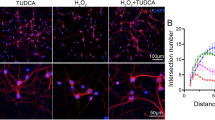
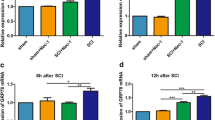
Abstract
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is generally divided into primary and secondary injuries, and apoptosis is an important event of the secondary injury. As an endogenous bile acid and recognized endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inhibitor, tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) administration has been reported to have a potentially therapeutic effect on neurodegenerative diseases, but its real mechanism is still unclear. In this study, we evaluated whether TUDCA could alleviate traumatic damage of the spinal cord and improve locomotion function in a mouse model of SCI. Traumatic SCI mice were intraperitoneally injected with TUDCA, and the effects were evaluated based on motor function assessment, histopathology, apoptosis detection, qRT-PCR, and western blot at different time periods. TUDCA administration can improve motor function and reduce secondary injury and lesion area after SCI. Furthermore, the apoptotic ratios were significantly reduced; Grp78, Erdj4, and CHOP were attenuated by the treatment. Unexpectedly, the levels of CIBZ, a novel therapeutic target for SCI, were specifically up-regulated. Taken together, it is suggested that TUDCA effectively suppressed ER stress through targeted up-regulation of CIBZ. This study also provides a new strategy for relieving secondary damage by inhibiting apoptosis in the early treatment of spinal cord injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn YH, Lee G, Kang SK (2006) Molecular insights of the injured lesions of rat spinal cords: inflammation, apoptosis, and cell survival. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:560–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.105
Basso DM, Fisher LC, Anderson AJ, Jakeman LB, McTigue DM, Popovich PG (2006) Basso Mouse Scale for locomotion detects differences in recovery after spinal cord injury in five common mouse strains. J Neurotrauma 23:635–659. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2006.23.635
Boyce M, Yuan J (2006) Cellular response to endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death Differ 13:363–373. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401817
Cai Y, Fan R, Hua T, Liu H, Li J (2011) Nimodipine alleviates apoptosis-mediated impairments through the mitochondrial pathway after spinal cord injury. Curr Zool 57:340–349
Cai Y, Li J, Yang S, Li P, Zhang X, Liu H (2012) CIBZ, a novel BTB domain-containing protein, is involved in mouse spinal cord injury via mitochondrial pathway independent of p53 gene. PLoS One 7:e33156. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033156
Cai Y, Li J, Zhang Z, Chen J, Zhu Y, Li R, Chen J, Gao L, Liu R, Teng Y (2017) Zbtb38 is a novel target for spinal cord injury. Oncotarget 8:45356–45366. 10.18632/oncotarget.17487
Crowe MJ, Bresnahan JC, Shuman SL, Masters JN, Beattie MS (1997) Apoptosis and delayed degeneration after spinal cord injury in rats and monkeys. Nat Med 3:73–76
Furlan JC, Fehlings MG (2008) Cardiovascular complications after acute spinal cord injury: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Neurosurg Focus 25:E13. https://doi.org/10.3171/FOC.2008.25.11.E13
Keene CD, Rodrigues CM, Eich T, Chhabra MS, Steer CJ, Low WC (2002) Tauroursodeoxycholic acid, a bile acid, is neuroprotective in a transgenic animal model of Huntington’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:10671–10676. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.162362299
Kotaka K, Nagai J, Hensley K, Ohshima T (2017) Lanthionine ketimine ester promotes locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury by reducing neuroinflammation and promoting axon growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483:759–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.12.069
Kurisu J, Honma A, Miyajima H, Kondo S, Okumura M, Imaizumi K (2003) MDG1/ERdj4, an ER-resident DnaJ family member, suppresses cell death induced by ER stress. Genes Cells 8:189–202
Lee YY, Hong SH, Lee YJ, Chung SS, Jung HS, Park SG, Park KS (2010) Tauroursodeoxycholate (TUDCA), chemical chaperone, enhances function of islets by reducing ER stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:735–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.022
Lu J, Ashwell KW, Waite P (2000) Advances in secondary spinal cord injury: role of apoptosis. Spine 25:1859–1866
McDonald JW, Sadowsky C (2002) Spinal-cord injury. Lancet 359:417–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07603-1
Nishii T, Oikawa Y, Ishida Y, Kawaichi M, Matsuda E (2012) CtBP-interacting BTB zinc finger protein (CIBZ) promotes proliferation and G1/S transition in embryonic stem cells via Nanog. J Biol Chem 287:12417–12424. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.333856
Noreau L, Proulx P, Gagnon L, Drolet M, Laramee MT (2000) Secondary impairments after spinal cord injury: a population-based study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 79:526–535
Ohri SS, Maddie MA, Zhao Y, Qiu MS, Hetman M, Whittemore SR (2011) Attenuating the endoplasmic reticulum stress response improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Glia 59:1489–1502
Oikawa Y, Matsuda E, Nishii T, Ishida Y, Kawaichi M (2008) Down-regulation of CIBZ, a novel substrate of caspase-3, induces apoptosis. J Biol Chem 283:14242–14247. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M802257200
Penas C, Guzman MS, Verdu E, Fores J, Navarro X, Casas C (2007) Spinal cord injury induces endoplasmic reticulum stress with different cell-type dependent response. J Neurochem 102:1242–1255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04671.x
Podda M, Crosignani A, Battezzati P, Buscarini L, Conte D, Notarbartolo A, Floreani A, Stabilini R, Manghisi OG (1995) Tauroursodeoxycholic acid for the treatment of chronic hepatitis: a dose-response study. Hepatology 22:A120
Ramalho RM, Ribeiro PS, Sola S, Castro RE, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM (2004) Inhibition of the E2F-1/p53/Bax pathway by tauroursodeoxycholic acid in amyloid beta-peptide-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells. J Neurochem 90:567–575. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02517.x
Ramalho RM, Viana RJ, Low WC, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM (2008) Bile acids and apoptosis modulation: an emerging role in experimental Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 14:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2007.12.001
Rodrigues CM, Sola S, Nan Z, Castro RE, Ribeiro PS, Low WC, Steer CJ (2003) Tauroursodeoxycholic acid reduces apoptosis and protects against neurological injury after acute hemorrhagic stroke in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:6087–6092. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1031632100
Romero-Ramirez L, Nieto-Sampedro M, Yanguas-Casas N (2017) Tauroursodeoxycholic acid: more than just a neuroprotective bile conjugate. Neural Regen Res 12:62–63. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.198979
Schroeder GD, Kepler CK, Vaccaro AR (2016) The use of cell transplantation in spinal cord injuries. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 24:266–275. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00375
Shuda M, Kondoh N, Imazeki N, Tanaka K, Okada T, Mori K, Hada A, Arai M, Wakatsuki T, Matsubara O, Yamamoto N, Yamamoto M (2003) Activation of the ATF6, XBP1 and grp78 genes in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a possible involvement of the ER stress pathway in hepatocarcinogenesis. J Hepatol 38:605–614
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM, Samali A (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7:880–885. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400779
Takayanagi S, Fukuda R, Takeuchi Y, Tsukada S, Yoshida K (2013) Gene regulatory network of unfolded protein response genes in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Stress Chaperones 18:11–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-012-0351-5
Vang S, Longley K, Steer CJ, Low WC (2014) The unexpected uses of urso- and tauroursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of non-liver diseases. Glob Adv Health Med 3:58–69. https://doi.org/10.7453/gahmj.2014.017
Wang M, Wang P, Peng JL, Wu S, Zhao XP, Li L, Shen GX (2009) The altered expression of glucose-regulated proteins 78 in different phase of streptozotocin-affected pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 14:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-008-0053-1
Wang Z, Zhang C, Hong Z, Chen H, Chen W, Chen G (2013) C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) mediates neuronal apoptosis in rats with spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med 5:107–111. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2012.745
Wang C, Liu C, Gao K, Zhao H, Zhou Z, Shen Z, Guo Y, Li Z, Yao T, Mei X (2016) Metformin preconditioning provide neuroprotection through enhancement of autophagy and suppression of inflammation and apoptosis after spinal cord injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 477:534–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.148
Wells JE, Hurlbert RJ, Fehlings MG, Yong VW (2003) Neuroprotection by minocycline facilitates significant recovery from spinal cord injury in mice. Brain 126:1628
Xie Q, Khaoustov VI, Chung CC, Sohn J, Krishnan B, Lewis DE, Yoffe B (2002) Effect of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase-12 activation. Hepatology 36:592–601. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2002.35441
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Reed JC (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin Invest 115:2656–2664. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI26373
Yanguas-Casas N, Barreda-Manso MA, Nieto-Sampedro M, Romero-Ramirez L (2014) Tauroursodeoxycholic acid reduces glial cell activation in an animal model of acute neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 11:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-50
Yanguas-Casas N, Barreda-Manso MA, Perez-Rial S, Nieto-Sampedro M, Romero-Ramirez L (2016) TGFbeta contributes to the anti-inflammatory effects of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on an animal model of acute neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0142-6
Yin X, Yin Y, Cao FL, Chen YF, Peng Y, Hou WG, Sun SK, Luo ZJ (2012) Tanshinone IIA attenuates the inflammatory response and apoptosis after traumatic injury of the spinal cord in adult rats. PLoS One 7:e38381. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038381
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 31372207 and 81570094), the Innovation Team of Scientific Research Platform in Anhui Province, a start-up grant from Nanjing Agricultural University (804090), and the “Sanxin” Research Program of Jiangsu Province (SXGC[2016]312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All animal experiments complied with the ARRIVE guidelines and were carried out according to the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. All animal experiments were approved by the Anhui Normal University Academic Ethics Committee.
Additional information
Zongmeng Zhang, Jie Chen, and Fanghui Chen are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Chen, F. et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid alleviates secondary injury in the spinal cord via up-regulation of CIBZ gene. Cell Stress and Chaperones 23, 551–560 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0862-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0862-1