Abstract
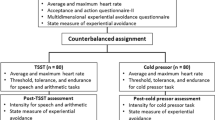
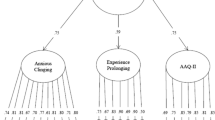
Because experiential avoidance is considered by some to be the root of most forms of psychopathology, it is often a primary intervention and research target. Yet, the current literature is limited by its assessment and conceptualization of experiential avoidance as a trait variable. Little attention is paid to how it operates as a context-dependent state-based factor. Further, more information is needed to determine how experiential avoidance relates to affective states in specific contexts. Links have been established between experiential avoidance and negative affect intensity in the contextual behavior science (CBS) literature. Studying more specific elements of state-based experiential avoidance as potential mediators of negative affect is an important next step. Thus, the overarching goal of the present study was to measure the indirect effect of state experiential avoidance on the relationship between trait experiential avoidance and dimensions of negative affect following exposure to several challenging tasks. Participants (N = 160) in the current study completed both the cold pressor test and Trier Social Stress Test (TSST) in a counterbalanced order. Non-parametric bootstrapping analyses revealed a significant indirect effect of state experiential avoidance on negative affect for the TSST condition. As predicted, these effects were strongest under interpersonal contexts rather than when physiological discomfort was evoked. Implications for conceptualizing experiential avoidance as state and trait and how these relate to CBS interventions are proposed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset generated during the study is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Anderson, N. L., & Crowther, J. H. (2012). Using the experiential avoidance model of non-suicidal self-injury: Understanding who stops and who continues. Archives of Suicide Research, 16, 124–134.
Asher, M., Hofmann, S. G., & Aderka, I. M. (2021). I’m not feeling it: Momentary experiential avoidance and social anxiety among individuals with social anxiety disorder. Behavior Therapy, 52(1), 183–194.
Bond, F. W., Hayes, S. C., Baer, R. A., Carpenter, K. M., Guenole, N., Orcutt, H. K., Waltz, T., & Zettle, R. D. (2011). Preliminary psychometric properties of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire – II: A revised measure of psychological flexibility and experiential avoidance. Behavior Therapy, 42, 676–688.
Bordieri, M. J., Tull, M. T., McDermott, M. J., & Gratz, K. L. (2014). The moderating role of experiential avoidance in the relationship between posttraumatic stress disorder symptom severity and cannabis dependence. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 3, 273–278.
Brown, B. T. (2018). The relationship between experiential avoidance and physiological reactivity. Brigham Young University.
Buckner, J. D., Zvolensky, M. J., Farris, S. G., & Hogan, J. (2014). Social anxiety and coping motives for cannabis use: The impact of experiential avoidance. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 28, 568–574.
Buckner, J. D., Farris, S. G., Zvolensky, M. J., Shah, S. M., Leventhal, A. M., Minnix, J. A., & Schmidt, N. B. (2015). Dysphoria and smoking among treatment seeking smokers: The role of smoking-related inflexibility/avoidance. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 41, 45–51.
Cheavens, J. S., & Heiy, J. (2011). The differential roles of affect and avoidance in major depressive and borderline personality disorder symptoms. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 30, 441–457.
Ciarrochi, J., Kashdan, T. B., Leeson, P., Heaven, P., & Jordan, C. (2011). On being aware and accepting: A one-year longitudinal study into adolescent well-being. Journal of Adolescence, 34, 695–703.
Cochrane, A., Barnes-Holmes, D., Barnes-Holmes, Y., Stewart, I., & Luciano, C. (2007). Experiential avoidance and aversive visual images: Response delays and event related potentials on a simple matching task. Behavior Research and Therapy, 45, 1379–1388.
Farris, S. G., Zvolensky, M. J., & Schmidt, N. B. (2015). Smoking-specific experiential avoidance cognition: Explanatory relevance to pre- and post-cessation nicotine withdrawal, craving, and negative affect. Addictive Behaviors, 44, 58–64.
Faul, F., Erdfelner, E., Lang, A. G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39, 175–191.
Feldner, M. T., Zvolensky, M. J., Eifert, G. H., & Spira, A. P. (2003). Emotional avoidance: An experimental test of individual differences and response suppression using biological challenge. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 41, 403–411.
Gámez, W., Chmielewski, M., Kotov, R., Ruggero, C., & Watson, D. (2011). Development of a measure of experiential avoidance: The Multidimensional Experiential Avoidance Questionnaire. Psychological Assessment, 23, 692–713.
Gámez, W., Chmielewski, M., Kotov, R., Ruggero, C., Suzuki, N., & Watson, D. (2014). The brief experiential avoidance questionnaire: Development and initial validation. Psychological Assessment, 26, 35–45.
Ghiasi, S., Greco, A., Barbieri, R., Scilingo, E. P., & Valenza, G. (2020). Assessing autonomic function from electrodermal activity and heart rate variability during cold-pressor test and emotional challenge. Scientific reports, 10, 5406.
Goodman, F. R., Larrazabal, M. A., West, J. T., & Kashdan, T. B. (2019). Experiential avoidance. In B. O. Olatunji (Ed.), The Cambridge handbook of anxiety and related disorders (pp. 255–281). Cambridge University Press.
Greer, R. D. (2020). The Selector in Behavior Selection. Psychological Record, 70, 543–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40732-020-00385-3
Hayes, A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Communication Monographs, 76, 408–420.
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach (2nd ed.). New York: The Guilford Press.
Hayes, S. C., Wilson, K. G., Gifford, E. V., Follette, V. M., & Strosahl, K. (1996). Experiential avoidance and behavioral disorders: A functional dimensional approach to diagnosis and treatment. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64, 1152.
Helsen, K., Goubert, L., Peters, M. L., & Vlaeyen, J. W. (2011). Observational learning and pain-related fear: An experimental study with colored cold pressor tasks. The Journal of Pain, 12(12), 1230–1239.
Hooper, N., Stewart, I., Duffy, C., Freegard, G., & McHugh, L. (2012). Modelling the direct and indirect effects of thought suppression on behavioral preference. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 1, 73–82.
Jacob, G. A., Ower, N., & Buchholz, A. (2013). The role of experiential avoidance, psychopathology, and borderline personality features in experiencing positive emotions: A path analysis. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 44, 61–68.
Karekla, M., & Panayiotou, G. (2011). Coping and experiential avoidance: Unique or overlapping constructs? Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 42, 163–170.
Karekla, M., Forsyth, J. P., & Kelly, M. M. (2004). Emotional avoidance and panicogenic responding to a biological challenge procedure. Behavior Therapy, 35, 725–746.
Kashdan, T. B., Barrios, V., Forsyth, J. P., & Steger, M. F. (2006). Experiential avoidance as a generalized psychological vulnerability: Comparisons with coping and emotion regulation strategies. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 44, 1301–1320.
Kashdan, T. B., Farmer, A. S., Adams, L. M., Ferssizidis, P., McKnight, P. E., & Nezlek, J. B. (2013). Distinguishing healthy adults from people with social anxiety disorder: Evidence for the value of experiential avoidance and positive emotions in everyday social interactions. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 122, 645.
Kashdan, T. B., Goodman, F. R., Machell, K. A., Kleiman, E. M., Monfort, S. S., Ciarrochi, J., & Nezlek, J. B. (2014). A contextual approach to experiential avoidance and social anxiety: Evidence from an experimental interaction and daily interactions of people with social anxiety disorder. Emotion, 14, 769–781.
Kingston, J., Clarke, S., & Remington, B. (2010). Experiential avoidance and problem behavior: A mediational analysis. Behavior Modification, 34, 145–163.
Kirk, A., Meyer, J. M., Whisman, M. A., Deacon, B. J., & Arch, J. J. (2019). Safety behaviors, experiential avoidance, and anxiety: A path analysis approach. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 64, 9–15.
Kirschbaum, C., Pirke, K. M., & Hellhammer, D. H. (1993). The ‘trier social stress test’ – a tool for investigating psychobiological stress responses in a laboratory setting. Neuropsychobiology, 28, 76–81.
Levin, M. E., Lillis, J., & Hayes, S. C. (2012a). When is online pornography viewing problematic among college males? examining the moderating role of experiential avoidance. Sexual Addiction & Compulsivity, 19, 168–180.
Levin, M. E., Lillis, J., Seeley, J., Hayes, S. C., Pistorello, J., & Biglan, A. (2012b). Exploring the relationship between experiential avoidance, alcohol use disorders, and alcohol-related problems among first-year college students. Journal of American College Health, 60, 443–448.
Levin, M. E., Krafft, J., Pierce, B., & Potts, S. (2018). When is experiential avoidance harmful in the moment? Examining global experiential avoidance as a moderator. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 61, 158–163.
Levin, M. E., Lee, E. B., & Twohig, M. P. (2019). The role of experiential avoidance in problematic pornography viewing. The Psychological Record, 69, 1–12.
Little, T. D., Card, N. A., Bovaird, J. A., Preacher, K. J., & Crandall, C. S. (2007). Structural equation modeling of mediation and moderation with contextual factors. Modeling Contextual Effects in Longitudinal Studies, 1, 207–230.
Litwin, R., Goldbacher, E. M., Cardaciotto, L., & Gambrel, L. E. (2017). Negative emotions and emotional eating: The mediating role of experiential avoidance. Eating and Weight Disorders, 22, 97–104.
López, J. C., Ruiz, F. J., Feder, J., Barbero Rubio, A., Suárez Aguirre, J. J., Rodríguez, J. A., & Luciano, C. (2010). The role of experiential avoidance in the performance on a high cognitive demand task. International Journal of Psychology and Psychological Therapy, 10, 475–488.
Luoma, J. B., Pierce, B., & Levin, M. E. (2020). Experiential avoidance and negative affect as predictors of daily drinking. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 34, 421.
Machell, K. A., Goodman, F. R., & Kashdan, T. B. (2015). Experiential avoidance and well-being: A daily diary analysis. Cognition and Emotion, 29, 351–359.
Moroz, M., & Dunkley, D. M. (2019). Self-critical perfectionism, experiential avoidance, and depressive and anxious symptoms over two years: A three-wave longitudinal study. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 112, 18–27.
Palmeira, L., Cunha, M., Pinto-Gouveia, J., Carvalho, S., & Lillis, J. (2016). New developments in the assessment of weight-related experiential avoidance (AAQW-revised). Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 5, 193–200.
Pavlacic, J. M., Schulenberg, S. E., & Buchanan, E. M. (2021). Experiential avoidance and meaning in life as predictors of valued living: A daily diary study. Journal of Prevention and Health Promotion, 2, 135–159.
Riley, B. (2014). Experiential avoidance mediates the association between thought suppression and mindfulness with problem gambling. Journal of Gambling Studies, 30, 163–171.
Roche, B., Forsyth, J. P., & Maher, E. (2007). The impact of demand characteristics on brief acceptance-and control-based interventions for pain tolerance. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 14(4), 381–393.
Rochefort, C., Baldwin, A. S., & Chmielewski, M. (2018). Experiential avoidance: An examination of the construct validity of the AAQ-II and MEAQ. Behavior Therapy, 49, 435–449.
Salters-Pedneault, K., & Diller, J. W. (2013). A preliminary study of anxiety, negative affect, experiential avoidance, and delaying of aversive events. Behaviour Change, 30, 241–248.
Schönbrodt, F. D., & Perugini, M. (2013). At what sample size do correlations stabilize? Journal of Research in Personality, 47, 609–612.
Shahar, B., & Herr, N. R. (2011). Depressive symptoms predict inflexibly high levels of experiential avoidance in response to daily negative affect: A daily diary study. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 49, 676–681.
Sharp, C., Kalpakci, A., Mellick, W., Venta, A., & Temple, J. R. (2015). First evidence of a prospective relation between avoidance of internal states and borderline personality disorder features in adolescents. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 24, 283–290.
Shimoda, Y., Ishizu, K., & Ohtsuki, T. (2018). The reciprocal relations between experiential avoidance and social anxiety among early adolescents: A prospective cohort study. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 10, 115–119.
Shorey, R. C., Gawrysiak, M. J., Elmquist, J., Brem, M., Anderson, S., & Stuart, G. L. (2017). Experiential avoidance, distress tolerance, and substance use cravings among adults in residential treatment for substance use disorders. Journal of Addictive Diseases, 36, 151–157.
Spinhoven, P., Drost, J., de Rooij, M., van Hemert, A. M., & Penninx, B. W. (2014). A longitudinal study of experiential avoidance in emotional disorders. Behavior Therapy, 45, 840.
Stotts, A. L., Vujanovic, A., Heads, A., Suchting, R., Green, C. E., & Schmitz, J. M. (2015). The role of avoidance and inflexibility in characterizing response to contingency management for cocaine use disorders: A secondary profile analysis. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 29, 408–413.
Tyndall, I., Waldeck, D., Pancani, L., Whelan, R., Roche, B., & Dawson, D. L. (2019). The acceptance and action questionnaire-II (AAQ-II) as a measure of experiential avoidance: Concerns over discriminant validity. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 12, 278–284.
Wang, Y., Qi, Z., Hofmann, S. G., Si, M., Liu, X., & Xu, W. (2019). Effect of acceptance versus attention on pain tolerance: Dissecting two components of mindfulness. Mindfulness, 10, 1352–1359.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54, 1063–1070.
Wetterneck, C. T., Burgess, A. J., Short, M. B., Smith, A. H., & Cervantes, M. E. (2012). The role of sexual compulsivity, impulsivity, and experiential avoidance in internet pornography use. The Psychological Record, 62, 3–18.
Wolgast, M. (2014). What does the acceptance and action questionnaire (AAQ-II) really measure? Behavior Therapy, 45, 831–839.
Zettle, R. D., Barner, S. L., Gird, S. R., Boone, L. T., Renollet, D. L., & Burdsal, C. A. (2012). A psychological biathlon: The relationship between level of experiential avoidance and perseverance on two challenging tasks. The Psychological Record, 62, 433–445.
Zvolensky, M. J., Vujanovic, A. A., Bernstein, A., & Leyro, T. (2010). Distress tolerance: Theory, measurement, and relations to psychopathology. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 19, 406–410.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan student award. This research was also supported by the Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Academic Affiliations Advanced Fellowship Program in Mental Illness Research and Treatment, and the Department of Veterans Affairs Portland Health Care System Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Center (MIRECC). The contents do not represent the views of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government. Since Dr. Lewis is an employee of the U.S. Government and contributed to the manuscript “The Indirect Effects of State Experiential Avoidance on Trait Experiential Avoidance and Negative Affect in the Moment” as part of her official duties, the work is not subject to U.S. copyright.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, M.M., Naugle, A.E., Katte, K. et al. The indirect effects of state experiential avoidance on trait experiential avoidance and negative affect in the moment. Curr Psychol 43, 6284–6296 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04798-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04798-5