Abstract
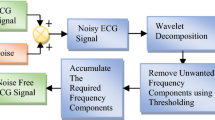
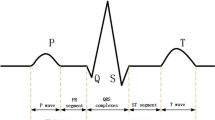
Cardiovascular diseases are the world’s leading cause of death; therefore cardiac health of the human heart has been a fascinating topic for decades. The electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is a comprehensive non-invasive method for determining cardiac health. Various health practitioners use the ECG signal to ascertain critical information about the human heart. In this article, swarm intelligence approaches are used in the biomedical signal processing sector to enhance adaptive hybrid filters and empirical wavelet transforms (EWTs). At first, the white Gaussian noise is added to the input ECG signal and then applied to the EWT. The ECG signals are denoised by the proposed adaptive hybrid filter. The honey badge optimization (HBO) algorithm is utilized to optimize the EWT window function and adaptive hybrid filter weight parameters. The proposed approach is simulated by MATLAB 2018a using the MIT-BIH dataset with white Gaussian, electromyogram and electrode motion artifact noises. A comparison of the HBO approach with recursive least square-based adaptive filter, multichannel least means square, and discrete wavelet transform methods has been done in order to show the efficiency of the proposed adaptive hybrid filter. The experimental results show that the HBO approach supported by EWT and adaptive hybrid filter can be employed efficiently for cardiovascular signal denoising.
摘要
心血管疾病是世界上最主要的死亡原因。几十年来,人类心脏的健康一直是一个令人感兴趣 的话题。心电图(ECG)信号是判断心脏健康状况的一种综合性的无创方法。许多健康医师利用心 电图信号来确定心脏的关键信息。本文将群体智能方法应用于生物医学信号处理领域,以增强自适 应混合滤波器和经验小波变换(EWT)。首先对输入心电信号加入高斯白噪声,然后对其进行EWT; 采用提出的自适应混合滤波器对ECG信号进行去噪处理。利用蜜獾优化(HBO)算法优化EWT窗 函数和自适应混合滤波器权重参数。所提方法在MATLAB 2018a中使用MIT-BIH数据集进行仿真, 该数据集包含高斯白噪声、肌电图噪声和电极运动伪影噪声。与基于递归最小二乘的自适应滤波器、 多通道最小均方方法和离散小波变换方法进行比较,验证了HBO方法的有效性。实验结果表明,在 EWT和自适应混合滤波的支持下,HBO方法可以有效应用于心血管信号去噪。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG G, YANG L, LIU M, et al. ECG signal denoising based on deep factor analysis [J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 57: 101824.
LASTRE-DOMÍNGUEZ C, SHMALIY Y S, IBARRA-MANZANO O, et al. ECG signal denoising and features extraction using unbiased FIR smoothing [J]. BioMed Research International, 2019, 2019: 2608547.
CHIANG H T, HSIEH Y Y, FU S W, et al. Noise reduction in ECG signals using fully convolutional denoising autoencoders [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 60806–60813.
CHATTERJEE S, THAKUR R S, YADAV R N, et al. Review of noise removal techniques in ECG signals [J]. IET Signal Processing, 2020, 14(9): 569–590.
BING P P, LIU W, ZHANG Z H. DeepCEDNet: An efficient deep convolutional encoder-decoder networks for ECG signal enhancement [J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 56699–56708.
ZHANG D Y, WANG S S, LI F, et al. An efficient ECG denoising method based on empirical mode decomposition, sample entropy, and improved threshold function [J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2020, 2020: 1–11.
MUKHERJEE P, BAKSHI A. System for ECG signal denoising [C]//2020 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing. Chennai: IEEE, 2020: 321–325.
SUNDARARAJ V. Optimised denoising scheme via opposition-based self-adaptive learning PSO algorithm for wavelet-based ECG signal noise reduction [J]. International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology, 2019, 31(4): 325.
CHANDRA M, GOEL P, ANAND A, et al. Design and analysis of improved high-speed adaptive filter architectures for ECG signal denoising [J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 63: 102221.
VARGAS R N, VEIGA A C P. Electrocardiogram signal denoising by a new noise variation estimate [J]. Research on Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 36(1): 13–20.
HAO H Q, LIU M, XIONG P, et al. Multi-lead model-based ECG signal denoising by guided filter [J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 79: 34–44.
BING P P, LIU W, WANG Z, et al. Noise reduction in ECG signal using an effective hybrid scheme [J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 160790–160801.
KUMAR A, TOMAR H, MEHLA V K, et al. Stationary wavelet transform based ECG signal denoising method [J]. ISA Transactions, 2021, 114: 251–262.
GUPTA V, MITTAL M. Arrhythmia detection in ECG signal using fractional wavelet transform with principal component analysis [J]. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, 2020, 101(5): 451–461.
MANJU B R, SNEHA M R. ECG denoising using Wiener filter and Kalman filter [J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 171: 273–281.
WASIMUDDIN M, ELLEITHY K, ABUZNEID A S, et al. Stages-based ECG signal analysis from traditional signal processing to machine learning approaches: A survey [J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 177782–177803.
WIDROW B, GLOVER J R, MCCOOL J M, et al. Adaptive noise cancelling: Principles and applications [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1975, 63(12): 1692–1716.
SHELTON L Y, CANO G G, COAST D A, et al. Detection of late potentials by adaptive filtering [J]. Journal of Electrocardiology, 1990, 23: 138–143.
MIRZA A, KABIR S M, AYUB S, et al. Impulsive Noise Cancellation of ECG signal based on SSRLS [J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2015, 62: 196–202.
DONG S P, YUAN M, WANG Q S, et al. A modified empirical wavelet transform for acoustic emission signal decomposition in structural health monitoring [J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1645.
WANG D, ZHAO Y, YI C, et al. Sparsity guided empirical wavelet transform for fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings [J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 101: 292–308.
LIU W, CHEN W. Recent advancements in empirical wavelet transform and its applications [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 103770–103780.
FRANCIS A, MURUGANANTHAM C. An adaptive denoising method using empirical wavelet transform [J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2015, 117(21): 18–20.
DAS M, KUMAR R, SAHANA B. Implementation of effective hybrid window function for E.C.G signal denoising [J]. Traitement Du Signal, 2020, 37(1): 119–128.
HASHIM F A, HOUSSEIN E H, HUSSAIN K, et al. Honey Badger Algorithm: New metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems [J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2022, 192: 84–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramanian, S., Naruk, M.S. & Tewari, G. Electrocardiogram Signal Denoising Using Optimized Adaptive Hybrid Filter with Empirical Wavelet Transform. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-023-2591-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-023-2591-1
Key words
- electrocardiogram (ECG) signal denoising
- empirical wavelet transform (EWT)
- honey badge optimization (HBO)
- adaptive hybrid filter
- window function