Abstract
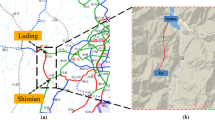
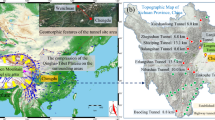
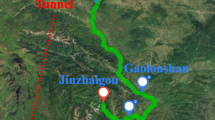
The issue of large deformation mechanism in soft rock tunnels has puzzled tunnel scholars for decades. Previous studies have not evolved a clear and common understanding. Therefore, detailed on-site measurement, full investigation and statistical analysis have been conducted on the instability and failure of Muzhailing Tunnel since its construction, whose length is beyond 15 km. The study aims at systematically analyzing the failure mechanisms and modes of Muzhailing Tunnel in monoclinic and soft-hard interbedded rock strata. Study results show that the angle between strata strike and tunnel axis greatly determines the magnitude of deformation, the dip direction significantly controls the bias direction and maximum deformation direction, and the dip angle deeply affects the deformation form. The failure modes of surrounding rock mainly include four types: spalling and overturning failure, bending failure, shear slip failure and buckling failure. Large deformation characteristics are summarized from six aspects: failure form, groundwater, sensitivity to influencing factors, deformation degree, deformation speed and deformation duration. The instability modes of primary lining include in-plane (transverse) instability and out-plane (longitudinal) instability. Finally, the causes of large deformation are analyzed from geological, structural, engineering and human factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Interlaminar cohesion
- F f :
-
Interlaminar friction
- F h :
-
Horizontal squeezing force
- F l :
-
Longitudinal squeezing force
- F s :
-
Shear resistance of rock mass
- F v :
-
Vertical stress
- N :
-
Interlaminar force
- N v :
-
Vertical resistance of foundation
- S :
-
Resistance of supporting structure
References
Anagnostou G (1993) A model for swelling rock in tunneling. Rock mechanics and Rock Engineering 26(4):307–331, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01027115
Aydan O, Akagi T, Kawamoto T (1993) The squeezing potential of rock around tunnels: Theory and prediction. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 26(2):137–163, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01023620
Barla G (1995) Squeezing rocks in tunnels. ISRM News Journal 2:44–49
Barla G (2001) Tunnelling under squeezing rock conditions. In: Kolymbas D (ed) Tunnelling mechanics, Eurosummer school. Logos Verlag, Innsbruck, Germany, 169–268
Chen M, Yang SQ, Zhang YC, Zang CW (2016) Analysis of the failure mechanism and support technology for the Dongtan deep coal roadway. Geomechanics and Engineering 11(3):401–420, DOI: https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2016.11.3.401
Chen ZM, Zhao DA, Yu YY (2011) The interaction mechanism of surrounding rock and supporting structure in high geostress extrusion fault. Advanced Materials Research 243–249:3588–3598, DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.243-249.3588
Feng WK, Huang RQ, Li TB (2012) Deformation analysis of a soft-hard rock contact zone surrounding a tunnel. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 32:190–197, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.06.011
Gao FQ, Stead D, Kang HP (2014) Simulation of roof shear failure in coal mine roadways using an innovative UDEC trigon approach. Computers and Geotechnics 61:33–41, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.04.009
Guo FL (2009) Research on large deformation mechanism of soft rock of Baozhen Tunnel. PhD Thesis, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing, China, DOI: https://doi.org/10.7666/d.y1781729 (in Chinese)
He MC (2011) Physical modeling of an underground roadway excavation in geologically 45° inclined rock using infrared thermography. Engineering Geology 121(3–4):165–176, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.12.001
He MC, Jia XN, Gong WL, Faramarzi L (2010a) Physical modeling of an underground roadway excavation in vertically stratified rock using infrared thermography. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences 47(7):1212–1221, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.06.020
He MC, Jing HH, Sun XM (2002) Engineering mechanics of soft rock. Science Press, Beijing, China, 1–44 (in Chinese)
He MC, Gong WL, Zhai HM, Zhang HP (2010b) Physical modeling of deep ground excavation in geologically horizontal strata based on infrared thermography. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 25(4):366–376, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2010.01.012
Huang X, Pan YC, Liu JP, Liu QS (2015) Mechanism and constitutive model of large deformation in TBM tunneling. Journal of China Coal Society 40(6):1245–1256, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.3040 (in Chinese)
Jiang Y, Li YL, Li TB, Wang LS (2004) Study of the classified system of types and mechanism of great distortion in tunnel and underground engineering. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation 15(4):46–51, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2004.04.012 (in Chinese)
Jing HW, Song HW, Guo ZH (1999) Study on deformation mechanism of broken zone around soft rock roadway and its control technique. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology 28(6):560–564, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.1999.06.010 (in Chinese)
Li TB, Meng LB, Wang LS (2016a) Stability of high-stress tunnels and prevention of rock burst and large deformation disasters. Science Press, Beijing, China, 524–535 (in Chinese)
Li PF, Zhao Y, Zhou XJ (2016b) Displacement characteristics of high-speed railway tunnel construction in loess ground by using multi-step excavation method. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 51:41–45, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2015.10.009
Liu Y, Wu XJ, Liu ZQ, Liu YY, Shu B (2014) Discussion of and solutions for the large deformation mechanism of a tunnel in carbonaceous slate. Modern Tunnelling Technology 51(6):19–24, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2014.06.004 (in Chinese)
Liu ZC, Zhu YQ, Li WJ, Liu PX (2008) Mechanism and classification criterion for large deformation of squeezing ground tunnels. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 30(5):690–697, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2008.05.012 (in Chinese)
Luo YB, Chen JX, Huang P, Tang MQ, Qiao X, Liu Q (2017a) Deformation and mechanical model of temporary support sidewall in tunnel cutting partial section. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 61:40–49, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2016.09.007
Luo YB, Chen JX, Wang HY, Sun PL (2017b) Deformation rule and mechanical characteristics of temporary support in soil tunnel constructed by sequential excavation method. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 21(6):2439–2449, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0978-3
Meng LB, Li TB, Jiang Y, Wang R, Li YR (2013) Characteristics and mechanisms of large deformation in the Zhegu mountain tunnel on the Sichuan-Tibet highway. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 37:157–164, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2013.03.009
Qing SH, Huang RQ (2005) Study on the large deformation characteristics of the soft rocks in Wushaoling tunnel. Modern Tunnel Technology 42(2):7–14, DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2005.02.002 (in Chinese)
Singh B, Jethwa JL, Dube AK (1992) Correlation between observed support pressure and rock mass quality. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 7(1):59–74, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0886-7798(92)90114-W
Sun J (2014) Study and application on key technology of tunnel structure design. People’s Communications Publishing Co., Ltd., Beijing, China, 123–136
Tan TK (1982) The mechanical problems for the long-term stability of underground galleries. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 1(1):1–20 (in Chinese)
Tan TK, Wen XM (1983) Swelling rocks and stability of tunnels. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 2(1):1–10 (in Chinese)
Tanimoto C (1984) NATM-1. Morikita Shuppan, Tokyo, Japan, 168–175 (in Japanese)
Tao ZG, Zhu C, Zheng XH, Wang DS, Liu YP, He MC, Wang YB (2018) Failure mechanisms of soft rock roadways in steeply inclined layered rock formations. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk 9(1):1186–1206, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2018.1497712
Terzaghi K (1946) Rock defects and loads on tunnel supports. In: Proctor RV, White TL (eds) Rock tunneling with steel supports, vol 1. Commercial Shearing and Stamping Company, Youngtown, OH, USA, 17–99
Wu FQ, Miao JL, Bao H (2015) Large deformation of tunnel in slate-schistose rock. Engineering Geology for Society and Territory 6:17–23, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09060-33
Yang SQ, Chen M, Fang G, Wang YC, Meng B, Li YH, Jing HW (2018) Physical experiment and numerical modelling of tunnel excavation in slanted upper-soft and lower-hard strata. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology 82:248–264, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2018.08.049
Zhang HJ, Li HY, Li SC, Bai JW, Hao TY, Li, HW (2015) Deformation mechanism of surrounding rock and support technology in deep soft rock roadway. Journal of Mining and Safety Engineering 32(6):955–962, DOI: https://doi.org/10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2015.06.014 (in Chinese)
Zhao Y, He HW, Li PF (2018) Key techniques for the construction of high-speed railway large-section loess tunnels. Engineering 4(2):254–2509, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2017.07.003
Zhu YQ, Li WJ, Zhao Y (2012) Stability and deformation control technology of soft rock tunnel. People’s Communications Press, Beijing, China, 81–108 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The present work is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.41831286). This support is gratefully acknowledged. The authors of this article are so grateful to editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Liu, W., Chen, L. et al. Failure Mechanisms and Modes of Tunnels in Monoclinic and Soft-Hard Interbedded Rocks: A Case Study. KSCE J Civ Eng 24, 1357–1373 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1324-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1324-3