Abstract
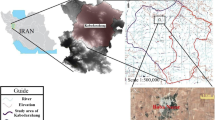
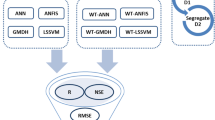
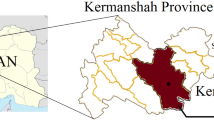
The main objective of this study is to predict groundwater levels (GWLs) using modified hybrid algorithms with two levels of improvement. The observed GWLs, precipitation, and temperature were used as input variables in the prediction algorithms. Two widely used machine learning algorithms, namely support vector machine (SVM) and random forest (RF), were used first as the base algorithm, then the wavelet transform (WT), with seven wavelet types, was employed as a preprocessing method. SVM and RF combined WT, namely W-SVM and W-RF, respectively, constructed the first-level hybrid algorithm, taking all of the components together. In addition, the approximation and detail components were separately used to construct the second-level hybrid algorithm, coupling SVM and RF with WT, namely W-SVM-D and W-RF-D, respectively. Four statistical metrics were used to evaluate and validate the predictive accuracies of algorithms. According to the obtained results, The W-SVM-D and W-RF-D hybrid algorithms demonstrated the highest predictive accuracies of GWLs, followed by the first-level hybrid and single algorithms. In addition, the mother wavelet types affected the prediction accuracy of W-SVM and W-RF algorithms, while W-SVM-D and W-RF-D algorithms showed the highest predictive accuracies of GWLs for all the selected wavelets. It is suggested that the modified hybrid model can be effectively used to predict groundwater levels.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Adamowski J, Chan HF (2011) A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J Hydrol 407:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.06.013
Alizamir M, Kisi O, Zounemat-Kermani M (2018) Modelling long-term groundwater fluctuations by extreme learning machine using hydro-climatic data. Hydrolog Sci J 63(1):63–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2017.1410891
Barzegar R, Fijani E, Moghaddam AA, Tziritis E (2017) Forecasting of groundwater level fluctuations using ensemble hybrid multi-wavelet neural network-based models. Sci Total Environ 599–600:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.189
Brédy J, Gallichand J, Celicourt P, Gumiere SJ (2020) Water table depth forecasting in cranberry fields using two decision-tree-modeling approaches. Agr Water Manage 233:106090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106090
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Cannas B, Fanni A, See L, Sias G (2006) Data preprocessing for river flow forecasting using neural networks: wavelet transforms and data partitioning. Phys Chem Earth 31(18):1164–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.03.020
Du K, Zhao Y, Lei J (2017) The incorrect usage of singular spectral analysis and discrete wavelet transform in hybrid models to predict hydrological time series. J Hydrol 552:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.019
Ebrahimi H, Rajaee T (2017) Simulation of groundwater level variations using wavelet combined with neural network, linear regression and support vector machine. Glob Planet Chang 148:181–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.11.014
Ghazi B, Jeihouni E, Kalantari Z (2021) Predicting groundwater level fluctuations under climate change scenarios for Tasuj plain. Iran Arab J Geosci 14(2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06508-6
Grossmann A, Morlet J (1984) Decomposition of hardy functions into square integrable wavelets of constant shape. SIAM J Math Anal 15(4):723–736. https://doi.org/10.1137/0515056
Iqbal M, Naeem UA, Ahmad A, Rehman H, Ghani U, Farid T (2020) Relating groundwater levels with meteorological parameters using ANN technique. Measurement 166:108163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108163
Jafari H, Rajaee T, Kisi O (2020) Improved water quality prediction with hybrid wavelet-genetic programming model and shannon entropy. Nat Resour Res 29:3819–3840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09702-7
Jiang Z, Yang S, Liu Z, Xu Y, Shen T, Qi S, Pang Q, Xu J, Liu F, Xu T (2022) Can ensemble machine learning be used to predict the groundwater level dynamics of farmland under future climate: a 10-year study on Huaibei plain. Environ Sci Pollut R 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18809-8
Koch J, Berger H, Henriksen HJ, Sonnenborg TO (2019) Modelling of the shallow water table at high spatial resolution using random forests. Hydrol Earth Syst Sc 23(11):4603–4619. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-2019-212
Kumar D, Roshni T, Singh A, Jha MK, Samui P (2020) Predicting groundwater depth fluctuations using deep learning, extreme learning machine and Gaussian process: a comparative study. Earth Sci Inform 13(4):1237–1250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00508-y
Lee S, Lee KK, Yoon H (2019) Using artificial neural network models for groundwater level forecasting and assessment of the relative impacts of influencing factors. Hydrogeol J 27(2):567–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1866-3
Malekzadeh M, Kardar S, Saeb K, Shabanlou S, Taghavi L (2019) A novel approach for prediction of monthly ground water level using a hybrid wavelet and non-tuned self-adaptive machine learning model. Water Resour Manag 33(4):1609–1628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-2193-8
Mohapatra JB, Jha P, Jha MK, Biswal S (2021) Efficacy of machine learning techniques in predicting groundwater fluctuations in agro-ecological zones of India. Sci Total Environ 785:147319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147319
Moosavi V, Vafakhah M, Shirmohammadi B, Behnia N (2013) A wavelet-ANFIS hybrid model for groundwater level forecasting for different prediction periods. Water Resour Manag 27(5):1301–1321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0239-2
Mosavi A, Sajedi Hosseini F, Choubin B, Goodarzi M, Dineva AA, Rafiei Sardooi E (2021) Ensemble boosting and bagging based machine learning models for groundwater potential prediction. Water Resour Manag 35(1):23–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02704-3
Norouzi H, Shahmohammadi-Kalalagh S (2019) Locating groundwater artificial recharge sites using random forest: a case study of Shabestar region. Iran Environ Earth Sci 78(13):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8381-2
Nourani V, Baghanam AH, Adamowski J, Kisi O (2014) Applications of hybrid wavelet–artificial intelligence models in hydrology: a review. J Hydrol 514:358–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.03.057
Panahi M, Sadhasivam N, Pourghasemi HR, Rezaie F, Lee S (2020) Spatial prediction of groundwater potential mapping based on convolutional neural network (CNN) and support vector regression (SVR). J Hydrol 588:125033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125033
Pham QB, Kumar M, Di Nunno F, Elbeltagi A, Granata F, Islam ARM, Talukdar S, Nguyen XC, Ahmed AN, Anh DT (2022) Groundwater level prediction using machine learning algorithms in a drought-prone area. Neural Computi Appl 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07009-7
Rahman AS, Hosono T, Quilty JM, Das J Basak A (2020) Multiscale groundwater level forecasting: coupling new machine learning approaches with wavelet transforms. Adv Water Resour 141:103595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103595
Rajaee T, Ebrahimi H, Nourani V (2019) A review of the artificial intelligence methods in groundwater level modeling. J Hydrol 572:336–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.037
Ranjbar A, Mahjouri N (2019) Multi-objective freshwater management in coastal aquifers under uncertainty in hydraulic parameters. Nat Resour Res 1-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-019-09585-3
Rezaie-balf M, Naganna SR, Ghaemi A, Deka PC (2017) Wavelet coupled MARS and M5 model tree approaches for groundwater level forecasting. J Hydrol 553:356–373
Roy DK, Biswas SK, Saha KK, Murad KFI (2021) Groundwater level forecast via a discrete space-state modelling approach as a surrogate to complex groundwater simulation modelling. Water Resour Manag 35(6):1653–1672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02787-6
Sachdeva S, Kumar B (2021) Comparison of gradient boosted decision trees and random forest for groundwater potential mapping in Dholpur (Rajasthan), India. Stoch Env Res Risk A 35(2):287–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01891-0
Sapitang M, Ridwan WM, Ahmed AN, Fai CM, El-Shafie A (2021) Groundwater level as an input to monthly predicting of water level using various machine learning algorithms. Earth Sci Inform 14(3):1269–1283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00654-x
Shiri J, Kisi O, Yoon H, Lee KK, Nazemi AH (2013) Predicting groundwater level fluctuations with meteorological effect implications—a comparative study among soft computing techniques. Comput Geosci 56:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.01.007
Wang X, Liu T, Zheng X, Peng H, Xin J, Zhang B (2018) Short-term prediction of groundwater level using improved random forest regression with a combination of random features. Appl Water Sci 8(5):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0742-6
Wen X, Lu J, Wu J, Lin Y, Luo Y (2019) Influence of coastal groundwater salinization on the distribution and risks of heavy metals. Sci Total Environ 652:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.250
Wu C, Zhang X, Wang W, Lu C, Zhang Y, Qin W, Tick GR, Liu B, Shu L (2021) Groundwater level modeling framework by combining the wavelet transform with a long short-term memory data-driven model. Sci Total Environ 783:146948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146948
Yadav B, Gupta PK, Patidar N, Himanshu SK (2020) Ensemble modelling framework for groundwater level prediction in urban areas of India. Sci Total Environ 712:135539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135539
Yoon H, Jun SC, Hyun Y, Bae GO, Lee KK (2011) A comparative study of artificial neural networks and support vector machines for predicting groundwater levels in a coastal aquifer. J Hydrol 396(1–2):128–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.11.002
Yosefvand F, Shabanlou S (2020) Forecasting of groundwater level using ensemble hybrid wavelet–self-adaptive extreme learning machine-based models. Nat Resour Res 29(5):3215–3232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09642-2
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the anonymous reviewers and the editors, who significantly improved the quality of the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by S&T Program of Hebei (D2019403194).
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, A., Chen, Y., Li, D. et al. Prediction of groundwater level using the hybrid model combining wavelet transform and machine learning algorithms. Earth Sci Inform 15, 1951–1962 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00853-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00853-0