Abstract
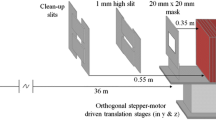
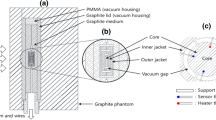
In this study, we implemented a practical dosimetry procedure of air kerma for kilovoltage X-ray beams using a 0.6-cc cylindrical ionization chamber, and validated the procedure with the accuracy of the measurements using the 0.6-cc chamber compared to the measurements using a 6-cc chamber and a semiconductor device. In addition, the kerma area products (KAPs) were compared with the dose reference levels of radiology. A modified air kerma formalism using a 0.6-cc cylindrical ionization chamber air kerma formalism with a cobalt absorbed dose-to-water calibration coefficient was implemented. Validation of the formalism showed good agreement between the 0.6-cc chamber and the 6-cc chamber (< 5%), and between the 0.6-cc chamber and the semiconductor device (< 2%) in the 60–120 kV range. The KAPs for four RO machines had difference factors of 0.04–15.4 and 0.01–4.1 from their median and maximum dose reference levels in radiology, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gregoire V, Guckenberger M, Haustermans K, Lagendijk JJW, Menard C, Potter R, et al. Image guidance in radiation therapy for better cure of cancer. Mol Oncol. 2020;14:1470–91.
Zou W, Dong L, Kevin Teo BK. Current state of image guidance in radiation oncology: implications for PTV margin expansion and adaptive therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2018;28:238–47.
Ding GX, Alaei P, Curran B, Flynn R, Gossman M, Mackie TR, et al. Image guidance doses delivered during radiotherapy: Quantification, management, and reduction: report of the AAPM therapy physics committee task group 180. Med Phys. 2018;45:e84–99.
Murphy MJ, Balter J, Balter S, BenComo JA Jr, Das IJ, Jiang SB, et al. The management of imaging dose during image-guided radiotherapy: report of the AAPM task group 75. Med Phys. 2007;34:4041–63.
de Crevoisier R, Bayar MA, Pommier P, Muracciole X, Pene F, Dudouet P, et al. Daily versus weekly prostate cancer image guided radiation therapy: phase 3 multicenter randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;102:1420–9.
Wachabauer D, Rothlin F, Moshammer HM, Homolka P. Diagnostic reference levels for conventional radiography and fluoroscopy in austria: results and updated National diagnostic reference levels derived from a nationwide survey. Eur J Radiol. 2019;113:135–9.
Rana VK, Rudin S, Bednarek DR. A tracking system to calculate patient skin dose in real-time during neurointerventional procedures using a biplane x-ray imaging system. Med Phys. 2016;43:5131.
Sonig A, Setlur Nagesh SV, Fennell VS, Gandhi S, Rangel-Castilla L, Ionita CN, et al. A Patient dose-reduction technique for neuroendovascular image-guided interventions: image-quality comparison study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39:734–41.
Ma CM, Nahum AE. Monte Carlo calculated stem effect correction for NE2561 and NE2571 chambers in medium-energy x-ray beams. Phys Med Biol. 1995;40:63–72.
Seuntjens J, Thierens H, Plaetsen AV, Segaert O. Determination of absorbed dose to water with ionisation chambers calibrated in free air for medium-energy X-rays. Phys Med Biol. 1988;33:1171–85.
Seuntjens J, Thierens H, Schneider U. Correction factors for a cylindrical ionization chamber used in medium-energy x-ray beams. Phys Med Biol. 1993;38:805–32.
Klein EE, Hanley J, Bayouth J, Yin FF, Simon W, Dresser S, et al. Task Group 142 report: quality assurance of medical accelerators. Med Phys. 2009;36:4197–212.
Araki F, Ohno T, Umeno S. Ionization chamber dosimetry based on 60Co absorbed dose to water calibration for diagnostic kilovoltage x-ray beams. Phys Med Biol. 2018;63: 185018.
Vassileva J, Rehani M. Diagnostic reference levels. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;204:W1-3.
ICRP. Diagnostic Reference Levels in Medical Imaging: Review and additional advice. ICRP Supporting Guidance 2. Ann ICRP. 2001;31:33–52.
Ma CM, Coffey CW, DeWerd LA, Liu C, Nath R, Seltzer SM, et al. AAPM protocol for 40–300 kV x-ray beam dosimetry in radiotherapy and radiobiology. Med Phys. 2001;28:868–93.
Araki F, Kouno T, Ohno T, Kakei K, Yoshiyama F, Kawamura S. Measurement of absorbed dose-to-water for an HDR 192Ir source with ionization chambers in a sandwich setup. Med Phys. 2013;40:092101.
Sarfehnia A, Kawrakow I, Seuntjens J. Direct measurement of absorbed dose to water in HDR 192Ir brachytherapy: water calorimetry, ionization chamber, Gafchromic film, and TG-43. Med Phys. 2010;37:1924–32.
Falco MD, D’Andrea M, Strigari L, D’Alessio D, Quagliani F, Santoni R, et al. Characterization of a cable-free system based on p-type MOSFET detectors for “in vivo” entrance skin dose measurements in interventional radiology. Med Phys. 2012;39:4866–74.
Ohno T, Araki F, Onizuka R, Hatemura M, Shimonobou T, Sakamoto T, et al. Comparison of dosimetric properties among four commercial multi-detector computed tomography scanners. Phys Med. 2017;35:50–8.
Ohno T, Araki F, Onizuka R, Hioki K, Tomiyama Y, Yamashita Y. New absorbed dose measurement with cylindrical water phantoms for multidetector CT. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60:4517–31.
ICRU. Stopping Powers for Electrons and Positrons, ICRU Report 37. ICRU. 1984.
JSMP. Standard dosimetry of absorbed dose to water in external beam radiotherapy (in Japanese). Tokyo: Tsusyo-sangyo-kenkyusya; 2012.
JCGM100. Evaluation of measurement data-Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement. International Organization for Standardization (ISO), in measurement. International Organization for Standardization (ISO), Joint Committee for Guides in Metrology. 2008.
JSMP. Standard dosimetry of absorbed dose to water in brachytherapy (in Japanese). Tokyo: Tsusyo-sangyo-kenkyusya; 2018.
Seuntjens J, Thierens H, Vanderplaetsen A, Segaert O. Determination of absorbed dose to water with ionization chambers calibrated in free air for medium-energy X-Rays. Phys Med Biol. 1988;33:1171–85.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Takanori Matsuoka for providing critical advice and comments in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Tachibana, H., Takahashi, R., Kogure, T. et al. Practical dosimetry procedure of air kerma for kilovoltage X-ray imaging in radiation oncology using a 0.6-cc cylindrical ionization chamber with a cobalt absorbed dose-to-water calibration coefficient. Radiol Phys Technol 15, 264–270 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-022-00665-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-022-00665-3