Abstract
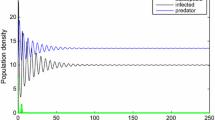
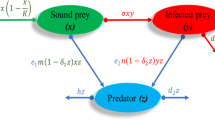
This paper formulates and explores a nonautonomous impulsive stochastic predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis (BD) functional response, where only the prey has a disease, which incorporates modified saturated incidence. The sufficient criteria of extinction and non-persistence in the mean of the target model are established, revealing that different intensities of stochastic perturbations contribute to dynamics of the system mentioned above. Stochastically ultimate boundedness is examined, and we further establish sufficient conditions for global attractivity. Our analytical findings are verified through numerical simulations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernoulli, D.: Essai d’une nouvelle analyse de la mortalité cause par la petite vérole et des avantages de l’inoculation pour la prévenir. Mémoires de l’Académie Roy. des Sci. de Paris. (1760)
Harmer, W.: Epidemic disease in England-The evidence of variability and of persistency of type. Lancet. 167(4306), 733–739 (1906)
Ross, S.R.: The prevention of malaria. London Murray, London (1911)
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics-I. B. Math. Biol. 53(1–2), 33–55 (1991)
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G.: Contributions to the mathematical theory of epidemics-II. The problem of endemicity. B. Math. Biol. 53(1–2), 57–87 (1991)
May, R.M., Anderson, R.M., Irwin, M.E.: The transmission dynamics of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. B. 321(1207), 565–607 (1988)
Chattopadhyay, J., Arino, O.: A predator-prey model with disease in the prey. Nonlinear Anal-Theor. 36(6), 747–766 (1999)
Getz, W.M., Pickering, J.: Epidemic models: Thresholds and population regulation. Am. Nat. 121(6), 892–898 (1983)
Bairagi, N., Roy, P.K., Chattopadhyay, J.: Role of infection on the stability of a predator-prey system with several response functions-a comparative study. J. Theor. Biol. 248(1), 10–25 (2007)
Lu, C., Ding, X.H.: Periodic solutions and stationary distribution for a stochastic predator-prey system with impulsive perturbations. Appl. Math. Comput. 350, 313–322 (2019)
Xu, C.H., Yu, Y.G., Ren, G.J.: Dynamic analysis of a stochastic predator-prey model with Crowley-Martin functional response, disease in predator, and saturation incidence. J. Comput. Nonlin. Dyn. 15(7), 071004 (2020)
Liu, G.D., Wang, X., Meng, X.Z., Gao, S.J.: Extinction and persistence in mean of a novel delay impulsive stochastic infected predator-prey system with jumps. Complexity. 2017, 1950970 (2017)
Xu, C.H., Yu, Y.G., Ren, G.J., Hai, X.D., Lu, Z.Z.: Extinction and permanence analysis of stochastic predator-prey model with disease, ratio-dependent type functional response and nonlinear incidence rate. J. Comput. Nonlin. Dyn. 16(11), 111004 (2021)
Levi, T., Kilpatrick, A.M., Mangel, M., Wilmers, C.C.: Deer, predators, and the emergence of Lyme disease. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109(27), 10942–10947 (2012)
Biswas, S., Sasmal, S., Samanta, S., Saifuddin, M., Khan, Q.J.A., Chattopadhyay, J.: A delayed eco-epidemiological system with infected prey and predator subject to the weak Allee effect. Math. Biosci. 263, 198–208 (2015)
Zhang, X.L., Huang, Y.H., Weng, P.X.: Permanence and stability of a diffusive predator-prey model with disease in the prey. Comput. Math. Appl. 68(10), 1431–1445 (2014)
Abhijit, M., Debadatta, A., Nandadulal, B.: Persistence and extinction of species in a disease-induced ecological system under environmental stochasticity. Phys. Rev. E. 103(3), 032412 (2021)
Deng, M.L., Fan, Y.B.: Invariant measure of a stochastic hybrid predator-prey model with infected prey. Appl. Math. Lett. 124, 107670 (2022)
Foryś, U., Qiao, M.H.: Asymptotic dynamics of a deterministic and stochastic predator-prey model with disease in the prey species. Math. Method. Appl. Sci. 37(3), 306–320 (2014)
Ji, C.Y., Jiang, D.Q.: Dynamics of a stochastic density dependent predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 381(1), 441–453 (2011)
Jana, S., Kar, T.K.: Modeling and analysis of a prey-predator system with disease in the prey. Chaos Solitons Fractals 47, 42–53 (2013)
Chakraborty, K., Das, K., Haldar, S., Kar, T.K.: A mathematical study of an eco-epidemiological system on disease persistence and extinction perspective. Appl. Math. Comput. 254, 99–112 (2015)
Anderson, R., May, R.: Population biological of infectious disease. Heidelberg. Germany, Springer, Berlin (1982)
Capasso, V., Serio, G.: Generalization of the Kermack-McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 42(1–2), 43–61 (1978)
Wei, C.J., Chen, L.S.: A delayed epidemic model with pulse vaccination. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2008(1), 746951 (2008)
Kaddar, A.: On the dynamics of a delayed SIR epidemic model with a modified saturated incidence rate. Electron. J. Differ. Eq. 2009(133), 1–7 (2009)
Liu, Z.J.: Dynamics of positive solutions to SIR and SEIR epidemic models with saturated incidence rates. Nonlinear Anal-Real. 14(3), 1286–1299 (2013)
Suryanto, A., Kusumawinahyu, W.M., Darti, I., Yanti, I.: Dynamically consistent discrete epidemic model with modified saturated incidence rate. Comput. Appl. Math. 32(2), 373–383 (2013)
Tan, R.H., Liu, Z.J., Guo, S.L., Xiang, H.L.: On a nonautonomous competitive system subject to stochastic and impulsive perturbations. Appl. Math. Comput. 256, 702–714 (2015)
Liu, M., Wang, K.: On a stochastic logistic equation with impulsive perturbations. Comput. Math. Appl. 63(5), 871–886 (2012)
Liu, M., Wang, K.: Persistence, extinction and global asymptotical stability of a non-autonomous predator-prey model with random perturbation. Appl. Math. Model. 36(11), 5344–5353 (2012)
Mao, X., Yuan, C.: Stochastic differential equations with Markovian switching. Imperial College Press, London (2006)
Mao, X.: Stochastic differential equations and applications. Horwood Publishing, Chichester (1997)
Liu, M., Wang, K.: Dynamics and simulations of a logistic model with impulsive perturbations in a random environment. Math. Comput. Simulat. 92, 53–75 (2013)
Wu, R.H., Zou, X.L., Wang, K.: Asymptotic behavior of a stochastic non-autonomous predator-prey model with impulsive perturbations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 20(3), 965–974 (2015)
Shi, R.Q., Jiang, X.W., Chen, L.S.: A predator-prey model with disease in the prey and two impulses for integrated pest management. Appl. Math. Model. 33(5), 2248–2256 (2008)
Liu, Z.J., Wu, J.H., Chen, Y.P., Haque, M.: Impulsive perturbations in a periodic delay differential equation model of plankton allelopathy. Nonlinear Anal-Real. 11(1), 432–445 (2010)
Wei, C.J., Chen, L.S.: Periodic solution and heteroclinic bifurcation in a predator-prey system with Allee effect and impulsive harvesting. Nonlinear Dynam. 76(2), 1109–1117 (2014)
Hardy, G.H., Littlewood, J.E., Polya, G.: Inequalities. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1952)
Karatzas, I., Shreve, S.E.: Brownian motion and stochastic calculus. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1998)
Barblart, I.: Systemes d’équations différentielles d’oscillations non linéaires. RevueRoumaine de Mathematiques Pures et Appliquees. 4(2), 267–270 (1959)
Acknowledgements
The work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11901059), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei province, China (No. 2019CFB353).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., He, X. & Li, Y. Dynamical analysis of an impulsive stochastic infected predator-prey system with BD functional response and modified saturated incidence. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 68, 4075–4098 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01678-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01678-8