Abstract
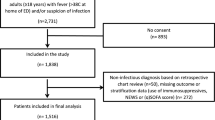
It has been shown that Fas, Fas-L, TNF and TNFR-1 display high serum concentrations in subjects with sepsis. This suggests that these are potential severity markers. However, the serum concentration of these molecules in children with leukemia and suspected sepsis has to be established before proposing their use as diagnostic biomarkers. We included children <17 years of age diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia with neutropenia and fever (NF). The subjects were divided into two groups: (1) leukemia and NF with sepsis, (2) leukemia and NF without sepsis. Determination of serum levels of TNF-α, TNFR-1, Fas and Fas-L was performed using ELISA tests, and apoptosis percentage using flow cytometry. Seventy-two subjects with ALL and NF were included in the two groups. The highest serum levels of TNF-α (35.2 ± 7.6 pg/ml) and TNF-R1 (4102 ± 2440) and the lowest levels of Fas-L (19.4 ± 7.3 pg/ml) were found in group 2: however, the difference in comparison with patients without sepsis was not statistically significant. Low levels of Fas-L and low percentage of apoptotic cells are observed in septic subjects. This pattern may reflect the presence of sepsis among subjects with NF secondary to leukemia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wesche D, Lomas NJ, Perl M, Shiang C, Ayala A. Leukocyte apoptosis and its significance in sepsis shock. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:325–37.
Kam P, Ferch N. Apoptosis: mechanism and clinical implications. Anaesthesia. 2000;55:1081–98.
Lowe S, Lin A. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21(3):485–95.
Wong R. Apoptosis in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Res. 2011;30:87.
Oberholzer C, Oberholzer A, Clare-Salzler M, Moldawer L. Apoptosis in sepsis: a new target for therapeutic exploration. Faseb J. 2001;15:879–92.
Peter M, Budd R, Desbarats J, Hedrick S, Hueber A, Karen M, et al. The CD95 receptor: apoptosis revisited. Cell. 2007;129:447–50.
Vick J. First demonstration of the role of tnf in the pathogenesis of disease. J Immunol. 2008;181:5–6.
Chun SC, Song G, Lomas J, Simms H, Chaudry I, Ayala A. Inhibition of Fas/Fas ligand signaling improves septic survival: differential effects on macrophage apoptotic and functional capacity. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;74:344–51.
Dougthy L, Clark R, Carcillo J. Soluble Fas receptor and Fas ligand in sepsis-induced multiple organ failure. Pediatr Res. 1998;43:35.
De Freitas I, Fernandez SM, Essenfeld SA, Cardier J. Serum levels of the apoptosis-associated molecules, tumor necrosis factor α/tumor necrosis factor type-1 receptor and Fas/FasL, in sepsis. Chest. 2004;125:2238–46.
Konstadoulakis M, Messaris E. Are cancer patients adequate candidates for studying apoptosis in septic and ARDS models? Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1501.
Regueira T, Andresen M, Djafarzadeh S. Disfunción mitocondrial en sepsis, impacto y posible papel regulador del factor inducible por hipoxia (HIF-1alfa). Med Intensiv (revista en la internet). 2009 (citado 2015 Mayo 13) 33(8):385–92. http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0210-56912009000800004&lng=es.
Faix JD. Biomarkers of sepsis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2013; 50(1):23–36.
Reyna FJ, Lagunas MA, Martínez MP, Madrid MV. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic biomarker of sepsis in children with cancer, fever and neutropenia: literature review. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2015;113(1):46–52.
Dhainaut JF, Claessens YE, Janes J, Nelson D. Underlying disorders and their impact on the host response to infection. CID 2005; 41(Suppl 7):S481–9.
Sack U, Burkhardt U, Borte M, Schadlich H, Berg K, Emmrich F. Age-dependent levels of select immunological mediators in sera of healthy children. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1998;1(5):28–32.
Reyna FJ, Lagunas MA, Fernández BMF, Ortiz IFJ, Madrid MV. Sepsis en el niño con cáncer: problemas en su identificación y retos para su disminución. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2015;37(1):97–104.
Schuler D, Szende B. Apoptosis and acute lymphotic leukemia in children. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1997;824:28–37.
Wu Q, Chen H, Xie W, Hong M, Xia L. Elevated Fas/FasL system and endotelial cell microparticles are involved in endotelial damage in acute graft-versus-host diseases: a clinical analysis. Leuk Res. 2012;36(3):275–80.
dos Santos C. Shedding metaboligth on the search for sepsis biokmarkers. Crit Care. 2015;19(277):2–3.
Oberholzer C, Oberholzer A, Clare C, Moldawer I. Apoptosis in sepsis: a new target for therapeutic exploration Faseb J 2001; 15:879–92.
Rastogi RP, Sinha R, Sinha RP. Apoptosis: molecular mechanisms and pathogenicity. EXCLI J. 2009;8:155–81.
Aoyagi T, Terracina KP, Raza A, Matsubara H, Takabe K. Cancer cachexia, mechanism and treatment. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015;7(4):17–29.
Coffelt SB, de Visser KE. Immune-mediated mechanisms influencing the efficacy of anticancer therapies. Trends Immunol. 2015;36(4):198–216.
Nosair N, Abd El Bar E, Taha A, Gawaly A. Fas (CD95) expression as a prognostic marker in acute leukemia and blastic transformation phase in chronic myeloid leukemia. Egypt J Hematol. 2014;39:25–31.
Papathanassoglou ED, Mpouzika MD, Giannakopoulou M, Bozas E, Middleton N, Boti S, Karabinis A. Pilot investigation of the association between serum stress neuropeptide levels and lymphocyte expression of Fas and Fas ligand in critical illness. Biol Res Nurs. 2014 (Epub ahead of print).
Spooner CE, Markowitz NP, Saravolatz LD. The role of tumor necrosis factor in sepsis Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992;62:S11–7.
Van Vliet MW, Hermie JM, Harmsen H. The role of intestinal microbiota in the development and severity of chemotherapy-induced mucositis. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6(5):e1000879.
Lin CW, Lo S, Hsu C, Hsieh CH, Chang YF, Hou BS, et al. T-cell autophagy deficiency increases mortality and suppresses immune responses after sepsis. PLoS One. 2014; 16 9(7):e102066.
Gozal D, Serpero L, Kheirandish L, Sans O, Khalyfa A, Tauman R. Sleep measures and morning plasma TNF-α levels in children with sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep. 2010;33(3):319–25.
Tsaoussoglou M, Bixler E, Calhoun S, Chrousos G, Sauder K, Vgontzas A. Sleep-disordered breathing in obese children is associated with prevalent excessive daytime sleepiness, inflamation, and metabolic abnormalities. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(1):143–50.
Cunha BA. Fever in malignant disorders. Infect Dis Pract. 2004;29:335–6.
Barber GN. Host defense, viruses and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2001;8:113–26.
O´Brien V. Viruses and apoptosis J Gen Virol 1998, 79:1833–45.
Fransson J, Tornberg UC, Borrebaeck CA, Carlsson R, Frendéus B. Rapid induction of apoptosis in B-cell lymphoma by functionally isolated human antibodies. Int J Cancer 2006; 119(2):349–58.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT) Mexico, by the supported with the scholarship awarded for postgraduate study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Reyna-Figueroa, J., Lagunas-Martínez, A., Galindo-Delgado, P. et al. Serum concentrations of apoptosis-associated molecules in septic children with leukemia, neutropenia and fever. Int J Hematol 105, 668–675 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-2175-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-016-2175-z