Abstract
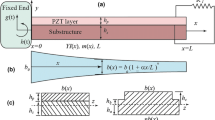
An FEM-based topology optimization approach is proposed to calculate the topologies of a substrate plate and a piezoelectric layer used for vibrating unimorph cantilevered plate-like electricity generators (energy harvesters). The Mindlin plate theory was combined with a topology optimization algorithm to consider the shear effect. Each optimum topology for a plate and a piezoelectric layer is computed and combined by reflecting the natural frequencies of the substrate plate, electromechanical couplings of piezoelectric materials, tip masses and method of moving asymptotes. The piezoelectric coefficients such as elasticity, piezoelectric coupling and capacitance are interpolated by element density variables. The cantilevered plate generators with optimal topologies were designed for three piezoelectric materials such as PZT, PMN-PT and PMN-PT single crystal fiber MFC, and their voltage outputs were compared using a developed FEM-based optimization code to investigate the suitable material for harvesters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. J. Holler, D. A. Skoog and S. R. Crouch, Principles of instrumental analysis, Chapter 1, 6th ed., Cengage Learning (2007).
A. Manbachi and R. S. C. Cobbold, Development and application of piezoelectric materials for ultrasound generation and detection, Ultrasound, 19(4) (2011) 187–196.
P. G. Jones, S. P. Beeby and N. M. White. Towards a piezoelectric vibration-powered microgenerator, IEEE Science, Measurement and Technology, 148 (2001) 68–72.
T. Sterken, K. Baert, C. van Hoof, R. Puers, G. Borghs, P. Fiorini, I. Mcp and B. Leuven, Comparative modeling for vibration scavengers, Proc. IEEE sensors (2004) 1249–1252.
S. Roundy and P. K. Wright, A piezoelectric vibration based generator for wireless electronics, Smart Mater, 13(5) (2004) 1131–1142.
Y. Liao and H. A. Sodano, Model of a single mode energy harvester and properties for optimal power generation, Smart Mater. Struct., 17(6) (2008) 065026.
A. Erturk and D. J. Inman, On mechanical modeling of cantilevered piezoelectric vibration energy harvester, J. Intel. Mat. Sys. Struct., 19 (2008) 1311–1325.
D. J. Inman and A. Erturk, A distributed parameter electromechanical model for cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvesters, J. Vib. Acoust., 130 (2008) 325–329.
J. Park, S. Lee and B. M. Kwak, Design optimization of piezoelectric energy harvester subject tip excitation, J. mech. Sci. Tech., 26(1) (2012) 137–143.
M. Kögl amd E. C. N. Silva, Topology optimization of smart structures: design of piezoelectric plate and shell actuators, J. Smart mater. Struct., 14 (2005) 387–399.
C. J. Rupp, A. Evgrafov, K. Maute and M. L. Dunn, Design of piezoelectric energy harvesting systems: A topology optimization approach based on multilayer plates and shells, J. Intel. Mat. Sys. Struct., 20 (2009) 1923–1939.
B. Zheng, C. J. Chang and H. C. Gea, Topology optimization of energy harvesting devices using piezoelectric materials, Struct. Multidisc. Optim., 38 (2008) 17–23.
A. Donoso and O. Sigmund, Optimization of piezoelectric bimorph actuators with active damping for static and dynamic loads, Struct. Multidiscip. Optim., 38(2) (2009) 171–183.
A. Donoso, J. C. Bellido and J. M. Chacon, Numerical and analytical method for the design of piezoelectric modal sensors/actuators for shell-type structures, Int. J. Mumer. Methods Eng., 81 (2010) 1700–1712.
E. C. N. Silva and N. Kikuchi, Design of piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization, Smart mater. Struct., 8(3) (1999) 350–364.
E. C. N. Silva et al., Design of piezoelectric materials and piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization — part I, Arch. Comput. Methods Eng., 6(3) (1999) 117–182.
E. C. N. Silva, S. Nishiwaki and N. Kikuchi, Design of piezoelectric materials and piezoelectric transducers using topology optimization — part II, Arch. Comput. Methods Eng., 6(3) (1999) 191–222.
R. C. Carbonari, E. C. N. Silva and S. Nishiwaki, Optimum placement of piezoelectric material in piezoactuator design, Smart. Mater. Struct., 16(1) (2007) 207–220.
Z. Luo, L. Tong, J. Luo and M. Y. Wang, Design of piezoelectric actuators using a multiphase level set method piecewise constants, J. Comput. Phys., 228(7) (2009) 2643–2659.
S. Chen, S. Gonella, W. Chen and W. K. Liu, A level set approach for optimal design of smart energy harvesters, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 199(37–40) (2010) 2532–2543.
Z. Kang and X. Wang, Topology optimization of bending actuators with multilayer piezoelectric material, Smart Mater. Struct., 19 (2010) 075018.
J. E. Kim, D. S. Kim, P. S. Ma and Y. Y. Kim, Multiphysics interpolation for the topology optimization of piezoelectric systems, Comput. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 199 (2010) 3153–3168.
J. Y. Noh and G. H. Yoon, Topology optimization of piezoelectric energy harvesting devices considering static and harmonic dynamic loads, Adv. Eng. Software, 53 (2012) 45–60.
M. P. Bendsøe and O. Sigmund, Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods and Applications, Springer, Berlin (2003).
K. J. Bathe, Finite element procedures in engineering analysis, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey (1982).
O. Sigmund, A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab, Struct. Multidisc. Optim., 21(2) (2011) 120–127.
ANSYS, ANSYS Release 8.0 documentation (2003).
S. Zhang, J. Luo, W. Hackenberger and T. R. Shrout, Characterization of Pb(In1/2Nb1/2)O3-Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 ferroelectric crystal with enhanced phase transition temperatures, J. Appl. Phys., 104(6) (2008) 064106.
M. W. Hyer, Stress analysis of fiber-reinforced composite materials, McGraw-Hill, New York (1998).
J. S. Park and J. H. Kim, Analytical development of single crystal macro fiber composite actuators for active twist rotor blades, Smart Mat. Struct., 14(4) (2005) 745–753.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Gang-Won Jang
Cheol Kim received a B.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Yonsei University in 1985, his M.S. from Georgia Institute of Technology in 1989 and Ph.D. from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA, in 1994. He is currently a professor at the School of Mechanical Engineering at Kyungpook National University (KNU) in Daegu, Korea. His research interests include design optimization with smart materials, analysis of strength and structural vibration, and automotive battery materials.
Jinwoo Lee is currently a researcher in Hyundai Heavy Industries R&D Center. He received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in 2011 and 2013 respectively, from Kyungpook National University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C., Lee, J. Topology optimum design of unimorph piezoelectric cantilevered Mindlin plates as a vibrating electric harvester. J MECH SCI TECHNOL 28, 4131–4138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0925-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0925-5