Abstract
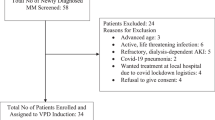
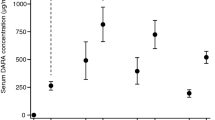
The BLd regimen, which is a triplet regimen of bortezomib (Bor), lenalidomide (Len), and dexamethasone (Dex), is effective against newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM). However, non-hematological toxicities, such as peripheral neuropathy (PN), often hamper long-term continuation of the regimen, particularly in older adult patients. In this study, we examined the efficacy and safety of the modified BLd regimen with reduced-intensity Bor and standard-dose Len. The chemotherapy regimen consisted of 1.3 mg/m2 Bor administered subcutaneously on days 1 and 8, 25 mg Len administered on days 1–14, and 20 mg Dex on days 1–2 and 8–9 of a 3 week cycle for 8 cycles, followed by a 4 week cycle of Dex (40 mg weekly). Among the 30 patients enrolled, 60.0% (95% CI 40.6–77.3) had a very good partial response or better, and the best overall response rate was 96.7% (95% CI 82.8–99.9). Eight patients (26.7%) achieved a complete response. Grade 3 or higher PN was not observed and hematological toxicity was the most common adverse event. The modified BLd regimen showed favorable efficacy with a manageable safety profile, which suggests it could be a treatment option for transplant-ineligible NDMM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Totani H, Ri M, Kato C, Nakashima T, Suzuki N, Hagiwara S, et al. Phase I study of once weekly treatment with bortezomib in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Int J Hematol. 2016;103:316–21.
Richardson PG, Xie W, Jagannath S, Jakubowiak A, Lonial S, Raje NS, et al. A phase 2 trial of lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed and relapsed/refractory myeloma. Blood. 2014;123:1461–9.
Dimopoulos MA, Kastritis E, Christoulas D, Migkou M, Gavriatopoulou M, Gkotzamanidou M, et al. Treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma with lenalidomide and dexamethasone with or without bortezomib: prospective evaluation of the impact of cytogenetic abnormalities and of previous therapies. Leukemia. 2010;24:1769–78.
Jakubowiak AJ, Griffith KA, Reece DE, Hofmeister CC, Lonial S, Zimmerman TM, et al. Lenalidomide, bortezomib, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, and dexamethasone in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a phase 1/2 multiple myeloma research consortium trial. Blood. 2011;118:535–43.
Moreau P, Avet-Loiseau H, Facon T, Attal M, Tiab M, Hulin C, et al. Bortezomib plus dexamethasone versus reduced-dose bortezomib, thalidomide plus dexamethasone as induction treatment before autologous stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood. 2011;118:5752–8.
Richardson PG, Weller E, Lonial S, Jakubowiak AJ, Jagannath S, Raje NS, et al. Lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone combination therapy in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood. 2010;116:679–86.
Roussel M, Facon T, Moreau P, Harousseau JL, Attal M. Firstline treatment and maintenance in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011;183:189–206.
Kumar S, Flinn I, Richardson PG, Hari P, Callander N, Noga SJ, et al. Randomized, multicenter, phase 2 study (EVOLUTION) of combinations of bortezomib, dexamethasone, cyclophosphamide, and lenalidomide in previously untreated multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;119:4375–82.
Iida S, Ishida T, Murakami H, Ozaki S, Abe M, Hata H, et al. JSH practical guidelines for hematological malignancies, 2018: III. Myeloma-1 multiple myeloma (MM). Int J Hematol. 2019;109:509–38.
Durie BGM, Hoering A, Abidi MH, Rajkumar SV, Epstein J, Kahanic SP, et al. Bortezomib with lenalidomide and dexamethasone versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone alone in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma without intent for immediate autologous stem-cell transplant (SWOG S0777): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389:519–27.
Durie BGM, Hoering A, Sexton R, Abidi MH, Epstein J, Rajkumar SV, et al. Longer term follow-up of the randomized phase III trial SWOG S0777: bortezomib, lenalidomide and dexamethasone vs. lenalidomide and dexamethasone in patients (Pts) with previously untreated multiple myeloma without an intent for immediate autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). Blood Cancer J. 2020;10:53.
O’Donnell EK, Laubach JP, Yee AJ, Chen T, Huff CA, Basile FG, et al. A phase 2 study of modified lenalidomide, bortezomib and dexamethasone in transplant-ineligible multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol. 2018;182:222–30.
Greipp PR, San Miguel J, Durie BG, Crowley JJ, Barlogie B, Bladé J, et al. International staging system for multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:3412–20.
Inagaki A, Tajima E, Uranishi M, Totani H, Asao Y, Ogura H, et al. Global real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction detecting proto-oncogenes associated with 14q32 chromosomal translocation as a valuable marker for predicting survival in multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 2013;37:1648–55.
Suzuki K, Shinagawa A, Uchida T, Taniwaki M, Hirata H, Ishizawa K, et al. Lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in Japanese patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a phase II study. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:653–8.
Voorhees PM, Kaufman JL, Laubach J, Sborov DW, Reeves B, Rodriguez C, et al. Daratumumab, lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for transplant-eligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: the GRIFFIN trial. Blood. 2020;136:936–45.
Abdallah N, Kumar SK. Daratumumab in untreated newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Ther Adv Hematol. 2019;10:2040620719894871.
Ocio EM, Rodriguez Otero P, Bringhen S, Oliva S, Nogai A, Attal M, et al. Preliminary results from a Phase I study of Isatuximab (ISA) in combination with bortezomib, lenalidomide, dexamethasone (VRd), and in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (NDMM) non-eligible for transplant. Blood. 2018;132:595.
Dimopoulos MA, Gay F, Schjesvold F, Beksac M, Hajek R, Weisel KC, et al. Oral ixazomib maintenance following autologous stem cell transplantation (TOURMALINE-MM3): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;393:253–64.
Alonso R, Cedena MT, Wong S, Shah N, Ríos-Tamayo R, Moraleda JM, et al. Prolonged lenalidomide maintenance therapy improves the depth of response in multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2163–71.
Jackson GH, Davies FE, Pawlyn C, Cairns DA, Striha A, Collett C, et al. Lenalidomide maintenance versus observation for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (myeloma XI): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:57–73.
Acknowledgements
The study received financial support from Celgene Co., Ltd. We are grateful to the members of the Data and Safety Monitoring Committee of this study, Hirohiko Shibayama, and Yoichi Imai. We are also grateful for the assistance and cooperation of all members at collaborating institutes and the Japanese Data Center for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation, especially Ms. Noriko Mizutani and Ms. Shizuka Kobayashi, for their assistance with data management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MR received research funding from Celgene Co., Ltd. JK received declares Honoraria from Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., and Celgene Co., Ltd. SI received research funding and declared Honoraria from Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. and Celgene Co., Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, S., Ri, M., Ito, M. et al. Efficacy and safety of modified BLd therapy for Japanese patients with transplant-ineligible multiple myeloma. Int J Hematol 116, 563–569 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03379-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03379-9