Abstract
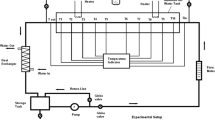
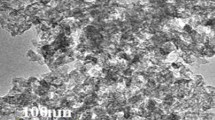
The effect of nanofluids on heat transfer inside circular tubes under uniform constant heat flux boundary condition was investigated. The working nanofluid was a suspension of γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles of average diameter 20 nm. The heat transfer coefficients were calculated experimentally in the range of 1057 < Re < 2070 with different particle volume concentrations of 0.1%, 0.3% and 0.9%. Increasing the particle volume fraction led to enhancement of the convective heat transfer coefficient. The results show that the average heat transfer coefficient increased 16.8% at 0.9% volume concentration and Reynolds number of 2070 compared with distilled water. In addition, the enhancement of the convective heat transfer was particularly significant in the entrance region and decreased with axial distance. Finally, an empirical correlation for Nusselt number has been proposed for the present range of nanofluids. The mean deviation between the predicted Nusselt number and experimental values for the new correlation is 3.57%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. W. Duangthongsuk and S. B. Wongwises, Comparison of the effects of measured and computed thermo-physical properties of nanofluids on heat transfer performance, Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci., 34 (2010) 616–624.
J. H. Lee, K. S. Hwang, S. P. Jang, B. H. Lee, J. H. Kim, S. U. S. Choi and C. J. Choi, Effective viscosities and thermal conductivities of aqueous nanofluids containing low volume concentrations of Al2O3 nanoparticles, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 51 (2008) 2651–2656.
S. U. S. Choi, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, ASME FED, 231 (1995) 99–105.
J. A. Eastman, S. U. S. Choi, S. Li, W. Yu and L. J. Thompson, Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles, Appl. Phys. Lett., 78 (2001) 718–720.
S. Lee, S. U. S. Choi, S. Li and J. A. Eastman, Measuring thermal conductivity of fluids containing oxide nanoparticles, J. Heat Transf., 121 (1999) 280–289.
Y. M. Xuan and Q. Li, Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids, Int. J. Heat. Fluid. Flow, 21 (2000) 58–64.
H. Xie, J. Wang, T. G. Xie, Y. Liu and F. Ai, Thermal conductivity enhancement of suspensions containing nanosized alumina particles, J. Appl. Phys., 91 (2002) 4568–4572.
S. K. Das, S. U. S. Choi and H. E. Patel, Heat transfer in nanofluids-a review, Heat. Transf. Eng., 37 (2006) 3–19.
S. Choi and J. A. Eastman, Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, ASME Int. Mech. Eng. Congr. Expos., San Francisco, CA (1995) 99–105.
X. W. Wang and X. F. Xu, Thermal conductivity of nanoparticle-fluid mixture, J. Thermophys. Heat. Transf., 13 (1999) 474–480.
W. Daungthongsuk and S. Wongwises, A critical review of convective heat transfer nanofluids, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 11 (2007) 797–817.
V. Trisaksri and S. Wongwises, Critical review of heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 11 (2007) 512–523.
M. Chandrasekar, S. Suresh and T. Senthilkumar, Mechanisms proposed through experimental investigations on thermophysical properties and forced convective heat transfer characteristics of various nanofluids -A review, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., 16 (2012) 3917–3938.
D. Wen and Y. Ding, Experimental investigation into convective heat transfer of nanofluids at the entrance region under laminar flow conditions, Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf., 47 (2004) 5181–5188.
S. Z. Heris, S. Gh. Etemad and M. N. Esfahany, Experimental investigation of oxide nanofluids laminar flow convective heat transfer, Int. Commun. Heat. Mass. Transf., 33 (2006) 529–535.
K. B. Anoop, T. Sundararajan and S. K. Das, Effect of particle size on the convective heat transfer in nanofluid in the developing region, Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf., 52 (2009) 2189–2195.
E. Esmaeilzadeh, H. Almohammadi, Sh. N. Vatan and A. N. Omrani, Experimental investigation of hydrodynamics and heat transfer characteristics of γ-Al2O3/water under laminar flow inside a horizontal tube, Int. J. of Therm. Sci., 63 (2013) 31–37.
L. S. Sundar and K. V. Sharma, Heat transfer enhancements of low volume concentration Al2O3 nanofluid and with longitudinal strip inserts in a circular tube, Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf., 53 (2010) 4280–4286.
P. C. Mukesh Kumar, J. Kumar and S. Suresh, Experimental investigation on convective heat transfer and friction factor in a helically coiled tube with Al2O3/water nanofluid, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 27 (2013) 239–245.
A. J. Chamkha, Unsteady laminar hydromagnetic fluidparticle flow and heat transfer in channels and circular pipes, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 21 (6) (2000) 740–746.
N. Akbar, Heat transfer and carbon nano tubes analysis for the peristaltic flow in a diverging tube, Meccanica, 50 (2015) 39–47.
M. A. Sheremet, T. Groşan and I. Pop, Free convection in shallow and slender porous cavities filled by a nanofluid using Buongiorno’s model, J. Heat. Transf., 136 (2014) 082501.
M. A. Sheremet and I. Pop, Conjugate natural convection in a square porous cavity filled by a nanofluid using Buongiorno’s mathematical model, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 79 (2014) 137–145.
J. Buongiorno, Convective transport in nanofluids, ASME J. Heat Transf., 128 (2006) 240–250.
A. Noghrehabadi, R. Pourrajab and M. Ghalambaz, Effect of partial slip boundary condition on the flow and heat transfer of nanofluids past stretching sheet prescribed constant wall temperature, Int. J. Thermal Sci., 54 (2012) 253–261.
O. D. Makinde, Effects of viscous dissipation and Newtonian heating on boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a flat plate, Int. J. Numer. Methods. Heat. & Fluid. Flow, 23 (2013) 1291–1303.
A. Zaraki, M. Ghalambaz, A. J. Chamkha, M. Ghalambaz and D. D. Rossi, Theoretical analysis of natural convection boundary layer heat and mass transfer of nanofluids: Effects of size, shapen and type of nanoparticles, type of base fluid and working temperature, Adv. Powder. Technol. (2015). doi:10.1016/j.apt.2015.03.012.
A. Noghrehabadi, M. Saffarian, R. Pourrajab and M. Ghalambaz, Entropy analysis for nanofluid flow over a stretching sheet in the presence of heat generation/absorption and partial slip, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 27 (2013) 927–937.
M. H. Mkwizu and O. D. Makinde, Entropy generation in a variable viscosity channel flow of nanofluids with convective cooling, Comptes Rendus Mécanique, 343 (2015) 38–56.
N. Akbar, Entropy generation analysis for a CNT suspension nanofluid in plumb ducts with peristalsis, Entropy, 17 (2015) 1411–1424.
L. S. Sundar, M. T. Naik, K. V. Sharma, M. K. Singh and T. Ch. S. Reddy, Experimental investigation of forced convection heat transfer and friction factor in a tube with Fe3O4 magnetic nanofluid, Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci., 37 (2012) 65–71.
H. R. Rayatzadeh, M. Saffar-Avval, M. Mansourkiaei and A. Abbassi, Effects of continuous sonication on laminar convective heat transfer inside a tube using water-TiO2 nanofluid, Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci., 48 (2013) 8–14.
B. Sahin, G. G. Gültekin, E. Manay and S. Karagoz, Experimental investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of Al2O3-water nanofluid, Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci., 50 (2013) 21–28.
W. H. Azmi, K. V. Sharma, P. K. Sarma, R. Mamat, S. Anuar and V. D. Rao, Experimental determination of turbulent forced convection heat transfer and friction factor with SiO2 nanofluid, Exp. Therm. Fluid. Sci., 51 (2013) 103–111.
S. K. Das, S. U. S. Choi, W. Yu and T. Pradeep, Nanofluids, Science and technology, Wiley (2008).
S. K. Das, N. Putra, P. Thiesen and W. Roetzel, Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids, J. Heat. Transf., 125 (2003) 567–574.
H. Xie, L. Chen and Q. Wu, Measurements of the viscosity of suspensions (nanofluids) containing nanosized Al2O3 particles, High Temperatures -High Pressures, 37 (2008) 127–135.
J. C. Maxwell, A treatise on electricity and magnetism, Second ed., Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK (1881).
B. Pak and Y. Cho, Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles, Exp. Heat Transf., 11 (1998) 151–170.
Y. Xuan and W. Roetzel, Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids, Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf., 43 (2000) 3701–3707.
S. E. B. Maïga, S. J. Palm, C. T. Nguyen, G. Roy and N. Galanis, Heat transfer enhancement by using nanofluids in forced convection flows, Int. J. Heat. Fluid. Flow., 26 (2005) 530–546.
J. Kline and F. A. McClintock, Describing uncertainties in single sample experiments, Mech. Eng., 75 (1953) 3–8.
R. K. Shah, Thermal entry length solutions for the circular tube and parallel plates, Proc. of Third National Heat. Mass. Transfer, Bombay (1975).
R. K. Shah and A. L. London, Laminar flow forced convection in ducts, New York: Supplement 1 to Advances in heat transfer, Academic Press (1978).
R. K. Shah and M. S. Bhatti, Laminar convective heat transfer in ducts, in: S. Kakaç, R. K. Shah and W. Aung (Eds), Handbook of single-phase convective heat transfer, Wiley, New York (1987).
G. P. Celata, M. Cumo and G. Zummo, Thermal-hydraulic characteristics of single phase flow in capillary pipes, Exp. Therm. Fluids Sci., 28 (2004) 87–95.
Z. Y. Guo and Z. X. Li, Size effect on single-phase channel flow and heat transfer at microscale, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 24 (2003) 284–329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Dae Hee Lee
Aminreza Noghrehabadi is an associate professor in Mechanical Engineering at Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz. His research interests are on the field of nanofluid heat and mass transfer, NEMS actuators and heat transfer in porous media.
Rashid Pourrajab is graduate M.S. in Mechanical Engineering at Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz. His research has been mainly focused on the development of new heat transfer enhancement fluid called nanofluids. He is working on modeling, production and experiments with nanofluids.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noghrehabadi, A., Pourrajab, R. Experimental investigation of forced convective heat transfer enhancement of γ-Al2O3/water nanofluid in a tube. J Mech Sci Technol 30, 943–952 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-016-0148-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-016-0148-z