Abstract
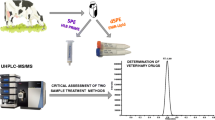
A high-throughput method was established for the simultaneous determination of 30 β-agonists, fluoroquinolones, and cephalosporins in milk powder by dispersive solid-phase extraction (dSPE) and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Samples were firstly dissolved in sodium acetate buffer, then extracted with formic acid-acetonitrile, and subsequently purified by dSPE. Thirty target analytes were separated on a C18 column by gradient elution, detected through electrospray ionization (ESI) source in the positive mode with multi-reaction monitoring (MRM) conditions. The developed method was validated in terms of linearity, accuracy, and precision. Results indicated that 30 target analytes displayed excellent linearity in their corresponding concentration ranges and that their correlation coefficients were all higher than 0.995. The limits of quantitation (LOQs) for these targets were in the range of 0.7–7.0 μg/kg. The mean recoveries for negative sample spiked at three concentration levels were calculated between 80.0 and 97.5% with the relative standard deviation (RSD, n = 6) values ranging from 2.8 to 10.8%. In addition, the inter-day precision (n = 5) of the second spiked concentration was less than 13% (4.4–12.4%). The established and validated method is accurate and rapid and suitable for the high-throughput analysis of β-agonist, fluoroquinolone, and cephalosporin multi-residues in milk powder.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Štajnbaher D, Schenck FJ (2003) Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int 86(2):412–431
Aufartová J, Brabcová I, Torres-Padrón ME, Solich P, Sosa-Ferrera Z, Santana-Rodríguez JJ (2017) Determination of fluoroquinolones in fishes using microwave-assisted extraction combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. J Food Compos Anal 56:140–146
Bousova K, Senyuva H, Mittendorf K (2013) Quantitative multi-residue method for determination antibiotics in chicken meat using turbulent flow chromatography coupled to liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1274:19–27
Chen D, Yu J, Tao Y, Pan Y, Xie S, Huang L, Peng D, Wang X, Wang Y, Liu Z, Yuan Z (2016) Qualitative screening of veterinary anti-microbial agents in tissues, milk, and eggs of food-producing animals using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences 1017-1018:82–88
Chiesa L, Nobile M, Arioli F, Britti D, Trutic N, Pavlovic R, Panseri S (2015) Determination of veterinary antibiotics in bovine urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 185:7–15
Chu L, Zheng S, Qu B, Geng S, Kang X (2017) Detection of β-agonists in pork tissue with novel electrospun nanofibers-based solid-phase extraction followed ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 227:315–321
Dang H, Liu D, Hou X, Wu Y, Wang B, Dong H, Xian Y (2017) One-step extraction prior to two-step detection by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) to determine different groups of antibacterial agents in infant disposable hygiene products. Anal Methods 9(3):482–489
Dasenaki ME, Thomaidis NS (2015) Multi-residue determination of 115 veterinary drugs and pharmaceutical residues in milk powder, butter, fish tissue and eggs using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 880:103–121
de Oliveira HL, da Silva Anacleto S, da Silva ATM, Pereira AC, de Souza Borges W, Figueiredo EC, Borges KB (2016) Molecularly imprinted pipette-tip solid phase extraction for selective determination of fluoroquinolones in human urine using HPLC-DAD. J Chromatogr B 1033–1034:27–39
Denadai M, Cass QB (2015) Simultaneous determination of fluoroquinolones in environmental water by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry with direct injection: a green approach. J Chromatogr A 1418:177–184
Dong H, Guo X, Xian Y, Luo H, Wang B, Wu Y (2015) A salting out-acetonitrile homogeneous extraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of thirteen N-nitrosamines in skin care cosmetics. J Chromatogr A 1422:82–88
Dong H, Luo D, Xian Y, Luo H, Guo X, Li C, Zhao M (2016) Adulteration identification of commercial honey with the C-4 sugar content of negative values by an elemental analyzer and liquid chromatography coupled to isotope ratio mass spectroscopy. J Agric Food Chem 64(16):3258–3265
Dong H, Xiao K (2017) Modified QuEChERS combined with ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry to determine seven biogenic amines in Chinese traditional condiment soy sauce. Food Chem 229:502–508
Guo X, Mu T, Xian Y, Luo D, Wang C (2016) Ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the rapid simultaneous analysis of nine organophosphate esters in milk powder. Food Chem 196:673–681
Jia W, Chu X, Chang J, Wang PG, Chen Y, Zhang F (2017) High-throughput untargeted screening of veterinary drug residues and metabolites in tilapia using high resolution orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 957:29–39
Jin Y, Zhang J, Zhao W, Zhang W, Wang L, Zhou J, Li Y (2017) Development and validation of a multiclass method for the quantification of veterinary drug residues in honey and royal jelly by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 221:1298–1307
Khezeli T, Daneshfar A (2017) Development of dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on micro and nano sorbents. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 89:99–118
Li W, Shen H, Hong Y, Zhang Y, Yuan F, Zhang F (2016) Simultaneous determination of 22 cephalosporins drug residues in pork muscle using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 1022:298–307
Liu X, Yu Y, Zhao M, Zhang H, Li Y, Duan G (2014) Solid phase extraction using magnetic core mesoporous shell microspheres with C18-modified interior pore-walls for residue analysis of cephalosporins in milk by LC–MS/MS. Food Chem 150:206–212
Luo D, Dong H, Luo H, Xian Y, Guo X, Wu Y (2016) Multi-element (C, N, H, O) stable isotope ratio analysis for determining the geographical origin of pure milk from different regions. Food Anal Methods 9(2):437–442
Luo D, Dong H, Luo H, Xian Y, Wan J, Guo X, Wu Y (2015) The application of stable isotope ratio analysis to determine the geographical origin of wheat. Food Chem 174:197–201
Masiá A, Suarez-Varela MM, Llopis-Gonzalez A, Picó Y (2016) Determination of pesticides and veterinary drug residues in food by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: a review. Anal Chim Acta 936:40–61
Matuszewski BK, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem 75(13):3019–3030
Mauro D, Ciardullo S, Civitareale C, Fiori M, Pastorelli AA, Stacchini P, Palleschi G (2014) Development and validation of a multi-residue method for determination of 18 β-agonists in bovine urine by UPLC–MS/MS. Microchem J 115:70–77
Rico A, Van den Brink PJ (2014) Probabilistic risk assessment of veterinary medicines applied to four major aquaculture species produced in Asia. Sci Total Environ 468–469:630–641
Wang P, Liu X, Su X, Zhu R (2015) Sensitive detection of β-agonists in pork tissue with novel molecularly imprinted polymer extraction followed liquid chromatography coupled tandem mass spectrometry detection. Food Chem 184:72–79
Wu Y, Luo D, Dong H, Wan J, Luo H, Xian Y, Guo X, Qin F, Han W, Wang L, Wang B (2015) Geographical origin of cereal grains based on element analyser-stable isotope ratio mass spectrometry (EA-SIRMS). Food Chem 174:553–557
Wu Z, Xu Y, Li M, Guo X, Xian Y, Dong H (2016a) Determination of three fluorescent whitening agents (FWAs) and their migration research in food contact plastic packaging containers and food simulants by UPLC-MS/MS method. RSC Adv 6(22):17941–17946
Wu Z, Xu Y, Li M, Guo X, Xian Y, Dong H (2016b) Simultaneous determination of fluorescent whitening agents (FWAs) and photoinitiators (PIs) in food packaging coated paper products by the UPLC-MS/MS method using ESI positive and negative switching modes. Anal Methods 8(5):1052–1059
Xian Y, Dong H, Wu Y, Guo X, Hou X, Wang B (2016) QuEChERS-based purification method coupled to ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC–MS/MS) to determine six quaternary ammonium compounds (QACs) in dairy products. Food Chem 212:96–103
Yang Y, Shao B, Zhang J, Wu Y, Duan H (2009) Determination of the residues of 50 anabolic hormones in muscle, milk and liver by very-high-pressure liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 877(5–6):489–496
Zeng X, Bai W, Xian Y, Dong H, Luo D (2016) Application of QuEChERS-based purification coupled with isotope dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the determination of N-nitrosamines in soy sauce. Anal Methods 8(26):5248–5254
Zhan J, Zhong YY, Yu XJ, Peng JF, Chen S, Yin JY, Zhang JJ, Zhu Y (2013) Multi-class method for determination of veterinary drug residues and other contaminants in infant formula by ultra performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 138(2–3):827–834
Zhu WX, Yang JZ, Wang Z-X, Wang CJ, Liu YF, Zhang L (2016) Rapid determination of 88 veterinary drug residues in milk using automated TurborFlow online clean-up mode coupled to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 148:401–411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Ruijiao Li declares that she has no conflict of interest. Moucheng Wu declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Wu, M. High-Throughput Determination of 30 Veterinary Drug Residues in Milk Powder by Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 10, 3753–3762 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0941-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0941-z