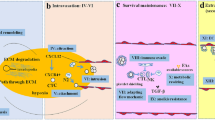
Abstract
Patients with cancer have a higher risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), compared to the general population. Cancer-associated thrombosis (CAT) is a thrombotic event that occurs as a complication of cancer or cancer therapy. Major factors determining VTE risk in cancer patients include not only treatment history and patient characteristics, but also cancer type and site. Cancer types can be broadly divided into three groups based on VTE risk: high risk (pancreatic, ovarian, brain, stomach, gynecologic, and hematologic), intermediate risk (colon and lung), and low risk (breast and prostate). This implies that the mechanism of VTE differs between cancer types and that specific VTE pathways may exist for different cancer types. This review summarizes the specific pathways that contribute to VTE in cancer patients, with a particular focus on leukocytosis, neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), tissue factor (TF), thrombocytosis, podoplanin (PDPN), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), the intrinsic coagulation pathway, and von Willebrand factor (VWF).





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Heit JA, Mohr DN, Silverstein MD, Petterson TM, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ 3rd. Predictors of recurrence after deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based cohort study. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:761–8.
Timp JF, Braekkan SK, Versteeg HH, Cannegieter SC. Epidemiology of cancer-associated venous thrombosis. Blood. 2013;122:1712–23.
Mulder FI, Horváth-Puhó E, van Es N, van Laarhoven HWM, Pedersen L, Moik F, et al. Venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: a population-based cohort study. Blood. 2021;137:1959–69.
Mahajan A, Brunson A, Adesina O, Keegan THM, Wun T. The incidence of cancer-associated thrombosis is increasing over time. Blood Adv. 2022;6:307–20.
Hisada Y, Mackman N. Mechanisms of cancer-associated thrombosis. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2023;7: 100123.
Hisada Y, Mackman N. Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis. Blood. 2017;130:1499–506.
Mukai M, Oka T. Mechanism and management of cancer-associated thrombosis. J Cardiol. 2018;72:89–93.
Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Kuderer NM, Lyman GH. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:632–4.
Khorana AA, Kuderer NM, McCrae K, Milentijevic D, Germain G, Laliberté F, et al. Cancer associated thrombosis and mortality in patients with cancer stratified by Khorana score risk levels. Cancer Med. 2020;9:8062–73.
Khorana AA. Cancer-associated thrombosis: updates and controversies. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:626–30.
Lee AYY, Peterson EA. Treatment of cancer-associated thrombosis. Blood. 2013;122:2310–7.
Raskob GE, van Es N, Verhamme P, Carrier M, Di Nisio M, Garcia D, et al. Edoxaban for the treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:615–24.
Young AM, Marshall A, Thirlwall J, Chapman O, Lokare A, Hill C, et al. Comparison of an oral factor Xa inhibitor with low molecular weight heparin in patients with cancer with venous thromboembolism: results of a randomized trial (SELECT-D). J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:2017–23.
Agnelli G, Becattini C, Meyer G, Muñoz A, Huisman MV, Connors JM, et al. Apixaban for the treatment of venous thromboembolism associated with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1599–607.
Poenou G, Heestermans M, Lafaie L, Accassat S, Moulin N, Rodière A, et al. Inhibition of factor XI: a new era in the treatment of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients? Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24:14433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241914433.
Khorana AA, Kuderer NM, Culakova E, Lyman GH, Francis CW. Development and validation of a predictive model for chemotherapy-associated thrombosis. Blood. 2008;111:4902–7.
Ay C, Dunkler D, Marosi C, Chiriac A-L, Vormittag R, Simanek R, et al. Prediction of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients. Blood. 2010;116:5377–82.
Verso M, Agnelli G, Barni S, Gasparini G, LaBianca R. A modified Khorana risk assessment score for venous thromboembolism in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: the Protecht score. Intern Emerg Med. 2012;7:291–2.
Pelzer U, Opitz B, Deutschinoff G, Stauch M, Reitzig PC, Hahnfeld S, et al. Efficacy of prophylactic low-molecular weight heparin for ambulatory patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: outcomes from the CONKO-004 trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:2028–34.
Cella CA, Di Minno G, Carlomagno C, Arcopinto M, Cerbone AM, Matano E, et al. Preventing venous thromboembolism in ambulatory cancer patients: the ONKOTEV study. Oncologist. 2017;22:601–8.
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Vignoli A. Coagulation and cancer: biological and clinical aspects. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:223–33.
Blom JW, Vanderschoot JPM, Oostindiër MJ, Osanto S, van der Meer FJM, Rosendaal FR. Incidence of venous thrombosis in a large cohort of 66,329 cancer patients: results of a record linkage study. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:529–35.
Chew HK, Wun T, Harvey D, Zhou H, White RH. Incidence of venous thromboembolism and its effect on survival among patients with common cancers. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:458–64.
Khorana AA, Connolly GC. Assessing risk of venous thromboembolism in the patient with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4839–47.
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Russo L. Venous thromboembolism in the hematologic malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol. 2012;24:702–10.
Paneesha S, McManus A, Arya R, Scriven N, Farren T, Nokes T, et al. Frequency, demographics and risk (according to tumour type or site) of cancer-associated thrombosis among patients seen at outpatient DVT clinics. Thromb Haemost. 2010;103:338–43.
Shoenfeld Y, Tal A, Berliner S, Pinkhas J. Leukocytosis in non hematological malignancies—a possible tumor-associated marker. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1986;111:54–8.
Granger JM, Kontoyiannis DP. Etiology and outcome of extreme leukocytosis in 758 nonhematologic cancer patients: a retrospective, single-institution study. Cancer. 2009;115:3919–23.
Kasuga I, Makino S, Kiyokawa H, Katoh H, Ebihara Y, Ohyashiki K. Tumor-related leukocytosis is linked with poor prognosis in patients with lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92:2399–405.
Pabinger I, Posch F. Flamethrowers: blood cells and cancer thrombosis risk. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2014;2014:410–7.
Blix K, Jensvoll H, Brækkan SK, Hansen J-B. White blood cell count measured prior to cancer development is associated with future risk of venous thromboembolism—the Tromsø study. PLoS ONE. 2013;8: e73447.
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1532–5.
Gregory SA, Morrissey JH, Edgington TS. Regulation of tissue factor gene expression in the monocyte procoagulant response to endotoxin. Mol Cell Biol. 1989;9:2752–5.
Hashimoto T, Ueki S, Kamide Y, Miyabe Y, Fukuchi M, Yokoyama Y, et al. Increased circulating cell-free DNA in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: implications for eosinophil extracellular traps and immunothrombosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 801897.
Thomas GM, Brill A, Mezouar S, Crescence L, Gallant M, Dubois C, et al. Tissue factor expressed by circulating cancer cell-derived microparticles drastically increases the incidence of deep vein thrombosis in mice. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13:1310–9.
Fuchs TA, Brill A, Duerschmied D, Schatzberg D, Monestier M, Myers DD Jr, et al. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:15880–5.
Massberg S, Grahl L, von Bruehl M-L, Manukyan D, Pfeiler S, Goosmann C, et al. Reciprocal coupling of coagulation and innate immunity via neutrophil serine proteases. Nat Med. 2010;16:887–96.
Demers M, Krause DS, Schatzberg D, Martinod K, Voorhees JR, Fuchs TA, et al. Cancers predispose neutrophils to release extracellular DNA traps that contribute to cancer-associated thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:13076–81.
Herre M, Cedervall J, Mackman N, Olsson A-K. Neutrophil extracellular traps in the pathology of cancer and other inflammatory diseases. Physiol Rev. 2023;103:277–312.
Yang C, Sun W, Cui W, Li X, Yao J, Jia X, et al. Procoagulant role of neutrophil extracellular traps in patients with gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:14075–86.
Thålin C, Demers M, Blomgren B, Wong SL, von Arbin M, von Heijne A, et al. NETosis promotes cancer-associated arterial microthrombosis presenting as ischemic stroke with troponin elevation. Thromb Res. 2016;139:56–64.
Thålin C, Lundström S, Seignez C, Daleskog M, Lundström A, Henriksson P, et al. Citrullinated histone H3 as a novel prognostic blood marker in patients with advanced cancer. PLoS ONE. 2018;13: e0191231.
Thålin C, Aguilera K, Hall NW, Marunde MR, Burg JM, Rosell A, et al. Quantification of citrullinated histones: development of an improved assay to reliably quantify nucleosomal H3Cit in human plasma. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:2732–43.
Rosell A, Aguilera K, Hisada Y, Schmedes C, Mackman N, Wallén H, et al. Prognostic value of circulating markers of neutrophil activation, neutrophil extracellular traps, coagulation and fibrinolysis in patients with terminal cancer. Sci Rep. 2021;11:5074.
Cedervall J, Herre M, Dragomir A, Rabelo-Melo F, Svensson A, Thålin C, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote cancer-associated inflammation and myocardial stress. Oncoimmunology. 2022;11:2049487.
Mauracher L-M, Posch F, Martinod K, Grilz E, Däullary T, Hell L, et al. Citrullinated histone H3, a biomarker of neutrophil extracellular trap formation, predicts the risk of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16:508–18.
Seo JD, Gu J-Y, Jung HS, Kim YJ, Kim HK. Contact system activation and neutrophil extracellular trap markers: risk factors for portal vein thrombosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019;25:1076029618825310.
Grilz E, Mauracher L-M, Posch F, Königsbrügge O, Zöchbauer-Müller S, Marosi C, et al. Citrullinated histone H3, a biomarker for neutrophil extracellular trap formation, predicts the risk of mortality in patients with cancer. Br J Haematol. 2019;186:311–20.
Grover SP, Mackman N. Tissue factor: an essential mediator of hemostasis and trigger of thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38:709–25.
Geddings JE, Hisada Y, Boulaftali Y, Getz TM, Whelihan M, Fuentes R, et al. Tissue factor-positive tumor microvesicles activate platelets and enhance thrombosis in mice. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:153–66.
Falanga A, Iacoviello L, Evangelista V, Belotti D, Consonni R, D’Orazio A, et al. Loss of blast cell procoagulant activity and improvement of hemostatic variables in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia administered all-trans-retinoic acid. Blood. 1995;86:1072–81.
Marchetti M, Diani E, ten Cate H, Falanga A. Characterization of the thrombin generation potential of leukemic and solid tumor cells by calibrated automated thrombography. Haematologica. 2012;97:1173–80.
Khorana AA, Ahrendt SA, Ryan CK, Francis CW, Hruban RH, Hu YC, et al. Tissue factor expression, angiogenesis, and thrombosis in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:2870–5.
Coumans FAW, Brisson AR, Buzas EI, Dignat-George F, Drees EEE, El-Andaloussi S, et al. Methodological guidelines to study extracellular vesicles. Circ Res. 2017;120:1632–48.
Gardiner C, Harrison P, Belting M, Böing A, Campello E, Carter BS, et al. Extracellular vesicles, tissue factor, cancer and thrombosis—discussion themes of the ISEV 2014 Educational Day. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26901.
György B, Szabó TG, Pásztói M, Pál Z, Misják P, Aradi B, et al. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68:2667–88.
Geddings JE, Mackman N. Tumor-derived tissue factor-positive microparticles and venous thrombosis in cancer patients. Blood. 2013;122:1873–80.
Khorana AA, Francis CW, Menzies KE, Wang J-G, Hyrien O, Hathcock J, et al. Plasma tissue factor may be predictive of venous thromboembolism in pancreatic cancer. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:1983–5.
Thaler J, Ay C, Mackman N, Bertina RM, Kaider A, Marosi C, et al. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity, venous thromboembolism and mortality in pancreatic, gastric, colorectal and brain cancer patients. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10:1363–70.
Bharthuar A, Khorana AA, Hutson A, Wang J-G, Key NS, Mackman N, et al. Circulating microparticle tissue factor, thromboembolism and survival in pancreaticobiliary cancers. Thromb Res. 2013;132:180–4.
Kasthuri RS, Hisada Y, Ilich A, Key NS, Mackman N. Effect of chemotherapy and longitudinal analysis of circulating extracellular vesicle tissue factor activity in patients with pancreatic and colorectal cancer. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2020;4:636–43.
Tesselaar MET, Romijn FPHTM, Van Der Linden IK, Prins FA, Bertina RM, Osanto S. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity: a link between cancer and thrombosis? J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:520–7.
Zwicker JI, Liebman HA, Neuberg D, Lacroix R, Bauer KA, Furie BC, et al. Tumor-derived tissue factor-bearing microparticles are associated with venous thromboembolic events in malignancy. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:6830–40.
Lee RD, Barcel DA, Williams JC, Wang JG, Boles JC, Manly DA, et al. Pre-analytical and analytical variables affecting the measurement of plasma-derived microparticle tissue factor activity. Thromb Res. 2012;129:80–5.
Tatsumi K, Antoniak S, Monroe DM 3rd, Khorana AA, Mackman N, Subcommittee on Hemostasis and Malignancy of the Scientific and Standardization Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Evaluation of a new commercial assay to measure microparticle tissue factor activity in plasma: communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12:1932–4.
Levin J, Conley CL. Thrombocytosis associated with malignant disease. Arch Intern Med. 1964;114:497–500.
Connolly GC, Phipps RP, Francis CW. Platelets and cancer-associated thrombosis. Semin Oncol. 2014;41:302–10.
Riedl J, Pabinger I, Ay C. Platelets in cancer and thrombosis. Hamostaseologie. 2014;34:54–62.
Khorana AA, Francis CW, Culakova E, Lyman GH. Risk factors for chemotherapy-associated venous thromboembolism in a prospective observational study. Cancer. 2005;104:2822–9.
Simanek R, Vormittag R, Ay C, Alguel G, Dunkler D, Schwarzinger I, et al. High platelet count associated with venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study (CATS). J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8:114–20.
Jensvoll H, Blix K, Brækkan SK, Hansen J-B. Platelet count measured prior to cancer development is a risk factor for future symptomatic venous thromboembolism: the Tromsø Study. PLoS ONE. 2014;9: e92011.
Stone RL, Nick AM, McNeish IA, Balkwill F, Han HD, Bottsford-Miller J, et al. Paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:610–8.
Matsuo K, Hasegawa K, Yoshino K, Murakami R, Hisamatsu T, Stone RL, et al. Venous thromboembolism, interleukin-6 and survival outcomes in patients with advanced ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51:1978–88.
Aleman MM, Gardiner C, Harrison P, Wolberg AS. Differential contributions of monocyte- and platelet-derived microparticles towards thrombin generation and fibrin formation and stability. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:2251–61.
Riedl J, Hell L, Kaider A, Koder S, Marosi C, Zielinski C, et al. Association of platelet activation markers with cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Platelets. 2016;27:80–5.
Poruk KE, Firpo MA, Huerter LM, Scaife CL, Emerson LL, Boucher KM, et al. Serum platelet factor 4 is an independent predictor of survival and venous thromboembolism in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:2605–10.
Ay C, Simanek R, Vormittag R, Dunkler D, Alguel G, Koder S, et al. High plasma levels of soluble P-selectin are predictive of venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: results from the Vienna Cancer and Thrombosis Study (CATS). Blood. 2008;112:2703–8.
Mezouar S, Darbousset R, Dignat-George F, Panicot-Dubois L, Dubois C. Inhibition of platelet activation prevents the P-selectin and integrin-dependent accumulation of cancer cell microparticles and reduces tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:462–75.
Suzuki-Inoue K, Inoue O, Ozaki Y. Novel platelet activation receptor CLEC-2: from discovery to prospects. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9(Suppl 1):44–55.
Krishnan H, Rayes J, Miyashita T, Ishii G, Retzbach EP, Sheehan SA, et al. Podoplanin: an emerging cancer biomarker and therapeutic target. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:1292–9.
Raica M, Cimpean AM, Ribatti D. The role of podoplanin in tumor progression and metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:2997–3006.
Suzuki-Inoue K, Kato Y, Inoue O, Kaneko MK, Mishima K, Yatomi Y, et al. Involvement of the snake toxin receptor CLEC-2, in podoplanin-mediated platelet activation, by cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:25993–6001.
Ernst A, Hofmann S, Ahmadi R, Becker N, Korshunov A, Engel F, et al. Genomic and expression profiling of glioblastoma stem cell-like spheroid cultures identifies novel tumor-relevant genes associated with survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:6541–50.
Thaler J, Ay C, Kaider A, Reitter E-M, Haselböck J, Mannhalter C, et al. Biomarkers predictive of venous thromboembolism in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16:1645–51.
Riedl J, Preusser M, Nazari PMS, Posch F, Panzer S, Marosi C, et al. Podoplanin expression in primary brain tumors induces platelet aggregation and increases risk of venous thromboembolism. Blood. 2017;129:1831–9.
Mege D, Panicot-Dubois L, Ouaissi M, Robert S, Sielezneff I, Sastre B, et al. The origin and concentration of circulating microparticles differ according to cancer type and evolution: a prospective single-center study. Int J Cancer. 2016;138:939–48.
Westrick RJ, Eitzman DT. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in vascular thrombosis. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8:966–1002.
Meltzer ME, Lisman T, de Groot PG, Meijers JCM, le Cessie S, Doggen CJM, et al. Venous thrombosis risk associated with plasma hypofibrinolysis is explained by elevated plasma levels of TAFI and PAI-1. Blood. 2010;116:113–21.
Bollen L, Peetermans M, Peeters M, Van Steen K, Hoylaerts MF, Declerck PJ, et al. Active PAI-1 as marker for venous thromboembolism: case-control study using a comprehensive panel of PAI-1 and TAFI assays. Thromb Res. 2014;134:1097–102.
Hanekom GS, Stubbings HM, Kidson SH. The active fraction of plasmatic plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 as a possible indicator of increased risk for metastatic melanoma. Cancer Detect Prev. 2002;26:50–9.
Herszènyi L, Plebani M, Carraro P, De Paoli M, Roveroni G, Cardin R, et al. The role of cysteine and serine proteases in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 1999;86:1135–42.
Ferroni P, Roselli M, Portarena I, Formica V, Riondino S, Farina FLA, et al. Plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) levels in breast cancer—relationship with clinical outcome. Anticancer Res. 2014;34:1153–61.
Andrén-Sandberg A, Lecander I, Martinsson G, Astedt B. Peaks in plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 concentration may explain thrombotic events in cases of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 1992;69:2884–7.
Hisada Y, Garratt KB, Maqsood A, Grover SP, Kawano T, Cooley BC, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and venous thrombosis in pancreatic cancer. Blood Adv. 2021;5:487–95.
McCann JV, Xiao L, Kim DJ, Khan OF, Kowalski PS, Anderson DG, et al. Endothelial miR-30c suppresses tumor growth via inhibition of TGF-β-induced Serpine1. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:1654–70.
Hisada Y, Grover SP, Maqsood A, Houston R, Ay C, Noubouossie DF, et al. Neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps enhance venous thrombosis in mice bearing human pancreatic tumors. Haematologica. 2020;105:218–25.
Leal AC, Mizurini DM, Gomes T, Rochael NC, Saraiva EM, Dias MS, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes induce the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps: implications for the establishment of cancer-associated thrombosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:6438.
Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DSB, Pantel K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:426–37.
Nickel KF, Ronquist G, Langer F, Labberton L, Fuchs TA, Bokemeyer C, et al. The polyphosphate-factor XII pathway drives coagulation in prostate cancer-associated thrombosis. Blood. 2015;126:1379–89.
Castellón Rubio VE, Segura PP-, Muñoz A, Farré AL, Ruiz LC, Lorente JA. High plasma levels of soluble P-Selectin and Factor VIII predict venous thromboembolism in non-small cell lung cancer patients: the Thrombo-Nsclc risk score. Thromb Res. 2020;196:349–54.
Tafur AJ, Dale G, Cherry M, Wren JD, Mansfield AS, Comp P, et al. Prospective evaluation of protein C and factor VIII in prediction of cancer-associated thrombosis. Thromb Res. 2015;136:1120–5.
Vormittag R, Simanek R, Ay C, Dunkler D, Quehenberger P, Marosi C, et al. High factor VIII levels independently predict venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: the cancer and thrombosis study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29:2176–81.
Sadler JE, Budde U, Eikenboom JCJ, Favaloro EJ, Hill FGH, Holmberg L, et al. Update on the pathophysiology and classification of von Willebrand disease: a report of the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:2103–14.
Gogia S, Neelamegham S. Role of fluid shear stress in regulating VWF structure, function and related blood disorders. Biorheology. 2015;52:319–35.
Onodera Y, Mitani S, Hosoda C, Takabayashi Y, Sakata A, Kawasaki R, et al. Regulation of von Willebrand factor by ADAMTS13 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice. Int J Hematol. 2023;118(6):699–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-023-03668-x.
Ono S, Matsui H, Noda M, Kasuda S, Yada N, Yoshimoto K, et al. Functional regulation of von Willebrand factor ameliorates acute ischemia-reperfusion kidney injury in mice. Sci Rep. 2019;9:14453.
Wang W-S, Lin J-K, Lin T-C, Chiou T-J, Liu J-H, Yen C-C, et al. Plasma von Willebrand factor level as a prognostic indicator of patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:2166–70.
Gadducci A, Baicchi U, Marrai R, Del Bravo B, Fosella PV, Facchini V. Pretreatment plasma levels of fibrinopeptide-A (FPA), D-dimer (DD), and von Willebrand factor (vWF) in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1994;53:352–6.
Karampinis I, Nowak K, Koett J, Mess C, Wagner L, Gaiser T, et al. Von Willebrand factor in the plasma and in the tumor tissue predicts cancer-associated thrombosis and mortality. Haematologica. 2023;108:261–6.
Pépin M, Kleinjan A, Hajage D, Büller HR, Di Nisio M, Kamphuisen PW, et al. ADAMTS-13 and von Willebrand factor predict venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14:306–15.
Federici AB, Budde U, Castaman G, Rand JH, Tiede A. Current diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to patients with acquired von Willebrand syndrome: a 2013 update. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2013;39:191–201.
Federici AB, Budde U, Rand JH. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome 2004: International Registry—diagnosis and management from online to bedside. Hamostaseologie. 2004;24:50–5.
Federici AB, Rand JH, Bucciarelli P, Budde U, van Genderen PJ, Mohri H, et al. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome: data from an international registry. Thromb Haemost. 2000;84:345–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
KT is a member of Medicinal Biology of Thrombosis and Hemostasis established by Nara Medical University and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Tatsumi, K. The pathogenesis of cancer-associated thrombosis. Int J Hematol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-024-03735-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-024-03735-x