Abstract
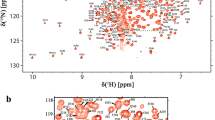
The periplasmic chaperone SurA in Gram-negative bacteria plays a central role in the biogenesis of integral outer membrane proteins and is critical to the maintenance of bacterial membrane integrity. SurA contains a core chaperone module comprising the N- and C-terminal domains, along with two peptidyl-prolyl isomerase (PPIase) domains. The chaperone activity of SurA has been demonstrated to rely on the core module, whereas recent works suggested that the PPIase domains may regulate the chaperone activity through large conformational rearrangements. Herein, we report the resonance assignments of 1H, 13C and 15N atoms of the second PPIase domain of Escherichia coli SurA, which provide valuable information for further studies of the structure, dynamics and interactions of this chaperone using NMR techniques.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behrens S, Maier R, de Cock H, Schmid FX, Gross CA (2001) The SurA periplasmic PPIase lacking its parvulin domains functions in vivo and has chaperone activity. EMBO J 20:285–294
Bitto E, McKay DB (2002) Crystallographic structure of SurA, a molecular chaperone that facilitates folding of outer membrane porins. Structure 10:1489–1498
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Johnson BA, Blevins RA (1994) NMR View: a computer program for the visualization and analysis of NMR data. J Biomol NMR 4:603–614
Lazar SW, Kolter R (1996) SurA assists the folding of Escherichia coli outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol 178:1770–1773
Marley J, Lu M, Bracken C (2001) A method for efficient isotopic labeling of recombinant proteins. J Biomol NMR 20:71–75
Nikaido H (2003) Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:593–656
Rouviere PE, Gross CA (1996) SurA, a periplasmic protein with peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity, participates in the assembly of outer membrane porins. Genes Dev 10:3170–3182
Ruiz N, Kahne D, Silhavy TJ (2006) Advances in understanding bacterial outer-membrane biogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:57–66
Sklar JG, Wu T, Kahne D, Silhavy TJ (2007) Defining the roles of the periplasmic chaperones SurA, Skp, and DegP in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev 21:2473–2484
Soltes GR, Schwalm J, Ricci DP, Silhavy TJ (2016) The activity of Escherichia coli chaperone SurA is regulated by conformational changes involving a parvulin domain. J Bacteriol 198:921–929
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) The 13C chemical-shift index: a simple method for the identification of protein secondary structure using 13C chemical-shift data. J Biomol NMR 4:171–180
Wulfing C, Pluckthun A (1994) Protein folding in the periplasm of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 12:685–692
Xu X, Wang S, Hu YX, McKay DB (2007) The periplasmic bacterial molecular chaperone SurA adapts its structure to bind peptides in different conformations to assert a sequence preference for aromatic residues. J Mol Biol 373:367–381
Acknowledgements
All NMR experiments were carried out at the Beijing NMR Center. We thank Dr. Hongwei Li at Beijing NMR Center for assistance in NMR data collection. This work was supported by Grant 31370718 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China to Y. H. and Grant 2016YFA0501201 from the National Key R&D Program of China to C. J.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, M., Hu, Y. & Jin, C. 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the second peptidyl-prolyl isomerase domain of chaperone SurA from Escherichia coli. Biomol NMR Assign 13, 183–186 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-019-09874-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-019-09874-1