Abstract
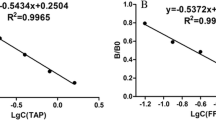
Antibodies are the most important reagents for the development of highly sensitive and specific immunoassays to quantify analytes of interest in food and environmental samples. While immunoglobulin G (IgG)-derived antibodies from rabbit and mouse are traditionally employed in immunoassays, recent findings suggest that chicken egg yolk antibody (immunoglobulin Y (IgY)) provides several advantages over mammalian IgG. However, limited studies to date have examined the possibility of replacing IgG with IgY in immunoassays. In the current investigation, the performance of chicken IgY and IgG derived from rabbit and mouse was systematically compared in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and matrix effect under parallel conditions with three typical assay formats, specifically, indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (icELISA), fluorescence polarization immunoassay (FPIA), and colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay (GICA), for detection of sulfamethazine (SMZ) as the reference molecule. We evaluated and discussed the influence of different coating antigens, tracers, and physicochemical factors on the performance of IgY and IgG in the immunoassays. Under optimized conditions, the sensitivities of icELISA (IC50 values of 6.70, 4.76, and 1.66 ng mL−1 with recoveries of 86.1–131.8% and precision of < 12%) and FPIA (IC50 values of 24.79, 20.87, and 10.83 ng mL−1 with recoveries of 81.8–120.2% and precision of < 17.3%) based on both IgY and IgG were sufficient to detect SMZ in milk while only GICA based on mouse IgG provided acceptable sensitivity. Our collective data indicate that IgY could be an acceptable alternative to mammalian antibodies in some situations (in icELISA and FPIA) for use in the development of effective immunoassays for screening and detection of veterinary drug residues in food samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bottari F, Oliveri P, Ugo P (2014) Electrochemical immunosensor based on ensemble of nanoelectrodes for immunoglobulin IgY detection: application to identify hen's egg yolk in tempera paintings. Biosens Bioelectron 52:403–410
Camenisch G, Tini M, Chilov D, Kvietikova I, Srinivas V, Caro J, Spielmann P, Wenger RH, Gassmann M (1999) General applicability of chicken egg yolk antibodies: the performance of IgY immunoglobulins raised against the hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. FASEB J 13:81–88
Chen Y, Wang Z, Wang Z, Tang S, Zhu Y, Xiao X (2008) Rapid enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and colloidal gold immunoassay for kanamycin and tobramycin in swine tissues. J Agric Food Chem 56:2944–2952
European Commission (2002) Regulation No. 235. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China
European Commission (EC) (2009) Commission Regulation (EC) no. 490/2009. Off J Europ Commun 16–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1316-9
Dixon-Holland DE, Katz SE (1988) Competitive direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of sulfamethazine residues in swine urine and muscle tissue. J AOAC Int 71:1137–1140
Eremin SA, Landon J, Smith DS, Jackman R (1994) Development of a polarization fluoroimmunoassay for sulfamethazine using an automated analyser. Analyst 119:2723–2726
Galarini R, Diana F, Moretti S, Puppini B, Saluti G, Persic L (2014) Development and validation of a new qualitative elisa screening for multiresidue detection of sulfonamides in food and feed. Food Control 35:300–310
He J, Hu J, Thirumalai D, Schade R, Du E, Zhang X (2016a) Development of indirect competitive elisa using egg yolk-derived immunoglobulin (IgY) for the detection of gentamicin residues. J Environ Sci Health, Part B 51:8–13
He J, Shen J, Suo X, Jiang H, Hou X (2005) Development of a monoclonal antibody-based ELISA for detection of sulfamethazine and N4−acetyl sulfamethazine in chicken breast muscle tissue. J Food Sci 70:C113–C117
He J, Wang Y, Zhang X (2016b) Preparation of artificial antigen and development of IgY-based indirect competitive ELISA for the detection of kanamycin residues. Food Anal Method 9:744–751
Hirai K, Arimitsu H, Umeda K, Yokota K, Shen L, Ayada K, Kodama Y, Tsuji T, Hirai Y, Oguma K (2010) Passive oral immunization by egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) to Vibrio cholerae effectively prevents cholera. Acta Med Okayama 64:163–170
Klimentzou P, Paravatou-Petsotas M, Zikos C, Beck A, Skopeliti M, Czarnecki J, Tsitsilonis O, Voelter W, Livaniou E, Evangelatos GP (2006) Development and immunochemical evaluation of antibodies Y for the poorly immunogenic polypeptide prothymosin alpha. Peptides 27:183–193
Larsson A, Sjöquist J (1990) Chicken IgY: utilizing the evolutionary difference. Comp Immunol Microb Infect Dis 13:199–201
Li C, Zhang Y, Eremin SA, Yakup O, Yao G, Zhang X (2017) Detection of kanamycin and gentamicin residues in animal-derived food using IgY antibody based ic-ELISA and FPIA. Food Chem 227:48–54
Li X, Luo P, Tang S, Beier RC, Wu X, Yang L, Li Y, Xiao X (2011) Development of an immunochromatographic strip test for rapid detection of melamine in raw milk, milk products and animal feed. J Agric Food Chem 59:6064–6070
Malekshahi ZV, Gargari SL, Rasooli I, Ebrahimizadeh W (2011) Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in mice with oral administration of egg yolk-driven anti-UreC immunoglobulin. Microb Pathog 51:366–372
Meng M, Xi R (2011) Review: current development of immunoassay for analyzing veterinary drug residue in foods and food products. Anal Lett 44:2543–2558
Mi T, Liang X, Ding L, Zhang S, Eremin SA, Beier RC, Shen J, Wang Z (2014) Development and optimization of a fluorescence polarization immunoassay for orbifloxacin in milk. Anal Methods 6:3849–3857
Mi T, Wang Z, Eremin SA, Shen J, Zhang S (2013) Simultaneous determination of multiple (fluoro) quinolone antibiotics in food samples by a one-step fluorescence polarization immunoassay. J Agric Food Chem 61:9347–9355
Mine Y, Kovacs-Nolan J (2002) Chicken egg yolk antibodies as therapeutics in enteric infectious disease: a review. J Med Food 5:159–169
Paek SH, Lee SH, Cho JH, Kim YS (2000) Development of rapid one-step immunochromatographic assay. Methods 22:53–60
Rahman S, Van Nguyen S, Icatlo FC Jr, Umeda K, Kodama Y (2013) Oral passive IgY-based immunotherapeutics: a novel solution for prevention and treatment of alimentary tract diseases. Hum Vaccin Immunother 9:1039–1048
Sheng YJ, Ni HJ, Zhang HY, Li YH, Wen K, Wang ZH (2015) Production of chicken yolk IgY to sulfamethazine: comparison with rabbit antiserum IgG. Food Agric Immunol 26:305–316
Smith DS, Eremin SA (2008) Fluorescence polarization immunoassays and related methods for simple, high-throughput screening of small molecules. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1499–1507
Sotiropoulou G, Pampalakis G, Prosnikli E, Evangelatos GP, Livaniou E (2012) Development and immunochemical evaluation of a novel chicken IgY antibody specific for KLK6. Chem Cent J 6:148
Toldrá F, Reig M (2006) Methods for rapid detection of chemical and veterinary drug residues in animal foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 17:482–489
Tu YY, Chen CC, Chang HM (2001) Isolation of immunoglobulin in yolk (IgY) and rabbit serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) specific against bovine lactoferrin by immunoaffinity chromatography. Food Res Int 34:783–789
Wang S, Xu B, Zhang Y, He JX (2009) Development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (elisa) for the detection of neomycin residues in pig muscle, chicken muscle, egg, fish, milk and kidney. Meat Sci 82:53–58
Wang Y, Kececi K, Mirkin MV, Mani V, Sardesai N, Rusling JF (2013a) Resistive-pulse measurements with nanopipettes: detection of Au nanoparticles and nanoparticle-bound anti-peanut IgY. Chem Sci 4:655–663
Wang ZH, Zhang SX, Shen JZ, Sergei AE (2007a) Analysis of sulfamethazine by fluorescence polarization immunoassay. Chin J Anal Chem 35:819–824
Wang Z, Beier RC, Sheng Y, Zhang S, Jiang W, Wang Z, Wang J, Shen J (2013b) Monoclonal antibodies with group specificity toward sulfonamides: selection of hapten and antibody selectivity. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:4027–4037
Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhang S, Shen J (2011) Heterologous structure of coating antigen on sensitivity of elisa for sulfamethazine: evidence from molecular similarity analysis. Food Agric Immunol 22:115–124
Wang Z, Zhang S, Ding S, Eremin SA, Shen J (2008) Simultaneous determination of sulphamerazine, sulphamethazine and sulphadiazine in honey and chicken muscle by a new monoclonal antibody-based fluorescence polarisation immunoassay. Food Addit Contam A 25:574–582
Wang Z, Zhang S, Nesterenko IS, Eremin SA, Shen J (2007b) Monoclonal antibody-based fluorescence polarization immunoassay for sulfamethoxypyridazine and sulfachloropyridazine. J Agric Food Chem 55:6871–6878
Zhang X, Wu C, Wen K, Jiang H, Shen J, Zhang S, Wang Z (2016) Comparison of fluorescent microspheres and colloidal gold as labels in lateral flow immunochromatographic assays for the detection of T-2 toxin. Molecules 21:26
Zhou Q, Peng D, Wang Y, Pan Y, Wan D, Zhang X, Yuan Z (2014) A novel hapten and monoclonal-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for sulfonamides in edible animal tissues. Food Chem 154:52–62
Zhu K, Li J, Wang ZH, Jiang HY, Beier RC, Xu F, Shen J, Ding SY (2011) Simultaneous detection of multiple chemical residues in milk using broad-specificity antibodies in a hybrid immunosorbent assay. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2716–2719
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31502123 and No. 31601194), China Agriculture Research System (Grant No. CARS-36), Qingdao Science and Technology Project (No. 17-3-3-69-nsh), and Priority Academic Talent Team Cultivation Program of Shandong Colleges and Universities.
Funding
Dr. Xiao Liang and Dr. Wanpeng Yu has received a research grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. Prof. Zhanhui Wang has received a research grant from China Agriculture Research System. Dr. Qidi Zhang has received a research grant from Qingdao Science and Technology Project. Dr. Xiao Liang has received a research grant from Priority Academic Talent Team Cultivation Program of Shandong Colleges and Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Xiao Liang has no conflict of interest. Yajie Sheng has no conflict of interest. Wanpeng Yu has no conflict of interest. Sijun Zhao has no conflict of interest. Hu Shan has no conflict of interest. Qidi Zhang has no conflict of interest. Zhanhui Wang has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
Informed consent is not applicable in this study.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1049 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, X., Sheng, Y., Yu, W. et al. Comparison of Chicken IgY and Mammalian IgG in Three Immunoassays for Detection of Sulfamethazine in Milk. Food Anal. Methods 11, 3452–3463 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1316-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1316-9