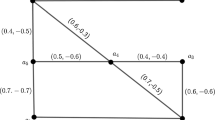
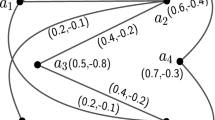
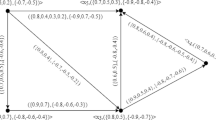
Abstract
Connectivity can be used to measure the strength and combined power of a connected network system. Randic index of graph is one such parameter and it can measure the total combined power of a connected graphical transmission system. For two opposite sided opinion of vertices as well as edges in a bipolar fuzzy graph, it can measure the uncertainty of vertices and edges along positive and negative sides. In this article, the Randic index of bipolar fuzzy graph and bipolar fuzzy subgraph are introduced with their properties. The upper and lower boundaries of Randic index of bipolar fuzzy graphs are studied with some isomorphic properties. Randic index of directed bipolar fuzzy graphs are introduced. Several formula’s are presented to calculate the Randic index of different types of regular bipolar fuzzy graphs and bipolar fuzzy cycles. Finally, two real life applications of Randic index in bipolar fuzzy graphs are described.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akram, M.: Bipolar fuzzy graphs. Inf. Sci. 181(24), 5548–5564 (2011)
Akram, M.: Bipolar fuzzy graphs with applications. Knowl. Based Syst. 39, 1–8 (2013)
Akram, M.: \(m\)-Polar Fuzzy Graphs: Theory. Methods & Applications. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Akram, M., Akmal, R., Alshehri, N.: On \(m\)-polar fuzzy graph structures. SpringerPlus 5, 1448 (2016)
Akram, M., Ali, G., Butt, M.A., Alcantud, J.C.R.: Novel MCGDM analysis under \(m\)-polar fuzzy soft expert sets. Neural Comput. Appl. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-05850-w
Akram, M., Amzad, U., Davvaz, B.: Decision-making analysis based on bipolar fuzzy \(N\)-soft information. Comput. Appl. Math. 40, 180 (2021)
Akram, M., Farooq, A.: Bipolar fuzzy tree. New Trends Math. Sci. 4(3), 58–72 (2016)
Akram, M., Karunambigal, M.G.: Metric in bipolar fuzzy graphs. World Appl. Sci. J. 14(12), 1920–1927 (2011)
Akram, M., Sarwar, M., Dudek, W.A.: Graphs for the Analysis of Bipolar Fuzzy Information. Springer, Berlin (2020)
Akram, M., Waseem, N.: Novel applications of bipolar fuzzy graphs to decision making problems. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 56, 73–91 (2018)
Binu, M., Mathew, S., Mordeson, J.N.: Wiener index of a fuzzy graph and application to illegal immigration networks. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 384, 132–147 (2020)
Cederbaum, I.: Some applications of graph theory to network analysis and synthesis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 31(1), 64–68 (1984)
Das, S., Ghorai, G.: Analysis of the effect of medicines over bacteria based on competition graphs with picture fuzzy environment. Comput. Appl. Math. 39, 183 (2020)
Das, S., Ghorai, G., Pal, M.: Certain competition graphs based on picture fuzzy environment with applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-020-09923-5
Ghorai, G., Pal, M.: A note on “Regular bipolar fuzzy graphs” Neural Comput. Appl 21(1), 197–205 (2012) Neural Comput. Appl. 30(5), 1569–1572 (2018)
Ghorai, G., Pal, M.: Some isomorphic properties of \(m\)-polar fuzzy graphs with applications. SpringerPlus 5(1), 2104 (2016)
Ghorai, G.: Characterization of regular bipolar fuzzy graphs. Afrika Matematika 32(5), 1043–1057 (2021)
Kaveh, A., Rahami, H., Shojaei, I.: Swift Analysis of Civil Engineering Structures Using Graph Theory Mathods. Springer, Berlin (2020)
Masarwah, A.A., Qamar, M.A.: Some new concepts of fuzzy soft graphs. Fuzzy Inf. Eng. 8(4), 427–438 (2016)
Masarwah, A.A., Qamar, M.A.: Certain types of fuzzy soft graphs. New Math. Natural Comput. 14(02), 145–156 (2018)
Mathew, S., Sunitha, M.S., Anjali, N.: Some connectivity concepts in bipolar fuzzy graphs. Ann. Pure Appl. Math. 7(2), 98–100 (2014)
Mathew, S., Sunitha, M.S.: Types of arcs in a fuzzy graph. Inf. Sci. 179(11), 1760–1768 (2009)
Minoli, D.: Combinatorial graph complexity, Atti della Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei. Class di Scienze Fisiche. Matematiche e Naturali. Rendiconti 59(6):651–661 (1975)
Mordeson, J.N., Nair, P.S.: Fuzzy Graphs and Fuzzy Hypergraphs. Physica-Verlag, Berlin (2000)
Nawaz, H.S., Akram, M.: Oligopolistic competition among the wireless internet service providers of Malaysia using fuzzy soft graphs. J. Appl. math. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01514-z
Poulik, S., Ghorai, G.: Certain indices of graphs under bipolar fuzzy environment with applications. Soft Comput. 24(7), 5119–5131 (2020)
Poulik, S., Ghorai, G.: Determination of journeys order based on graphs Wiener absolute index with bipolar fuzzy information. Inf. Sci. 545, 608–619 (2021)
Poulik, S., Ghorai, G.: Detour g-interior nodes and detour g-boundary nodes in bipolar fuzzy graph with applications. Hacettepe J. Math. Stat. 49(1), 106–119 (2020)
Poulik, S., Ghorai, G.: Empirical results on bipolar fuzzy graphs with their degree. Missouri J. Math. Sci. 32(2), 211–226 (2020)
Poulik, S., Ghorai, G.: Note on bipolar fuzzy graphs with applications. Knowl. Based Syst. 192, 1–5 (2020)
Poulik, S., Ghorai, G., Xin, Q.: Pragmatic results in Taiwan education system based IVFG & IVNG. Soft Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05180-4
Randic, M.: Characterization of molecular branching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97(23), 6609–6615 (1975)
Rosenfield, A.: Fuzzy graphs. Fuzzy Sets and Their Application (L. A. Zadeh, K. S. Fu, M. Shimura, Eds.): Academic press, New York, 77-95, (1975)
Shahzadi, S., Rasool, A., Sarwar, M., Akram, M.: A framework of decision making based on bipolar fuzzy competition hypergraphs. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-210216
Sarwar, M., Akram, M., Shahzadi, S.: Bipolar fuzzy soft information applied to hypergraphs. Soft Comput. 25(2), 1–23 (2021)
West, D.B.: Introduction to Graph Theory, Pearson Education India (2002)
Yager, R.R., Alajlan, N.: Approximate reasoning with generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. Inf. Fusion 38, 65–73 (2017)
Yager, R.R., Alajlan, N., Bazi, Y.: Aspects of generalized orthopair fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 33(11), 2154–2174 (2018)
Yang, H.L., Li, S.G., Yang, W.H., Lu, Y.: Notes on bipolar fuzzy graphs. Inf. Sci. 242, 113–121 (2013)
Yang, H.L., Li, S.G., Wang, S., Wang, J.: Bipolar fuzzy rough set model on two different universes and its application. Knowl. Based Syst. 35, 94–101 (2012)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Zhang, W.R.: Bipolar fuzzy sets and relations: a computational framework for cognitive modeling multiagent decision analysis. Proceeding of IEEE Conference 305–309 (1994)
Zhang, X., Zhao, Y., Zhou, L., Dong, W., Zhang, M., Lv, X.: Transmission tower tilt monitoring system using low-power wide-area network technology. IEEE Sensors J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2020.3004817
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere gratitude to the anonymous referees for valuable suggestions, which led to great deal of improvement of the original manuscript. The first author is thankful to the Department of Higher Education, Science and Technology and Biotechnology, Government of West Bengal, India, for the award of Swami Vivekananda merit-cum-means scholarship (Award No. 52-Edn (B)/5B-15/2017 dated 07/06/2017) to meet up the financial expenditure to carry out the research work. The third author acknowledges the support of DST-FIST, New Delhi (India) (Sanction No. SR/FST/MS- I/2018/21) for carrying out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poulik, S., Das, S. & Ghorai, G. Randic index of bipolar fuzzy graphs and its application in network systems. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 68, 2317–2341 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01619-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-021-01619-5