Abstract
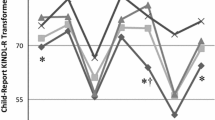
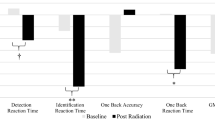
Several studies have emphasized the need for comprehensive neuropsychological assessment in pediatric cancer. To date, no study has analyzed Executive functions (EF) in children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) undergo treatment by means of both the Childhood Executive Functioning Inventory (CHEXI), parent form and performance-based measures. The aims of the present study were: (1) to explore the sensitivity of ratings vs. cognitive measures of EF to identify executive functions deficits in children with ALL and (2) to analyze the relationship between the parent-rated data and performance-based measures of EF in children with ALL. We assessed EF in typically developing (TD) children (n = 70) and children with ALL (n = 20) aged 6 to 12 years by means of performance-based measures of EFs (including working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibition) and the CHEXI parent form, also including IQ, depression, and anxiety measures. When controlling for age, IQ, depression and anxiety, children with ALL exhibited greater difficulties than their TD peers on working memory, cognitive flexibility (spontaneous and reactive) and inhibitory control tasks. Equally, at a behavioral level, differences between groups were observed regarding the CHEXI’s inhibition and WM subscales. However, the CHEXI parent related poorly to EF performance-based measures, supporting earlier research that suggests that ratings and laboratory measures would assess distinct underlying mental constructs. Overall, our results stress the importance of considering both measures when assessing EF in children with ALL as they would offer distinctive but relevant information. The clinical implications of findings are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aguilar-Alonso, Á., & Moreno-González, V. (2012). Neuropsychological differences between samples of dyslexic and reader children by means of NEPSY. The UB Journal of Psychology, 42, 35–50.
Aguilar-Alonso, Á., Torres-Viñals, M., & Aguilar-Mediavilla, E. M. (2014). The first Spanish version of the NEPSY for the assessment of the neuropsychological development in a sample of Spanish children. The UB Journal of Psychology, 44(2), 185–198 Retrieved from https://www.redalyc.org/html/970/97036175006/.
American Psychological Association. (2010). American Psychological Association ethical principles of psychologists and code of conduct. Recuperado de http://www.apa.org/ethics/code/index.aspx
Anderson, V., Godber, T., Smibert, E., & Ekert, H. (1997). Neurobehavioral sequelae following cranial irradiation and chemotherapy in children: An analysis of risk factors. Pediatric Rehabilitation, 1(2), 63–76.
Anderson, V. A., Anderson, P., Northam, E., Jacobs, R., & Mikiewicz, O. (2002). Relationships between cognitive and behavioral measures of executive function in children with brain disease. Child Neuropsychology, 8(4), 231–240.
Annett, R. D., Hile, S., Bedrick, E., Kunin-Batson, A. S., Krull, K. R., Embry, L., MacLean Jr., W. E., & Noll, R. B. (2015). Neuropsychological functioning of children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Impact of whole brain radiation therapy. Psycho-Oncology, 24(2), 181–189.
Arán Filippetti, V. (2013). Structure and invariance of executive functioning tasks across socioeconomic status: Evidence from Spanish-speaking children. The Spanish Journal of Psychology, e101, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1017/sjp.2013.102.
Arán Filippetti, V., & Allegri, R. F. (2011). Verbal fluency in Spanish-speaking children: Analysis model according to task type, clustering, and switching strategies and performance over time. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 25, 413–436. https://doi.org/10.1080/13854046.2011.559481.
Arán Filippetti, V., & Richaud, M. C. (2017). A structural equation modeling of executive functions, IQ and mathematical skills in primary students: Differential effects on number production, mental calculus and arithmetical problems. Child Neuropsychology, 23, 864–888. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297049.2016.1199665.
Ardila, A., & Rosselli, M. (1994). Development of language, memory, and visuospatial abilities in 5- to 12-year-old children using a neuropsychological battery. Developmental Neuropsychology, 10, 97–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565649409540571.
Ashford, J., Schoffstall, C., Reddick, W. E., Leone, C., Laningham, F. H., Glass, J. O., Pei, D., Cheng, C., Pui, C. H., & Conklin, H. M. (2010). Attention and working memory abilities in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer, 116(19), 4638–4645.
Balsamo, L. M., Mitchell, H. R., Ross, W., Metayer, C., Hardy, K. K., & Kadan-Lottick, N. S. (2019). Monitoring neurocognitive functioning in childhood cancer survivors: Evaluation of CogState computerized assessment and the behavior rating inventory of executive function (BRIEF). BMC Psychology, 7(1), 26.
Benton, A. L., & Hamsher, K. (1989). Multilingual Aphasia Examination manual. Iowa City, IA: AJA Associates.
Buizer, A. I., de Sonneville, L. M., & Veerman, A. J. (2009). Effects of chemotherapy on neurocognitive function in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A critical review of the literature. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 52(4), 447–454.
Calonge, I. (2009). Qué medimos y cómo medimos. La evaluación de las secuelas neurocognitivas. Psicooncología, 6(2–3), 291–309.
Camerota, M., Willoughby, M. T., Kuhn, L. J., & Blair, C. B. (2018). The childhood executive functioning inventory (CHEXI): Factor structure, measurement invariance, and correlates in US preschoolers. Child Neuropsychology, 24(3), 322–337.
Campbell, L., Scaduto, M., Van Slyke, D., Niarhos, F., Whitlock, J. y Compas, B. (2009). Executive function, coping, and behavior in survivors of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 34(3), 317–327.
Caron, J. E., Krull, K. R., Hockenberry, M., Jain, N., Kaemingk, K., & Moore, I. M. (2009). Oxidative stress and executive function in children receiving chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 53(4), 551–556.
Catale, C., Lejeune, C., Merbah, S., & Meulemans, T. (2011). Le CHEXI: Présentation d’une nouvelle mesure d’évaluation comportementale du fonctionnement exécutif chez l’enfant de 5 à 7 ans. Approche Neuropsychologique des Apprentissages chez l’Enfant, 115, 487–493.
Catale, C., Lejeune, C., Merbah, S., & Meulemans, T. (2013). French adaptation of the childhood executive functioning inventory (CHEXI). European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 29(2), 149–155.
Catale, C., Meulemans, T., & Thorell, L. B. (2015). The childhood executive function inventory: Confirmatory factor analyses and cross-cultural clinical validity in a sample of 8-to 11-year-old children. Journal of Attention Disorders, 19(6), 489–495.
Conklin, H. M., Ashford, J. M., Howarth, R. A., Merchant, T. E., Ogg, R. J., Santana, V. M., & Xiong, X. (2012). Working memory performance among childhood brain tumor survivors. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 18(6), 996–1005.
Conklin, H. M., Salorio, C. F., & Slomine, B. S. (2008). Working memory performance following paediatric traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 22(11), 847–857.
Davidson, F., Cherry, K., & Corkum, P. (2016). Validating the behavior rating inventory of executive functioning for children with ADHD and their typically developing peers. Applied Neuropsychology: Child, 5(2), 127–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622965.2015.1021957.
de Vries, M., de Ruiter, M. A., Oostrom, K. J., Schouten-Van Meeteren, A. Y. N., Maurice-Stam, H., Oosterlaan, J., & Grootenhuis, M. A. (2018). The association between the behavior rating inventory of executive functioning and cognitive testing in children diagnosed with a brain tumor. Child Neuropsychology, 24(6), 844–858.
Del Barrio, V., & Carrasco, M.A. (2004). Manual del Inventario de depresión infantil CDI. Adaptación española. Madrid: TEA.
Edelmann, M. N., Krull, K. R., Liu, W., Glass, J. O., Ji, Q., Ogg, R. J., Sabin, N. D., Srivastava, D. K., Robison, L. L., Hudson, M. M., & Reddick, W. E. (2014). Diffusion tensor imaging and neurocognition in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Brain, 137(11), 2973–2983.
ElAlfy, M., Ragab, I., Azab, I., Amin, S., & Abdel-Maguid, M. (2014). Neurocognitive outcome and white matter anisotropy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia survivors treated with different protocols. Pediatric Hematology and Oncology, 31(2), 194–204.
Ellenberg, L., Liu, Q., Gioia, G., Yasui, Y., Packer, R. J., Mertens, A., Donaldson, S. S., Stovall, M., Kadan-Lottick, N., Armstrong, G., Robison, L. L., & Zeltzer, L. K. (2009). Neurocognitive status in long-term survivors of childhood CNS malignancies: A report from the childhood Cancer survivor study. Neuropsychology, 23(6), 705–717.
Garon, N. M., Piccinin, C., & Smith, I. M. (2016). Does the BRIEF-P predict specific executive function components in preschoolers? Applied Neuropsychology: Child, 5, 110–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622965.2014.1002923.
Gioia, G. A., Isquith, P. K., Guy, S. A., & Kenworthy, L. (2017a). BRIEF-2. Evaluación Conductual de la Función Ejecutiva. Manual de aplicación, corrección e interpretación (M. J. Maldonado, M. C. Fournier, R. Martínez-Arias, J. González-Marquéz, J. M. Espejo-Saavedra y P. Santamaría, adaptadores). Madrid: TEA Ediciones.
Gioia, G. A., Isquith, P. K., Guy, S. A., & Kenworthy, L. (2017b). BRIEF-2. Evaluación Conductual de la Función Ejecutiva. Manual técnico (M. J. Maldonado, M. C. Fournier, R. Martínez-Arias, J. González-Marquéz, J. M. Espejo-Saavedra y P. Santamaría, adaptadores). Madrid: TEA Ediciones.
Gioia, G. A., Isquith, P. K., Guy, S. C., & Kenworthy, L. (2000). Test review behavior rating inventory of executive function. Child Neuropsychology, 6(3), 235–238.
Gutierrez, M., Arán Filippetti, V., & Lemos, V. (in press). The childhood executive functioning inventory (CHEXI) parent and teacher form: Factor structure and cognitive correlates in Spanish-speaking children from Argentina. Developmental Neuropsychology.
Harman, J. L., Molnar Jr., A. E., Cox, L. E., Jurbergs, N., Russell, K. M., Wise, J., & Willard, V. W. (2019). Parent-reported executive functioning in young children treated for cancer. Child Neuropsychology, 25(4), 548–560.
Harman, J. L., Wise, J., & Willard, V. W. (2018). Early intervention for infants and toddlers: Applications for pediatric oncology. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 65(5), e26921.
Holland, A. A., Clem, M. A., Lampson, E., & Stavinoha, P. L. (2020). Auditory attention late effects in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Child Neuropsychology, 1–16.
Hosseini, S. H., Hoeft, F., & Kesler, S. R. (2012). GAT: A graph-theoretical analysis toolbox for analyzing between-group differences in large-scale structural and functional brain networks. PLoS One, 7(7), e40709.
Howarth, R. A., Ashford, J. M., Merchant, T. E., Ogg, R. J., Santana, V., Wu, S., Xiong, X., & Conklin, H. M. (2013). The utility of parent report in the assessment of working memory among childhood brain tumor survivors. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society: JINS, 19(4), 380–389.
Howarth, R. A., Conklin, H. M., Ashford, J. M., Skinner, T. N., Merchant, T. E., Ogg, R. J., et al. (2011). Performance-and rater-based measures of working memory among childhood brain tumor survivors. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 25(4), 587–587.
Insel, K. C., Hockenberry, M. J., Harris, L. L., Koerner, K. M., Lu, Z., Adkins, K. B., et al. (2017, July). Decline in verbal working memory during treatment and association with achievement among children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncology Nursing Forum, 44(4), 503–511.
Iyer, N. S., Balsamo, L. M., Bracken, M. B., & Kadan-Lottick, N. S. (2015). Chemotherapy-only treatment effects on long-term neurocognitive functioning in childhood ALL survivors: A review and meta-analysis. Blood, 126(3), 346–353.
Jain, N., Brouwers, P., Okcu, M. F., Cirino, P. T., & Krull, K. R. (2009). Sex-specific attention problems in long-term survivors of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer: Interdisciplinary International Journal of the American Cancer Society, 115(18), 4238–4245.
Jones, R. M., & Pattwell, S. S. (2019). Future considerations for pediatric cancer survivorship: Translational perspectives from developmental neuroscience. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 38, 100657.
Kahalley, L. S., Conklin, H. M., Tyc, V. L., Hudson, M. M., Wilson, S. J., Wu, S., Xiong, X., & Hinds, P. S. (2013). Slower processing speed after treatment for pediatric brain tumor and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Psycho-Oncology, 22(9), 1979–1986.
Kayhan. (2010). A validation study of the executive functioning inventory: Behavioral correlates of executive functioning. Master thesis: Bogazici University, Turkey.
Kesler, S. R., Gugel, M., Huston-Warren, E., & Watson, C. (2016). Atypical structural connectome organization and cognitive impairment in young survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Brain Connectivity, 6(4), 273–282.
Kesler, S. R., Gugel, M., Pritchard-Berman, M., Lee, C., Kutner, E., Hosseini, S. H., et al. (2014). Altered resting state functional connectivity in young survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 61(7), 1295–1299.
Kesler, S. R., Lacayo, N. J., & Jo, B. (2011). A pilot study of an online cognitive rehabilitation program for executive function skills in children with cancer-related brain injury. Brain Injury, 25(1), 101–112.
Kesler, S. R., Ogg, R., Reddick, W. E., Phillips, N., Scoggins, M., Glass, J. O., Cheung, Y. T., Pui, C. H., Robison, L. L., Hudson, M. M., & Krull, K. R. (2018). Brain network connectivity and executive function in long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Brain Connectivity, 8(6), 333–342.
Kingma, A., Van Dommelen, R. I., Mooyaart, E. L., Wilmink, J. T., Deelman, B. G., & Kamps, W. A. (2002). No major cognitive impairment in young children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia using chemotherapy only: A prospective longitudinal study. Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, 24(2), 106–114.
Kolb, B., & Whishaw, I. Q. (2006). Neuropsicología humana. Ed. Médica Panamericana.
Korkman, M., Kirk, U., & Kemp, S. L. (1998). NEPSY. A developmental neuropsychological assessment. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation.
Kovacs, M. (1992). Children's depression inventory. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi-Health Systems.
Kreitler, S., Ben-Arush, M. W., & Martin, A. (Eds.). (2012). Pediatric psycho-oncology: Psychosocial aspects and clinical interventions. Oxford: John Wiley & Sons.
Lehto, J. E., Juujärvi, P., Kooistra, L., & Pulkkinen, L. (2003). Dimensions of executive functioning: Evidence from children. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 21(1), 59–80. https://doi.org/10.1348/026151003321164627.
Luria, A. R. (1966). Higher cortical functions in man. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Mainville, M., Brisson, J., Nougarou, F., Stipanicic, A., & Sirois, S. (2015). Inhibition development: Comparison of neuropsychological and eye tracking measures. Revista Argentina de Ciencias del Comportamiento, 7, 17–25.
Marusak, H. A., Iadipaolo, A. S., Harper, F. W., Elrahal, F., Taub, J. W., Goldberg, E., & Rabinak, C. A. (2018). Neurodevelopmental consequences of pediatric cancer and its treatment: Applying an early adversity framework to understanding cognitive, behavioral, and emotional outcomes. Neuropsychology Review, 28(2), 123–175.
McAuley, T., Chen, S., Goos, L., Schachar, R., & Crosbie, J. (2010). Is the behavior rating inventory of executive function more strongly associated with measures of impairment or executive function? Journal of International Neuropsychological Society, 16, 495–505. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617710000093.
Miyake, A., Friedman, N. P., Emerson, M. J., Witzki, A. H., Howerter, A., & Wager, T. D. (2000). The unity and diversity of executive functions and their contributions to complex “frontal lobe” tasks: A latent variable analysis. Cognitive Psychology, 41, 49–100. https://doi.org/10.1006/cogp.1999.0734.
Mucci, G. A., & Torno, L. R. (Eds.). (2015). Handbook of long term care of the childhood cancer survivor. New York: Springer.
Mulhern, R. K., Merchant, T. E., Gajjar, A., Reddick, W. E., & Kun, L. E. (2004). Late neurocognitive sequelae in survivors of brain tumours in childhood. The Lancet Oncology, 5(7), 399–408.
Netson, K. L., Ashford, J. M., Skinner, T., Carty, L., Wu, S., Merchant, T. E., & Conklin, H. M. (2016). Executive dysfunction is associated with poorer health-related quality of life in pediatric brain tumor survivors. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 128(2), 313–321.
Olson, K., & Sands, S. A. (2016). Cognitive training programs for childhood cancer patients and survivors: A critical review and future directions. Child Neuropsychology, 22, 509–536.
Parrish, J., Geary, E., Jones, J., Seth, R., Hermann, B., & Seidenberg, M. (2007). Executive functioning in childhood epilepsy: Parent-report and cognitive assessment. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 49(6), 412–416.
Peterson, C. C., Johnson, C. E., Ramirez, L. Y., Huestis, S., Pai, A. L., Demaree, H. A., & Drotar, D. (2008). A meta-analysis of the neuropsychological sequelae of chemotherapy-only treatment for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 51(1), 99–104.
Pino Muñoz, M., & Arán Filippetti, V. (2019). Confirmatory factor analysis of the BRIEF-2 parent and teacher form: Relationship to performance-based measures of executive functions and academic achievement. Applied Neuropsychology: Child, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622965.2019.1660984.
Pratt, M. L., Leonard, H. C., Adeyinka, H., & Hill, E. L. (2014). The effect of motor load on planning and inhibition in developmental coordination disorder. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 35, 1579–1587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2014.04.008.
Raven, J. C., Court, J. H., & Raven, J. (2008). Test de Matrices Progresivas. Escala Coloreada, General y Avanzada. Manual. Buenos Aires: Paidós.
Reddick, W. E., Taghipour, D. J., Glass, J. O., Ashford, J., Xiong, X., Wu, S., Bonner, M., Khan, R. B., & Conklin, H. M. (2014). Prognostic factors that increase the risk for reduced white matter volumes and deficits in attention and learning for survivors of childhood cancers. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 61(6), 1074–1079.
Reitan, R. M., & Wolfson, D. (1992). Neuropsychological evaluation of older children. Tucson, AZ: Neuropsychology Press.
Robinson, K. E., Livesay, K. L., Campbell, L. K., Scaduto, M., Cannistraci, C. J., Anderson, A. W., Whitlock, J. A., & Compas, B. E. (2010). Working memory in survivors of childhood acute lymphocytic leukemia: Functional neuroimaging analyses. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 54(4), 585–590.
Shuper, A., Stark, B., Kornreich, L., Cohen, I. J., Avrahami, G., & Yaniv, I. (2002). Methotrexate-related neurotoxicity in the treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. IMAJ-RAMAT GAN, 4(11), 1050–1053.
Spiegler, B. J., Bouffet, E., Greenberg, M. L., Rutka, J. T., & Mabbott, D. J. (2004). Change in neurocognitive functioning after treatment with cranial radiation in childhood. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 22(4), 706–713.
Spielberger, C. (1990). Manual cuestionario de autoevaluación ansiedad rasgo-estado en niños (STAIC). Madrid: TEA.
Spreen, O., & Strauss, E. (1998). A compendium of neuropsychological test: Administration, norms and commentary (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Stuss, D. T., & Benson, D. F. (1986). The frontal lobes. New York, NY: Raven Press.
Tamnes, C. K., Zeller, B., Amlien, I. K., Kanellopoulos, A., Andersson, S., Due-Tønnessen, P., Ruud, E., Walhovd, K. B., & Fjell, A. M. (2015). Cortical surface area and thickness in adult survivors of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 62(6), 1027–1034.
Thorell, L. B., & Catale, C. (2014). The assessment of executive functioning using the childhood executive functioning inventory (CHEXI). In Handbook of executive functioning (pp. 359−366). Springer New York.
Thorell, L. B., Eninger, L., Brocki, K. C., & Bohlin, G. (2010). Childhood executive function inventory (CHEXI): A promising measure for identifying young children with ADHD? Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 32(1), 38–43.
Thorell, L. B., & Nyberg, L. (2008). The childhood executive functioning inventory (CHEXI): A new rating instrument for parents and teachers. Developmental Neuropsychology, 33, 536–552. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565640802101516.
Thorell, L. B., Veleiro, A., Siu, A. F., & Mohammadi, H. (2013). Examining the relation between ratings of executive functioning and academic achievement: Findings from a cross-cultural study. Child Neuropsychology, 19, 630–638. https://doi.org/10.1080/09297049.2012.727792.
Toplak, M. E., West, R. F., & Stanovich, K. E. (2013). Practitioner review: Do performance-based measures and ratings of executive function assess the same construct? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 54(2), 131–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12001.
Viola, A., Balsamo, L., Neglia, J. P., Brouwers, P., Ma, X., & Kadan-Lottick, N. S. (2017). The behavior rating inventory of executive function (BRIEF) to identify pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) survivors at risk for neurocognitive impairment. Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, 39(3), 174–178.
Vriezen, E. R., & Pigott, S. E. (2002). The relationship between parental report on the BRIEF and performance-based tasks of executive function in children with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Child Neuropsychology, 8, 296–303. https://doi.org/10.1076/chin.8.4.296.13505.
Walsh, K. S., Paltin, I., Gioia, G. A., Isquith, P., Kadan-Lottick, N. S., Neglia, J. P., & Brouwers, P. (2015). Everyday executive function in standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia survivors. Child Neuropsychology, 21(1), 78–89.
Wechsler, D. (2003). Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children – Fourth Edition (WISC-IV). San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation. [Spanish adaptation (2005), Madrid: TEA Ediciones].
Wechsler, D. (2010). WISC IV, Escala de Inteligencia para niños de Wechsler – IV. Adaptacion Argentina. Buenos Aires: Paidos.
Winter, A. L., Conklin, H. M., Tyc, V. L., Stancel, H., Hinds, P. S., Hudson, M. M., & Kahalley, L. S. (2014). Executive function late effects in survivors of pediatric brain tumors and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 36(8), 818–830.
WMA (2013). Disponible en: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involvinghuman-subjects/.
Zeller, B., Tamnes, C. K., Kanellopoulos, A., Amlien, I. K., Andersson, S., Due-Tønnessen, P., Fjell, A. M., Walhovd, K. B., Westlye, L. T., & Ruud, E. (2013). Reduced neuroanatomic volumes in long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 31(17), 2078–2085.
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the Argentinean National Council for Scientific and Technical Research (CONICET). We are indebted to the schools and all the children and parents who contributed to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutierrez, M., Arán Filippetti, V. & Lemos, V. Executive functioning in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: CHEXI parent-report vs performance-based assessment. Curr Psychol 42, 1126–1136 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01524-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01524-x