Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to determine the radiation dosimetry for 177Lu-PSMA imaging and therapy (I&T) in Thai patients who were treated for metastatic prostate cancer.
Methods
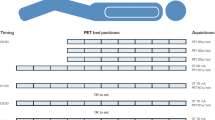
Whole-body planar images acquired at immediately, 4 and 24 h after 177Lu-PSMA I&T injection (range 4.44–8.51 GBq) were collected from 12 treatment cycles of 8 prostate cancer patients. Region of interests (ROIs) were manually contoured on the whole-body, liver, spleen, urinary bladder, lacrimal glands, parotid, and submandibular glands to determine time-integrated activity (TIA) in source organs and fitted time-activity curves using mono-exponential extrapolation. The S values calculated utilizing non-uniform rational B-splines (NURBS) computational phantoms were extracted from the OLINDA/EXM v. 2.0 to calculate the absorbed dose coefficient in target organs according to the Medical Internal Radiation Dose (MIRD) scheme. The absorbed doses to bone marrow were estimated using the planar two-compartment image-based method by separating the high-uptake and low-uptake compartment. The spherical model was used to calculate the lacrimal gland absorbed doses.
Results
Mean absorbed dose coefficients to the kidneys, bone marrow, liver, urinary bladder, spleen, lacrimal glands, parotid, and submandibular glands were 0.81 ± 0.24, 0.02 ± 0.01, 0.13 ± 0.10, 0.27 ± 0.25, 0.16 ± 0.07, 3.62 ± 1.78, 0.21 ± 0.14, and 0.09 ± 0.07 Gy/GBq, respectively. Dose constraints for the kidneys (23 Gy) and bone marrow (2 Gy) were not reached in any patients. The absorbed dose in lacrimal glands calculated by the NURBS computational phantoms was slightly lower than the calculation based on the Cristy–Eckerman computational phantoms using OLINDA/EXM v. 1.0 by 6.37 ± 0.14%.
Conclusion
Dosimetry results in this study suggested that 177Lu-PSMA I&T treatment with higher activities and more cycles is possible without the risk of damaging normal organs in prostate cancer patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, SoerJomataram I, SIegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent. Eur Urol. 2017;71(4):618–29.
Lindenberg L, Choyke P, Dahut W. Prostate cancer imaging with novel PET tracers. Curr Urol Rep. 2016;17(3):18.
Herrmann K, Larson SM, Weber WA. Theranostic concepts: more than just a fashion trend—introduction and overview. J Nucl Med. 2017;58(Supplement 2):1S-2S.
Gomes Marin JF, Nunes RF, Coutinho AM, Zaniboni EC, Costa LB, Barbosa FG, et al. Theranostics in nuclear medicine: emerging and Re-emerging Integrated Imaging and Therapies in the Era of Precision Oncology. Radiographics. 2020;40(6):1715–40.
Acar E, Özdoğan Ö, Aksu A, Derebek E, Bekiş R, Kaya GÇ. The use of molecular volumetric parameters for the evaluation of Lu-177 PSMA I&T therapy response and survival. Ann Nucl Med. 2019;33(9):681–8.
Mair C, Warwitz B, Fink K, Scarpa L, Nilica B, Maffey-Steffan J, et al. Radiation exposure after 177Lu-DOTATATE and 177Lu-PSMA-617 therapy. Ann Nucl Med. 2018;32(7):499–502.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Babich JW, Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, Eisenhut M, Kopka K, et al. The rise of PSMA ligands for diagnosis and therapy of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2016;57(Supplement 3):79S-89S.
Herrmann K, Bluemel C, Weineisen M, Schottelius M, Wester H-J, Czernin J, et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry for a probe targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen for imaging and therapy. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(6):855–61.
Afshar-Oromieh A, Hetzheim H, Kübler W, Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, Hope TA, et al. Radiation dosimetry of 68Ga-PSMA-11 (HBED-CC) and preliminary evaluation of optimal imaging timing. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag. 2016;43(9):1611–20.
Sgouros G, Bodei L, McDevitt MR, Nedrow JR. Radiopharmaceutical therapy in cancer: clinical advances and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2020;19(9):589–608.
Bolch WE, Eckerman KF, Sgouros G, Thomas SR. MIRD pamphlet no. 21: a generalized schema for radiopharmaceutical dosimetry—standardization of nomenclature. J Nucl Med. 2009;50(3):477–84.
Sandström M, Garske-Román U, Granberg D, Johansson S, Widström C, Eriksson B, et al. Individualized dosimetry of kidney and bone marrow in patients undergoing 177Lu-DOTA-octreotate treatment. J Nucl Med. 2013;54(1):33–41.
Bergsma H, Konijnenberg MW, Van Der Zwan WA, Kam BL, Teunissen JJ, Kooij PP, et al. Nephrotoxicity after PRRT with 177Lu-DOTA-octreotate. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag. 2016;43(10):1802–11.
Ljungberg M, Celler A, Konijnenberg MW, Eckerman KF, Dewaraja YK, Sjögreen-Gleisner K. MIRD pamphlet no 26: joint EANM/MIRD guidelines for quantitative 177Lu SPECT applied for dosimetry of radiopharmaceutical therapy. J Nucl Med. 2016;57(1):151–62.
Hagmarker L, Svensson J, Rydén T, van Essen M, Sundlöv A, Gleisner KS, et al. Bone marrow absorbed doses and correlations with hematologic response during 177Lu-DOTATATE treatments are influenced by image-based dosimetry method and presence of skeletal metastases. J Nucl Med. 2019;60(10):1406–13.
Rosset A, Spadola L, Ratib O. OsiriX: an open-source software for navigating in multidimensional DICOM images. J Digit Imag. 2004;17(3):205–16.
Sorenson JA. Methods for quantitating radioactivity, in vivo, by external counting measurements: University of Wisconsin–Madison; 1971.
Thomas SR, Maxon HR, Kereiakes JG. In vivo quantitation of lesion radioactivity using external counting methods. Med Phys. 1976;3(4):253–5.
Lee C, Lodwick D, Hurtado J, Pafundi D, Williams JL, Bolch WE. The UF family of reference hybrid phantoms for computational radiation dosimetry. Phys Med Biol. 2009;55(2):339.
Stabin MG, Xu XG, Emmons MA, Segars WP, Shi C, Fernald MJ. RADAR reference adult, pediatric, and pregnant female phantom series for internal and external dosimetry. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(11):1807–13.
Stabin MG, Siegel JA. RADAR dose estimate report: a compendium of radiopharmaceutical dose estimates based on OLINDA/EXM version 20. J Nucl Med. 2018;59(1):154–60.
Valentin J. Basic anatomical and physiological data for use in radiological protection: reference values: ICRP Publication 89. Ann ICRP. 2002;32(3–4):1–277.
Hohberg M, Eschner W, Schmidt M, Dietlein M, Kobe C, Fischer T, et al. Lacrimal glands may represent organs at risk for radionuclide therapy of prostate cancer with [177Lu] DKFZ-PSMA-617. Mol Imag Biol. 2016;18(3):437–45.
Svensson J, Rydén T, Hagmarker L, Hemmingsson J, Wängberg B, Bernhardt P. A novel planar image-based method for bone marrow dosimetry in 177Lu-DOTATATE treatment correlates with haematological toxicity. EJNMMI Phys. 2016;3(1):1–12.
Parsons JT, Bova FJ, Mendenhall WM, Million R, Fitzgerald CR. Response of the normal eye to high dose radiotherapy. Oncology (Williston Park). 1996;10(6):837–47 (discussion 47).
Buchali A, Schr C. Influence of the radiation dose to salivary glands on xerostomia in patients with head and neck carcinomas. J Cancer Ther. 2013;4:188–94.
Okamoto S, Thieme A, Allmann J, D’Alessandria C, Maurer T, Retz M, et al. Radiation dosimetry for 177Lu-PSMA I&T in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: absorbed dose in normal organs and tumor lesions. J Nucl Med. 2017;58(3):445–50.
Stabin MG, Sparks RB, Crowe E. OLINDA/EXM: the second-generation personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 2005;46(6):1023–7.
Delker A, Fendler WP, Kratochwil C, Brunegraf A, Gosewisch A, Gildehaus FJ, et al. Dosimetry for 177Lu-DKFZ-PSMA-617: a new radiopharmaceutical for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imag. 2016;43(1):42–51.
Götz TI, Schmidkonz C, Lang E, Maier A, Kuwert T, Ritt P. Factors affecting accuracy of S values and determination of time-integrated activity in clinical Lu-177 dosimetry. Ann Nucl Med. 2019;33(7):521–31.
Violet J, Jackson P, Ferdinandus J, Sandhu S, Akhurst T, Iravani A, et al. Dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA-617 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: correlations between pretherapeutic imaging and whole-body tumor dosimetry with treatment outcomes. J Nucl Med. 2019;60(4):517–23.
Kamaldeep, Wanage G, Sahu SK, Maletha P, Adnan A, Suman S, et al. Examining absorbed doses of indigenously developed 177Lu-PSMA-617 in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients at baseline and during course of peptide receptor radioligand therapy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021;36(3):292–304.
Xu XG. An exponential growth of computational phantom research in radiation protection, imaging, and radiotherapy: a review of the fifty-year history. Phys Med Biol. 2014;59(18):R233.
Yamauchi M, Ishikawa M, Hoshi M. A stylized computational model of the head for the reference Japanese male. Med Phys. 2005;32(1):85–92.
Qiu R, Li J, Zhang Z, Wu Z, Zeng Z, Fan J. Photon SAF calculation based on the Chinese mathematical phantom and comparison with the ORNL phantoms. Health Phys. 2008;95(6):716–24.
Lee C, Lee C, Lodwick D, Bolch WE. NURBS-based 3-D anthropomorphic computational phantoms for radiation dosimetry applications. Radiat Prot Dosim. 2007;127(1–4):227–32.
Weineisen M, Schottelius M, Simecek J, Baum RP, Yildiz A, Beykan S, et al. 68Ga-and 177Lu-labeled PSMA I&T: optimization of a PSMA-targeted theranostic concept and first proof-of-concept human studies. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(8):1169–76.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank all staff at the Division of Nuclear Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University and King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand, for their kind support in this study. The authors also thanks Dr. Chanan Sukprakun, MD, for his valuable advice. Miss Kotchakorn Chatachot was supported by the graduate school scholarship, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chatachot, K., Shiratori, S., Chaiwatanarat, T. et al. Patient dosimetry of 177Lu-PSMA I&T in metastatic prostate cancer treatment: the experience in Thailand. Ann Nucl Med 35, 1193–1202 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-021-01659-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-021-01659-8