Abstract
Objectives
To study the correlation of obesity with various metabolic parameters and correlation between insulin resistance and leptin and retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) levels.
Methods
This is a cross sectional study in a tertiary care children’s hospital wherein 98 obese children were included and their metabolic parameters analysed with regards to insulin resistance and RBP4 levels.
Results
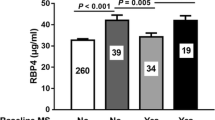
Leptin levels were abnormal for all children and high RBP4 levels were observed in 69.6 %. There was no significant association between insulin resistance and RBP4 levels (p 0.8).
Conclusions
RBP4, the sole retinol transporter in blood, secreted from adipocytes and liver has been implicated in insulin resistance. The index study however, did not show a significant positive association.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2087–102.
Huh SY, Rifas-Shiman SL, Taveras EM, Oken E, Gillman MW. Timing of solid food introduction and risk of obesity in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics. 2011;127:e544–51.
Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC, Mavri A, Morange PE. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, inflammation, obesity, insulin resistance and vascular risk. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:1575–9.
Fernández-Real JM, Ricart W. Insulin resistance and chronic cardiovascular inflammatory syndrome. Endocr Rev. 2003;24:278–301.
Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N, Preitner F, Peroni OD, Zabolotny JM, et al. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2005;436:356–62.
Ruiz-Extremera Á, Carazo Á, Salmerón Á, León J, Casado J, Goicoechea A, et al. Factors associated with hepatic steatosis in obese children and adolescents. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011;53:196–201.
Zimmermann MB, Aeberli I. Dietary determinants of subclinical inflammation, dyslipidemia and components of the metabolic syndrome in overweight children: a review. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008;32:S11–8.
Kanaka-Gantenbein C, Margeli A, Pervanidou P, Sakka S, Mastorakos G, Chrousos GP, et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 and lipocalin-2 in childhood and adolescent obesity: when children are not just “small adults”. Clin Chem. 2008;54:1176–82.
Tajtakova M, Petrasova D, Pidanicova A, Gallovicova A, Blanarova C, Petrovicova J. Serum levels of leptin, adiponectin, retinol binding protein 4 and leptin/adiponectin molar ratio as another possible marker of insulin resistance in obese. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2010;111:212–5.
Abaci A, Catli G, Anik A, Kume T, Bober E. The relation of serum nesfatin-1 level with metabolic and clinical parameters in obese and healthy children. Pediatr Diabetes. 2013;14:189–95.
Savoye M, Shaw M, Dziura J, Tamborlane WV, Rose P, Guandalini C, et al. Effects of a weight management program on body composition and metabolic parameters in overweight children: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;297:2697–704.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all the patients and their parents who have consented to be part of the research.
Contributions
VT: Formulated the study and oversaw the study from inception to completion of the manuscript; SA: Prepared the manuscript and did the literature search; RU: Done the data collection and statistical work co-ordination with the statistician; RPB: Has been instrumental in the laboratory work up in the research. VT will act as guarantor for this paper.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thiruvengadam, V., Amperayani, S., Babu, R.P. et al. Correlation of Childhood Obesity and Related Insulin Resistance with Leptin and Retinol Binding Protein 4. Indian J Pediatr 82, 799–804 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1706-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1706-6