Abstract
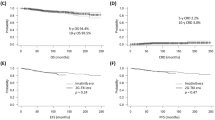
The introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors has dramatically improved outcomes for many patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), but some cases are resistant to this treatment. To compare the prognostic performance of Sokal, Hasford, and European Treatment and Outcome Study (EUTOS) scores, patient outcomes and treatment responses were investigated following the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) 2013 recommendations. Seventy-three patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase CML (CML-CP) treated with any tyrosine kinase inhibitor as initial therapy were analyzed. All scoring systems significantly predicted treatment response at 3 and 6 months; however, only the EUTOS score significantly predicted treatment response at 12 months, following the ELN 2013 recommendations. The 5-year event-free survival rates were 93 and 35 % in the low- and high-risk groups according to the EUTOS score (P < 0.0001). Moreover, the 5-year overall survival rates were 98 and 51 % in the low- and high-risk groups by EUTOS score (P < 0.0001). We suggest that the EUTOS score may provide a better stratification of CML-CP patients for predicting treatment response.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:994–1004.
Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, Jabbour E, Shan J, Ravandi F, Kadia T, et al. Impact of treatment end point definitions on perceived differences in long-term outcome with tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3173–8.
Tauchi T, Kizaki M, Okamoto S, Tanaka H, Tanimoto M, Inokuchi K, et al. Seven-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the treatment of newly diagnosed chronic myelogenous leukemia by the TARGET system. Leuk Res. 2011;35:585–90.
Kim D, Goh HG, Kim SH, Choi SY, Park SH, Jang EJ, et al. Comprehensive therapeutic outcomes of frontline imatinib mesylate in newly diagnosed chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients in Korea: feasibility assessment of current ELN recommendation. Int J Hematol. 2012;96:47–57.
Mitra D, Trask PC, Iyer S, Candrilli SD, Kaye JA. Patient characteristics and treatment patterns in chronic myeloid leukemia: evidence from a multi-country retrospective medical record chart review study. Int J Hematol. 2012;95:263–73.
Trask PC, Mitra D, Iyer S, Candrilli SD, Kaye JA. Patterns and prognostic indicators of response to CML treatment in a multi-country medical record review study. Int J Hematol. 2012;95:535–44.
Saglio G, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S, le Coutre P, Etienne G, Lobo C, et al. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2251–9.
Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, Cortes J, Shah S, Ayala M, et al. Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2260–70.
Sokal JE, Cox EB, Baccarani M, Tura S, Gomez GA, Robertson JE, et al. Prognostic discrimination in “good-risk” chronic granulocytic leukemia. Blood. 1984;63:789–99.
Hasford J, Pfirrmann M, Hehlmann R, Allan NC, Baccarani M, Kluin-Nelemans JC, et al. A new prognostic score for survival of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with interferon alfa. Writing Committee for the Collaborative CML Prognostic Factors Project Group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:850–8.
Hasford J, Baccarani M, Hoffmann V, Guilhot J, Saussele S, Rosti G, et al. Predicting complete cytogenetic response and subsequent progression-free survival in 2060 patients with CML on imatinib treatment: the EUTOS score. Blood. 2011;118:686–92.
Baccarani M, Deininger MW, Rosti G, Hochhaus A, Soverini S, Apperley JF, et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood. 2013;122:872–84.
Baccarani M, Cortes J, Pane F, Niederwieser D, Saglio G, Apperley J, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: an update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:6041–51.
Langabeer SE, Gale RE, Harvey RC, Cook RW, Mackinnon S, Linch DC. Transcription-mediated amplification and hybridisation protection assay to determine BCR-ABL transcript levels in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 2002;16:393–9.
Ohnishi K, Nakaseko C, Takeuchi J, Fujisawa S, Nagai T, Yamazaki H, et al. Long-term outcome following imatinib therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia, with assessment of dosage and blood levels: the JALSG CML202 study. Cancer Sci. 2012;103:1071–8.
Yamamoto E, Fujisawa S, Hagihara M, Tanaka M, Fujimaki K, Kishimoto K, et al. European treatment and outcome study score does not predict imatinib treatment response and outcome in chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Cancer Sci. 2014;105:105–9.
Jabbour E, Cortes J, Nazha A, O’Brien S, Quintas-Cardama A, Pierce S, et al. EUTOS score is not predictive for survival and outcome in patients with early chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a single institution experience. Blood. 2012;119:4524–6.
Hoffmann VS, Baccarani M, Lindoerfer D, Castagnetti F, Turkina A, Zaritsky A, et al. The EUTOS prognostic score: review and validation in 1288 patients with CML treated frontline with imatinib. Leukemia. 2013;27:2016–22.
Tiribelli M, Bonifacio M, Calistri E, Binotto G, Maino E, Marin L, et al. EUTOS score predicts long-term outcome but not optimal response to imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leuk Res. 2013;37:1457–60.
Bonifacio M, Binotto G, Calistri E, Maino E, Tiribelli M. Gruppo Triveneto LMC. EUTOS score predicts early optimal response to imatinib according to the revised 2013 ELN recommendations. Ann Hematol. 2014;93:163–4.
Conflict of interest
M.T. Received research grants from Bristol and Novartis. N.I. And Y.H. received honoraria from Bristol and Novartis. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Iriyama, N., Hatta, Y., Kobayashi, S. et al. The European Treatment and Outcome Study score is associated with clinical outcomes and treatment response following European LeukemiaNet 2013 recommendations in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol 100, 379–385 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1649-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-014-1649-0