Abstract
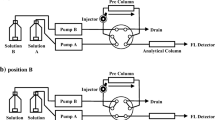
A high-performance liquid chromatography–fluorescence detection (HPLC-FLD) method was developed and validated for choline quantification in foods. Samples were extracted by homogenizing in chloroform/methanol/water and hydrolyzing in HCl-acetonitrile. Choline was derivatized using 1-naphthyl isocyanate and quantified by HPLC-fluorescence detection. Average recovery using choline iodide as the standard (n = 6) ranged from 84 ± 6 % for whole-wheat flour to 106 ± 5 % for milk. Recovery after addition of dietary lecithin to two different food matrices faba beans and for whole-wheat flour (n = 6) was 83 ± 5 %. The precision of the analysis (coefficient of variation) ranged from 2 to 13 %. Accuracy was evaluated by analyzing dietary lecithin using HPLC-FLD, liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, and nuclear magnetic resonance, which across the different methods agreed within 15 %. This method was applied to quantify the choline content in different food matrices, and provides a simple, inexpensive method that could be widely used.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrieux P, Kilinc T, Perrin C, Campos-Gimenez E (2008) Simultaneous determination of free carnitine and total choline by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry in infant formula and health-care products: single-laboratory validation. J AOAC Int 91:777–785
Aveldaño MI, Horrocks LA (1983) Quantitative release of fatty acids from lipids by a simple hydrolysis procedure. J Lipid Res 24:1101–1105
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Blusztajn JK (1998) Choline, a vital amine. Science 281:794–795. doi:10.1126/science.281.5378.794
Bruce SJ, Guy PA, Rezzi S, Ross AB (2010) Quantitative measurement of betaine and free choline in plasma, cereals and cereal products by isotope dilution LC-MS/MS. J Agric Food Chem 58:2055–2061. doi:10.1021/jf903930k
Craig SAS (2004) Betaine in human nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 80:539–549
Fu S, Tao B, Lai S, Zhang J, Yiping R (2012) Determination of total choline by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry in infant formulas. J AOAC Int 95:157–162
Graham SF, Hollis JH, Migaud M, Browne RA (2009) Analysis of betaine and choline contents of aleurone, bran, and flour fractions of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. J Agric Food Chem 57:1948–1951. doi:10.1021/jf802885m
Institute of Medicine. Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation Of Dietary Reference Intakes and Its Panel on Folate, other B vitamins, and Choline. (1998) Dietary reference intakes for thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, and choline. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114310/
Koc H, Mar M-H, Ranasinghe A, Swenberg JA, Zeisel SH (2002) Quantitation of choline and its metabolites in tissues and foods by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 74:4734–4740. doi:10.1021/ac025624x
Laikhtman M, Rohrer JS (1999) Determination of choline in infant formula by ion chromatography. J AOAC Int 82:115611–115662
Lee MB, Storer MK, Blunt JW, Lever M (2006) Validation of 1H NMR spectroscopy as an analytical tool for methylamine metabolites in urine. Clin Chim Acta 365:264–269
Lenky CC, McEntyre CJ, Lever M (2012) Measurement of marine osmolytes in mammalian serum by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Biochem 420:7–12. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2011.09.013
Lever M, Slow S (2010) The clinical significance of betaine, an osmolyte with a key role in methyl group metabolism. Clin Biochem 43:732–744. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2010.03.009
McEntyre CJ, Slow S, Lever M (2009) Measurement of plasma free choline by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection following derivatization with 1-naphthyl isocyanate. Anal Chim Acta 644:90–94
Patterson KY, Bhagwat SA, Williams JR, Howe JC, Holden JM (2008) USDA database for the choline content of common foods. Release Two. Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville Maryland
Phillips MM, Sander LC (2012) Microwave-assisted extraction and quantitative LC/ID-MS measurement of total choline and free carnitine in food standard reference materials. J AOAC Int 95:1479–1486
Ueland P (2011) Choline and betaine in health and disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 34:3–15. doi:10.1007/s10545-010-9088-4
Xiong Y, Zhao Y-Y, Goruk S, Oilund K, Field CJ, Jacobs RL, Curtis JM (2012) Validation of an LC–MS/MS method for the quantification of choline-related compounds and phospholipids in foods and tissues. J Chromatogr B 911:170–179
Zeisel SH, Blusztajn JK (1994) Choline and human nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr 14:269–296. doi:10.1146/annurev.nu.14.070194.001413
Zeisel SH, Da Costa K-A (2009) Choline: an essential nutrient for public health. Nutr Rev 67:615–623
Zhao Y-Y, Xiong Y, Curtis JM (2011) Measurement of phospholipids by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry: the determination of choline containing compounds in foods. J Chromatogr A 1218:5470–5479. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2011.06.025
Acknowledgments
Scholarship funding from the Partner Ownership initiative program (ParOwn, grant number 20150), the Ministry of Higher Education, Egypt, is gratefully acknowledged. Assistance from the National Heart Foundation of New Zealand and from the Maurice & Phyllis Paykel Trust is also acknowledged.
Conflict of Interest
Mohammed Hefni declares that he has no conflict of interest. Christopher McEntyre declares he has no conflict of interest. Michael Lever declares that he has no conflict of interest. Sandy Slow declares she has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hefni, M., McEntyre, C., Lever, M. et al. A Simple HPLC Method with Fluorescence Detection for Choline Quantification in Foods. Food Anal. Methods 8, 2401–2408 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0131-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0131-9