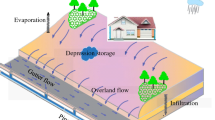
Abstract
Frequent urban rainstorm inundations can cause serious damages to human life and social economy. Reliable simulation of urban rainstorm inundation is an effective approach for performing flood risk analysis to reduce losses. In this work, a full 2D high-performance hydrodynamic model for urban rainstorm inundation simulation based on Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) was developed. The idealized V-shape catchment and sponge city district of Fengxi New City were selected as the study areas to assess performance of the model. The model was validated against analytical benchmark results of the idealized V-catchment test which show good agreement between the modelled flow and analytical solutions. The model was then applied to simulate actual urban rainstorm inundation process under measured rainfall. The results indicated that the model can be applied to high-resolution urban region simulations. Specifically, the validation results indicated that the proposed model had a good performance, with an accepted error of less than 15%. When applied to compute the Fengxi New city under design rainstorms with different annual return periods of 1, 5, 10, 20, 50, and 100 years, it was found that the model effectively evaluated the temporal and spatial variation process of urban inundation, and quantitatively investigated flood risks according to the water depth change. The model has been substantially accelerated on GPU to quickly predict urban inundation. The accuracy and rapid simulation speed of the model were verified based on the actual study area. Therefore, the proposed model can help to predict the dynamic processes of urban flood inundation and thus reduce flood inundation disasters. This is essential for future optimal sponge urban construction planning in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaguchi H, Kawamura A, Olsson J, Takasaki T (2012) Development and testing of a distributed urban storm runoff event model with a vector-based catchment delineation. Journal of Hydrology 420–421:205–215, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.12.003
Behera PK, Adams BJ, Li JY (2006) Runoff quality analysis of urban catchments with analytical probabilistic models. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 132(1):4–14, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9496(2006)132:1(4)
Beven K, Freer J (2001) A dynamic TOPMODEL. Hydrological Processes 15(10):1993–2011, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.252
Bi X, Cheng L, Yao D, Wang B, Wang L, Jin L, Yang X (2015) Analysis on urban rainstorm pattern of Xi’an. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences 43(35):295–297, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13989/j.cnki.0517-6611.2015.35.107 (in Chinese)
Bisht DS, Chatterjee C, Kalakoti S, Upadhyay P, Sahoo M, Panda A (2016) Modeling urban floods and drainage using SWMM and MIKE URBAN: A case study. Natural Hazards 84(2):749–776, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2455-1
Dazzi S, Vacondio, Mignosa P (2020) Internal boundary conditions for a GPU-accelerated 2D shallow water model: Implementation and applications. Advances in Water Resources 137:103525, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103525
Felder Q Zischg A, Weingartner R (2017) The effect of coupling hydrologic and hydrodynamic models on probable maximum flood estimation. Journal of Hydrology 550:157–165, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.04.052
Hapuarachchi HAP, Wang QJ, Pagano TC (2011) A review of advances in flash flood forecasting. Hydrological Processes 25(18):2771–2784, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.8040
Hou J, Li GY, Li GD, Liang Q, Zhi Z (2018a) Application of efficient high-resolution hydrodynamic model to simulations of flood propagation. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering 37(2):96–107 (in Chinese)
Hou J, Liang Q, Simons F, Hinkelmann R (2013a) A 2D well balanced shallow flow model for unstructured grids with novel slope source term treatment. Advances in Water Resources 52:107–131, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.08.003
Hou J, Liang Q, Simons F, Hinkelmann R (2013b) A stable 2D unstructured shallow flow model for simulations of wetting and drying over rough terrains. Computers & Fluids 82:132–147, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2013.04.015
Hou J, Wang R, Li GD, Li, GY (2018b) High-performance numerical model for high-resolution urban rainfall-runoff process based on dynamic wave method. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering 37(3):40–49 (in Chinese)
Iqbal M, Dahri Z, Querner E, Khan A, Hofstra N (2018) Impact of climate change on flood frequency and intensity in the Kabul River Basin. Geosciences 8(4):114, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8040114
Lacasta A, Morales-Hernández M, Murillo J, García-Navarro P (2014) An optimized GPU implementation of a 2D free surface simulation model on unstructured meshes. Advances in Engineering Software 78:1–15, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2014.08.007
Li C (2012) Ecohydrology and good urban design for urban storm water-logging in Beijing, China. Ecohydrology & Hydrobiology 12(4):287–300, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/v10104-012-0029-8
Li J, Li Y, Li Y (2016) SWMM-based evaluation of the effect of rain gardens on urbanized areas. Environmental Earth Sciences 75(1):1–14, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4807-7
Li Q, Wang F, Yu Y, Huang Z, Li M, Guan Y (2019) Comprehensive performance evaluation of LID practices for the sponge city construction: A case study in Guangxi, China. Journal of Environmental Management 231:10–20, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.024
Liang Q, Marche F (2009) Numerical resolution of well-balanced shallow water equations with complex source terms. Advances in Water Resources 32(6):873–884, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.02.010
Liang D, Özgen I, Hinkelmann R, Xiao, Chen JM (2015) Shallow water simulation of overland flows in idealised catchments. Environmental Earth Sciences 74:7307–7318, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4744-5
Liang Q, Smith L (2015) A high-performance integrated hydrodynamic modelling system for urban flood simulation. Journal of Hydroinformatics 17(4):518–533, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2015.029
Liang Q, Xia X, Hou J (2016) Catchment-scale high-resolution flash flood simulation using the GPU-based technology. Procedia Engineering 154:975–981, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.07.585
Lin T, Liu X, Song J, Zhang G, Jia Y, Tu Z, Zheng Z, Liu C (2018) Urban waterlogging risk assessment based on internet open data: A case study in China. Habitat International 71:88–96, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.11.013
Luo H, Chen W, Li Z, Pan J, Gao Q, Huang G (2019) Flood simulation of donghaochong basin in guangzhou city based on coupled hydrodynamic model. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering 30(3):46–52+65
Lv Y, Gao W, Yang C, Wang N (2018) Inundated areas extraction based on raindrop photometric model (RPM) in surveillance video. Water 10(10):1332, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101332
Meenar M, Fromuth R, Soro M (2018) Planning for watershed-wide flood-mitigation and stormwater management using an environmental justice framework. Environmental Practice 20(2–3):55–67, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14660466.2018.1507366
Meng X, Zhang M, Wen J, Du S, Xu H, Wang L, Yang Y (2019) A simple GIS-based model for urban rainstorm inundation simulation. Sustainability 11(10):2830, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102830
Mignot E, Paquier A, Haider S (2006) Modeling floods in a dense urban area using 2D shallow water equations. Journal of Hydrology 327(1–2):186–199, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.11.026
Ouyang W, Guo B, Hao F, Huang H, Li J, Gong Y (2012) Modeling urban storm rainfall runoff from diverse underlying surfaces and application for control design in Beijing. Journal of Environmental Management 113:467–473, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.10.017
Prosdocimi I, Kjeldsen TR, Miller JD (2015) Detection and attribution of urbanization effect on flood extremes using nonstationary flood-frequency models. Water Resource Research 51(6):4244–4262, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR017065
Qi W, Hou J, Liu J, Han H, Guo K, Ma Y (2018) Lake control on surface runoff causing urban flood inundation. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering 37(9):8–18 (in Chinese)
Quan R, Liu M, Lu M, Zhang L, Wang J, Xu S (2010) Waterlogging risk assessment based on land use/cover change: A case study in Pudong New Area, Shanghai. Environmental Earth Sciences 61(6):1113–1121, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0431-8
Razafison U, Cordier S, Delestre O, Darboux F, Lucas C, James F (2012) A shallow water model for the numerical simulation of overland flow on surfaces with ridges and furrows. European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids 31:44–52, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechflu.2011.07.002
Rong Y, Zhang T, Zheng Y, Hu C, Peng L, Feng P (2020) Three-dimensional urban flood inundation simulation based on digital aerial photogrammetry. Journal of Hydrology 584:124308, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124308
Schmid KA, Hadley BC, Wijekoon N (2011) Vertical accuracy and use of topographic LIDAR data in coastal marshes. Journal of Coastal Research 27(6A):221–227, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-10-00188.1
Smith L, Liang Q (2013) Towards a generalised GPU/CPU shallow-flow modelling tool. Computers & Fluids 88:17–20, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2013.09.018
Song L, Zhou J, Guo J, Zou Q, Liu Y (2011) A robust well balanced finite volume model for shallow water flows with wetting and drying over irregular terrain. Advances in Water Resources 34(7):915–932, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.04.017
Sun S, Zhai J, Li Y, Huang D, Wang G (2020) Urban waterlogging risk assessment in well-developed region of Eastern China. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth Parts A/B/C 115:102824
Tang X, Hong H, Shu Y, Tang H, Li J, Liu W (2019) Urban waterlogging susceptibility assessment based on a PSO-SVM method using a novel repeatedly random sampling idea to select negative samples. Journal of Hydrology 576:583–595, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.06.058
Vatanchi SM, Maghrebi MF (2019) Uncertainty in rating-curves due to manning roughness coefficient. Water Resources Management 33(15):5153–5167, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02421-6
Wang Y, Chen AS, Fu G, Djordjević S, Zhang C, Savić DA (2018) An integrated framework for high-resolution urban flood modelling considering multiple information sources and urban features. Environmental Modelling & Software 107:85–95, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.06.010
Wei N, Sun X, Bi X, Wang J, Li X (2019) The spatial characteristics of precipitation and water-logging disaster during rainy season for urban planning in Xi’an. Indoor Built Environment 28(9):1–9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X19856662
Xia X, Liang Q, Ming X (2019) A full-scale fluvial flood modelling framework based on a high-performance integrated hydrodynamic modelling system (HiPIMS). Advances in Water Resources 132:103392, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2019.103392
Xia X, Liang Q, Ming X, Hou J (2017) An efficient and stable hydrodynamic model with novel source term discretization schemes for overland flow and flood simulations. Water Resource Research 53(5):3730–3759, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2016WR020055
Yin J, Ye M, Yin Z, Xu S (2015) A review of advances in urban flood risk analysis over China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment 29(3):1063–1070, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-0939-7
Zhang S, Pan B (2014) An urban storm-inundation simulation method based on GIS. Journal of Hydrology 517:260–268, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.05.044
Zhang L, Ye Z, Shibata S (2020) Assessment of rain garden effects for the management of urban storm runoff in Japan. Sustainability 12(23):9982, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239982
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Open Research Fund of Beijing Key Laboratory of Urban Hydrological Cycle and Sponge City Technology, Beijing Normal University (No. HYD2018OF02); National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52079106, No. 52009104); Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi (No. 2021SF-484). The authors would like to thank Beijing Key Laboratory of Urban Hydrological Cycle and Sponge City Technology for providing with all the necessary technical support. We are also thankful to the editor and the four anonymous reviewers whose insightful and constructive comments helped us to improve the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Hou, J., Xu, Z. et al. A GPU-Accelerated Hydrodynamic Model for Urban Rainstorm Inundation Simulation: A Case Study in China. KSCE J Civ Eng 26, 1494–1504 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-2158-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-021-2158-3