theory from China University of Mining and Technology. Prof. Li is currently a Professor in the School of Mechanical Engineering of Hunan University of Science and Technology, China. His research interests include high-speed machining of difficult-to-cut materials and cutting tool design.
Tae Jo Ko is a Professor of mechanical engineering in Yeungnam University, South Korea. He obtained his B.S. and M.S. from Pusan National University, Korea, and his Ph.D. from POSTECH, Korea. His research interests include machine tools, metal cuttings, and non-traditional machining and surface texturing using metal cutting, grinding and bio-machining.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Qiu, X., Li, C. et al. Hole exit damage and tool wear during the drilling of CFRP with a double-point angle drill. J Mech Sci Technol 33, 2363–2370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0436-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-019-0436-5