Abstract
Objective
In mCRPC patients treated with 223Ra, a major issue is the validation of reliable prognostic and predictive biomarkers to maximize clinical benefit and minimize toxicities and costs. Bearing in mind how changes in tALP did not meet statistical requirements as surrogate marker for survival, aim of this single-center retrospective study was to characterize the prognostic and predictive role of baseline clinical variables associated with overall survival in patients receiving 223Ra treatment.
Methods
92 consecutive CRPC patients with symptomatic bone metastases receiving 223Ra treatment were included. Available baseline clinical data relevant to the survival analysis were retrospectively collected. The primary end-point of the study was overall survival, which was established from the first 223Ra administration until date of death from any cause.
Results
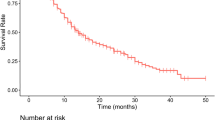
Median follow-up time from the first 223Ra administration was 6 months (range 1–31 months). The univariate analysis evaluating the prognostic value of all baseline clinical variables showed that patients’ weight, BMI, ECOG PS, Hb and tALP values were independently associated with OS. On multivariable analysis only baseline Hb value and ECOG PS remained significantly correlated with OS. To determine reliable baseline predictive factors for survival in patients receiving 223Ra treatment, we produced a predictive score. We tried all possible variable combinations, and found that the best score was obtained by combining baseline ECOG PS with Hb < 12 g/dl and PSA ≥ 20 ng/ml. This resulted in a score ranging from 0 to 4, with AUC 78.4% (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
We propose a multidimensional clinical evaluation to select those mCRPC subjects suitable to receive the maximum benefit from 223Ra treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthold DR, Pond GR, Roessner M, et al. Treatment of hormone-refractory prostate cancer with docetaxel or mitoxantrone: relationships between prostate-specific antigen, pain, and quality of life response and survival in the TAX-327 study. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2763–7. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0944.
Stein WD, Gulley JL, Schlom J, et al. Tumor regression and growth rates determined in five intramural NCI prostate cancer trials: the growth rate constant as an indicator of therapeutic efficacy. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:907–17.
Fossa SD, Vaage S, Letocha H, et al. Liposomal doxorubicin (Caelyx) in symptomatic androgen-independent prostate cancer (AIPC)—delayed response and flare phenomenon should be considered. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2002;36:34–9.
Scher HI, Heller G, Molina A. Evaluation of circulating tumor cell (CTC) enumeration as an efficacy response biomarker of overall survival (OS) in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC): planned final analysis (FA) of COA-AA-301, a randomized double-blind, placebo controlled phase III study of abiraterone acetate (AA) plus low-dose prednisone (P) post docetaxel. J Clin Oncol (Meet Abstr). 2011;29:LBA4517.
De Bono JS, Scher HI, Montgomery RB, et al. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6302–9.
Scher HI, Morris MJ, Basch E, et al. End points and outcomes in castration-resistant prostate cancer: from clinical trials to clinical practice. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3695–704.
Nilsson S, Franzen L, Parker C, et al. Bone-targeted radium-223 in symptomatic, hormone-refractory prostate cancer: a randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled phase II study. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:587–94.
Sonpavde G, Pond GR, Berry WR, et al. Serum alkaline phosphatase changes predict survival independent of PSA changes in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastasis receiving chemotherapy. Urol Oncol. 2012;30:607–13.
Fizazi K, Massard C, Smith M, et al. Bone-related parameters are the main prognostic factors for overall survival in men with bone metastases from castration resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2015;68(1):42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.10.001.
Baldari S, Boni G, Bortolus R, et al. Management of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a focus on radium-223. Opinions and suggestions from an expert multidisciplinary panel. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;113:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.03.001.
Finlay IG, Mason MD, Shelley M. Radioisotopes for the palliation of metastatic bone cancer: a systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:392–400.
Sartor O, Coleman RE, Morris MJ, et al. Baseline characteristics, number of radium-223 dichloride (radium-223) injections, and overall survival (OS) in US Expanded Access Program (EAP) and ALSYMPCA. In: 26th International prostate cancer update meeting; 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-8049(16)31349-1.
Vogelzang NJ, Fernandez DC, Morris MJ, et al. Radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) in US expanded access program (EAP). 2015 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(suppl 7; abstr 247).
Morris MJ, Sartor AO, Vogelzang NJ, et al. Effect of radium-223 dichloride (Ra-223) on pain from US EAP. 2015 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium., J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(suppl 7; abstr 160).
Yin L, Hu Q, Hartmann RW. Recent progress in pharmaceutical therapies for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(7):13958–78.
Xofigo (radium Ra 223 dichloride) injection, for intravenous use [package insert]. Wayne; Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc; 2013. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/203971lbl.pdf.
Soloway MS, Hardeman SW, Hickey D, et al. Stratification of patients with metastatic prostate cancer based on extent of disease on initial bone scan. Cancer. 1988;61(1):195–202.
Du Y, Carrio I, De Vincentis G, et al. Practical recommendations for radium-223 treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44(10):1671–8.
Suominen MI, Fagerlund KM, Rissanen JP, et al. Radium-223 inhibits osseous prostate cancer growth by dual targeting of cancer cells and bone microenvironment in mouse models. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2955.
De Vincentis G, Follacchio GA, Frantellizzi V, et al. Prostate-specific antigen flare phenomenon during 223Ra-dichloride treatment for bone metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a case report. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2016;14(5):e529–e533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2016.04.014.
Sartor O, Coleman RE, Nilsson S, et al. An exploratory analysis of alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase, and prostate-specific antigen dynamics in the phase 3 ALSYMPCA trial with radium-223. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(5):1090–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx044.
Parker C, Nilsson S, Heinrich D, et al. ALSYMPCA Investigators. Alpha emitter radium-223 and survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(3):213–23. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1213755.
Gravis G, Boher JM, Fizazi K, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in noncastrate metastatic prostate cancer: validation of the glass model and development of a novel simplified prognostic model. Eur Urol. 2015;68(2):196–204.
Nome R, Hernes E, Bogsrud TV, et al. Changes in prostate-specific antigen, markers of bone metabolism and bone scans after treatment with radium-223. Scand J Urol. 2015;49(3):211–7.
Etchebehere EC, Araujo JC, Milton DR, et al. Skeletal tumor burden on baseline 18F-fluoride PET/CT predicts bone marrow failure after 223Ra therapy. Clin Nucl Med. 2016;41(4):268–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Human and animal rights statement
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frantellizzi, V., Farcomeni, A., Follacchio, G.A. et al. A 3-variable prognostic score (3-PS) for overall survival prediction in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with 223Radium-dichloride. Ann Nucl Med 32, 142–148 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-017-1228-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-017-1228-6