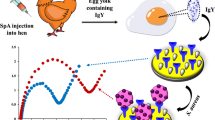
Abstract
Rapid and quantitative detection of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus at the strain level is important for quality control of probiotic products. In this study, an electrochemical magnetic bead-based immunosensor (EMBI) was developed for the specific quantification of probiotic L. rhamnosus strain GG (LGG) in dairy products. Magnetic beads coupled with a specific antibody against the pilus subunit SpaA of LGG (Ab-SpaA) were prepared to selectively capture LGG from the background, which were then detected using horseradish peroxidase-labeled Ab-SpaA. The resultant sandwich-type immunocomplexes were separated by magnetic force and detected by measuring current signals using a magnetic glassy carbon electrode (MGCE) and the hydroquinone (HQ)/H2O2 system. Under optimal experimental conditions, the developed EMBI showed a linear relationship between the peak current and the logarithmic value of LGG concentration ranging from 2.56 × 103 to 2.56 × 107 CFU mL−1 with a detection limit of 22 CFU mL−1. EMBI detection is LGG specific, and no cross-reaction was observed for tested strains of other lactic acid bacterial species. The EMBI was successfully applied for LGG determination in commercial milk, yogurt, milk beverage products, and spiked dairy samples, with a recovery rate in the range of 91.74–108.67%. The entire detection process could be completed within 3 h. The proposed biosensor shows low-cost, rapid response, and high sensitivity and specificity and could be a promising technique for quality detection and functional evaluation of probiotic products containing LGG.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilleos C, Berthier F (2013) Quantitative PCR for the specific quantification of Lactococcus lactis and Lactobacillus paracasei and its interest for Lactococcus lactis in cheese samples. Food Microbiol 36:286–295
Alves RC, Pimentel FB, Nouws HP, Marques RC, Gonzálezgarcía MB, Oliveira MB, Deleruematos C (2015) Detection of Ara h 1 (a major peanut allergen) in food using an electrochemical gold nanoparticle-coated screen-printed immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 64:19–24
Basu S, Chatterjee M, Ganguly S, Chandra PK (2007) Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in persistent diarrhea in Indian children: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Gastroenterol 41:756–760
Brandt K, Alatossava T (2003) Specific identification of certain probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains with PCR primers based on phage-related sequences. Int J Food Microbiol 84:189–196
Bunthof CJ, Bloemen K, Breeuwer P, Rombouts FM, Abee T (2001) Flow cytometric assessment of viability of lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2326–2335
Conzuelo F, Gamella M, Campuzano S, Reviejo AJ, Pingarrón JM (2012) Disposable amperometric magneto-immunosensor for direct detection of tetracyclines antibiotics residues in milk. Anal Chim Acta 737:29–36
Davis C (2014) Enumeration of probiotic strains: review of culture-dependent and alternative techniques to quantify viable bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 103:9–17
Debmandal M, Mandal S, Pal NK (2012) Detection of intestinal colonization of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus by stool culture in modified selective media. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 2:205–210
Doron S, Snydman DR, Gorbach SL (2005) Lactobacillus GG: bacteriology and clinical applications. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 34:483–498
Drouault S, Corthier G, Ehrlich SD, Renault P (1999) Survival, physiology, and lysis of Lactococcus lactis in the digestive tract. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4881
Duez H et al (2010) A colony immunoblotting method for quantitative detection of a Bifidobacterium animalis probiotic strain in human faeces. J Appl Microbiol 88:1019–1027
Erdem A, Pividori MI, Lermo A, Bonanni A, Valle MD, Alegret S (2006) Genomagnetic assay based on label-free electrochemical detection using magneto-composite electrodes. Sens Actuators B 114:591–598
FAO (2002) Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food
Guandalini S, Pensabene L, Zikri MA, Dias JA, Casali LG, Hoekstra H, Kolacek S, Massar K, Micetic–Turk D, Papadopoulou A, de Sousa JS, Sandhu B, Szajewska H, Weizman Z (2000) Lactobacillus GG administered in oral rehydration solution to children with acute diarrhea: a multicenter European trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 30:54–60
Guo S, Dong S (2009) ChemInform abstract: biomolecule-nanoparticle hybrids for electrochemical biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 28:96–109
Han E, Li X, Cai JR, Cui HY, Zhang XA (2014) Development of highly sensitive amperometric biosensor for glucose using carbon nanosphere/sodium alginate composite matrix for enzyme immobilization. Analytical sciences the international journal of the Japan society for Anal Chem 30:897–902
Hervás M, López MA, Escarpa A (2009) Electrochemical immunoassay using magnetic beads for the determination of zearalenone in baby food: an anticipated analytical tool for food safety. Anal Chim Acta 653:167–172
Hojsak I, Abdović S, Szajewska H, Milosević M, Krznarić Z, Kolacek S (2010) Lactobacillus GG in the prevention of nosocomial gastrointestinal and respiratory tract infections. Pediatrics 125:1171–1177
Hossain MI, Sadekuzzaman M, Ha SD (2017) Probiotics as potential alternative biocontrol agents in the agriculture and food industries: a review. Food Res Int 100:63–73
Huang CH, Chang MT, Huang L, Chu WS (2015) Simultaneous discrimination of species and strains in Lactobacillus rhamnosus using species-specific PCR combined with multiplex mini-sequencing technology. Mol Cell Probes 29:531–533
Huys G, Vancanneyt M, D'Haene K, Vankerckhoven V, Goossens H, Swings J (2006) Accuracy of species identity of commercial bacterial cultures intended for probiotic or nutritional use. Res Microbiol 157:803–810
Kalliomäki M, Salminen S, Arvilommi H, Kero P, Koskinen P, Isolauri E (2001) Probiotics in primary prevention of atopic disease: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 357:1076–1079
Lebeer S, Claes I, Tytgat HLP, Verhoeven TLA, Marien E, von Ossowski I, Reunanen J, Palva A, de Vos WM, de Keersmaecker SCJ, Vanderleyden J (2012) Functional analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG pili in relation to adhesion and immunomodulatory interactions with intestinal epithelial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:185–193
Lee JY, Park EJ, Min NK, Pak JJ (2009) Carbon nanotube based electrochemical immunosensors for high-sensitive detection of E. coli. Sensors:1176–1179
Lena MD, Quero GM, Santovito E, Verran J, Angelis MD, Fusco V (2015) A selective medium for isolation and accurate enumeration of Lactobacillus casei-group members in probiotic milks and dairy products. Int Dairy J 47:27–36
M Č, Metelka R, Holubová L, Horák D, Dvořáková V, Bílková Z, Korecká L (2015) Magnetic beads-based electrochemical immunosensor for monitoring allergenic food proteins. Anal Biochem 484:4–8
Ranadheera CS, Naumovski N, Ajlouni S (2018) Non-bovine milk products as emerging probiotic carriers: recent developments and innovations. Curr Opin Food Sci 22:109–114
Ruizvaldepeñas MV, Campuzano S, Torrenterodríguez RM, Reviejo AJ, Pingarrón JM (2016) Electrochemical magnetic beads-based immunosensing platform for the determination of α-lactalbumin in milk. Food Chem 213:595–601
Sakai T, Oishi K, Asahara T, Takada T, Yuki N, Matsumoto K, Nomoto K, Kushiro A (2010) M-RTLV agar, a novel selective medium to distinguish Lactobacillus casei and Lactobacillus paracasei from Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Int J Food Microbiol 139:154–160
Salam F, Tothill IE (2009) Detection of Salmonella typhimurium using an electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2630–2636
Shen ZQ, Wang JF, Qiu ZG, Jin M, Wang XW, Chen ZL, Li JW, Cao FH (2011) QCM immunosensor detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 based on beacon immunomagnetic nanoparticles and catalytic growth of colloidal gold. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3376–3381
Smita S, Pawas G, Rameshwar S, Knutj H (2009) Application of molecular identification tools for Lactobacillus, with a focus on discrimination between closely related species: a review. LWT- Food Sci Technol 42:448–457
Yang Y et al (2016a) A novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 90:31–38
Yang ZQ, Wei YF, Rao SQ, Gao L, Yin YQ, Xue F, Fang WM, Gu RX, Jiao XA (2016b) Immunomagnetic separation combined with colony immunoblotting for selective enrichment and detection of piliated Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains. J Appl Microbiol 121:1406–1415
Yang ZQ, Xue Y, Rao SQ, Zhang M, Gao L, Yin YQ, Chen DW, Zhou XH, Jiao XA (2017) Isolation of probiotic piliated Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains from human faecal microbiota using SpaA antiserum-based colony immunoblotting. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1971–1982
Ye L, Zhao G, Dou W (2018) An electrochemical immunoassay for Escherichia coli O157:H7 using double functionalized Au@Pt/SiO2 nanocomposites and immune magnetic nanoparticles. Talanta 182:354–362
Yun Z, Hang Y, Yu J, Wei H (2016) Rapid and sensitive detection of HIV-1 p24 antigen by immunomagnetic separation coupled with catalytic fluorescent immunoassay. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:6115–6121
Zhang X, Shen J, Ma H, Jiang Y, Huang C, Han E, Yao B, He Y (2016a) Optimized dendrimer-encapsulated gold nanoparticles and enhanced carbon nanotube nanoprobes for amplified electrochemical immunoassay of E. coli in dairy product based on enzymatically induced deposition of polyaniline. Biosens Bioelectron 80:666–673
Zhang X, Zhang F, Zhang H, Shen J, Han E, Dong X (2015) Functionalized gold nanorod-based labels for amplified electrochemical immunoassay of E. coli as indicator bacteria relevant to the quality of dairy product. Talanta 132:600–605
Zhang Y, Ge S, Wang S, Yan M, Yu J, Song X, Liu W (2012) Magnetic beads-based electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for determination of cancer markers using quantum dot functionalized PtRu alloys as labels. Analyst 137:2176–2182
Zhang Y, Zhang B, Ye X, Yan Y, Huang L, Jiang Z, Tan S, Cai X (2016b) Electrochemical immunosensor for interferon-γ based on disposable ITO detector and HRP-antibody-conjugated nano gold as signal tag. Mater Sci Eng C 59:577–584
Zhou CH, Long YM, Qi BP, Pang DW, Zhang ZL (2013) A magnetic bead-based bienzymatic electrochemical immunosensor for determination of H9N2 avian influenza virus. Electrochem Commun 31:129–132
Funding
This study was funded the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 31371806 and 31601535), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant number BK20160459), the Priority Academic Program Development of the Department of Education of Jiangsu Province (grant number 15KJA550004 and 16KJB550008), and a grant from Yangzhou University Science and Technology Innovation Team (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Author Yu Xue declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Dong-lei Jiang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Qin Hu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Sheng-qi Rao declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Lu Gao declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Zhen-quan Yang declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Y., Jiang, Dl., Hu, Q. et al. Electrochemical Magnetic Bead-Based Immunosensor for Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus in Dairy Products. Food Anal. Methods 12, 1197–1207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01457-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01457-z