Abstract
Objective
Accumulating evidence has been revealed that miR-590 is involved in the progression and carcinogenesis of various cancers. However, the molecular mechanism of miR-590 in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains unclear.
Methods
Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR), western blot, MTT, and transwell assay were applied to investigate the functional role of miR-590 in this study. Dual luciferase reporter assay was utilized to investigate the interaction between YAP1 and miR-590 expression. Cells transfected with miR-590 mimic or inhibitor were subjected to western blot to investigate the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in NSCLC modulated by miR-590.
Results
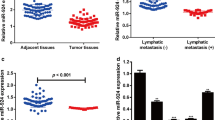
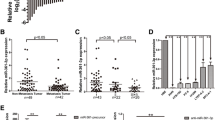
MiR-590 was down-regulated in NSCLC tissues and cells. Kaplan–Meier analysis found that the higher expression of miR-590 in NSCLC patients, the more improved survival rate of NSCLC patients. Over-expression of miR-590 inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Moreover, increasing miR-590 suppressed Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) expression and inhibited the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in NSCLC cells. Furthermore, miR-590 was negatively correlated with YAP1 expression.
Conclusion
These findings demonstrated that the miR-590/YAP1 axis exerted an important role in the progression of NSCLC, suggesting that miR-590 might be the appealing prognostic marker for NSCLC treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL, Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL, Paz-Ares L. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 2017;389:299–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30958-8.
Rosell R, Karachaliou N. Lung cancer in 2014: optimizing lung cancer treatment approaches. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12(2015):75–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.225.
Spiegel ML, Goldman JW, Wolf BR, Nameth DJ, Grogan TR, Lisberg AE, Wong DJL, Ledezma BA, Mendenhall MA, Genshaft SJ, Gutierrez AJ, Abtin F, Wallace WD, Adame CR, McKenzie JR, Abarca PA, Li AJ, Strunck JL, Famenini S, Carroll JM, Tucker DA, Sauer LM, Moghadam NM, Elashoff DA, Abaya CD, Brennan MB, Garon EB. Non-small cell lung cancer clinical trials requiring biopsies with biomarker-specific results for enrollment provide unique challenges. Cancer. 2017;123:4800–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31056.
Brule SY, Al-Baimani K, Jonker H, Zhang T, Nicholas G, Goss G, Laurie SA, Wheatley-Price P. Palliative systemic therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: investigating disparities between patients who are treated versus those who are not. Lung Cancer. 2016;97:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.04.007.
Nagasaka M, Gadgeel SM. Role of chemotherapy and targeted therapy in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018;18:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737140.2018.1409624.
Ernani V, Steuer CE, Jahanzeb M. The end of nihilism: systemic therapy of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2017;68:153–68. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-042915-102442.
Gupta GP, Massague J. Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 2006;127:679–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.001.
Kalluri R, Neilson EG. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J Clin Investig. 2003;112:1776–84. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI20530.
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, Ishi H, Beppu T, Nakamori S, Baba H, Mori M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:293–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01419.x.
Yang D, Sun Y, Hu L, Zheng H, Ji P, Pecot CV, Zhao Y, Reynolds S, Cheng H, Rupaimoole R, Cogdell D, Nykter M, Broaddus R, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Lopez-Berestein G, Liu J, Shmulevich I, Sood AK, Chen K, Zhang W. Integrated analyses identify a master microRNA regulatory network for the mesenchymal subtype in serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013;23:186–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.12.020.
Zhao B, Tumaneng K, Guan KL. The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:877–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2303.
Zhao B, Wei X, Li W, Udan RS, Yang Q, Kim J, Xie J, Ikenoue T, Yu J, Li L, Zheng P, Ye K, Chinnaiyan A, Halder G, Lai ZC, Guan KL. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007;21:2747–61. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1602907.
Pan D. The Hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev Cell. 2010;19:491–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.09.011.
Mo JS, Park HW, Guan KL. The Hippo signaling pathway in stem cell biology and cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15:642–56. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201438638.
Sohn BH, Shim JJ, Kim SB, Jang KY, Kim SM, Kim JH, Hwang JE, Jang HJ, Lee HS, Kim SC, Jeong W, Kim SS, Park ES, Heo J, Kim YJ, Kim DG, Leem SH, Kaseb A, Hassan MM, Cha M, Chu IS, Johnson RL, Park YY, Lee JS. Inactivation of Hippo pathway is significantly associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2016;22:1256–64. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1447.
Lee HJ, Diaz MF, Price KM, Ozuna JA, Zhang S, Sevick-Muraca EM, Hagan JP, Wenzel PL. Fluid shear stress activates YAP1 to promote cancer cell motility. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14122. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14122.
Cui R, Meng W, Sun HL, Kim T, Ye Z, Fassan M, Jeon YJ, Li B, Vicentini C, Peng Y, Lee TJ, Luo Z, Liu L, Xu D, Tili E, Jin V, Middleton J, Chakravarti A, Lautenschlaeger T, Croce CM. MicroRNA-224 promotes tumor progression in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:E4288-4297. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1502068112.
Joshi P, Jeon YJ, Lagana A, Middleton J, Secchiero P, Garofalo M, Croce CM. MicroRNA-148a reduces tumorigenesis and increases TRAIL-induced apoptosis in NSCLC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:8650–5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1500886112.
Cai J, Fang L, Huang Y, Li R, Yuan J, Yang Y, Zhu X, Chen B, Wu J, Li M. miR-205 targets PTEN and PHLPP2 to augment AKT signaling and drive malignant phenotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5402–15. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0297.
Faversani A, Amatori S, Augello C, Colombo F, Porretti L, Fanelli M, Ferrero S, Palleschi A, Pelicci PG, Belloni E, Ercoli G, Degrassi A, Baccarin M, Altieri DC, Vaira V, Bosari S. miR-494–3p is a novel tumor driver of lung carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:7231–47. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13933.
Abdolvahabi Z, Nourbakhsh M, Hosseinkhani S, Hesari Z, Alipour M, Jafarzadeh M, Ghorbanhosseini SS, Seiri P, Yousefi Z, Yarahmadi S, Golpour P. MicroRNA-590-3P suppresses cell survival and triggers breast cancer cell apoptosis via targeting sirtuin-1 and deacetylation of p53. J Cell Biochem. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28211.
Wang WT, Qi Q, Zhao P, Li CY, Yin XY, Yan RB. miR-590–3p is a novel microRNA which suppresses osteosarcoma progression by targeting SOX9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:1763–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.124.
Salem M, O’Brien JA, Bernaudo S, Shawer H, Ye G, Brkic J, Amleh A, Vanderhyden BC, Refky B, Yang BB, Krylov SN, Peng C. miR-590-3p promotes ovarian cancer growth and metastasis via a novel FOXA2-versican pathway. Can Res. 2018;78:4175–90. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3014.
Ma Z, Wang Y, He B, Cui J, Zhang C, Wang H, Feng W, Wang B, Wei D, Wu Y, Zeng Y, Yu G. Expression of miR-590 in lung cancer and its correlation with prognosis. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:1753–7. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7497.
Xu BB, Gu ZF, Ma M, Wang JY, Wang HN. MicroRNA-590–5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating GAB1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:5954–63. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201809_15926.
Piao L, Wang F, Wang Y, Yang Z, Li Q, Cui L, Yu Q. miR-424-5p regulates hepatoma cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2018.2625.
Sun Z, Ou C, Liu J, Chen C, Zhou Q, Yang S, Li G, Wang G, Song J, Li Z, Zhang Z, Yuan W, Li X. YAP1-induced MALAT1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenesis by sponging miR-126-5p in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0628-y.
Liu G, Huang K, Jie Z, Wu Y, Chen J, Chen Z, Fang X, Shen S. CircFAT1 sponges miR-375 to promote the expression of yes-associated protein 1 in osteosarcoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:170. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0917-7.
Cheng H, Dong H, Feng J, Tian H, Zhang H, Xu L. miR-497 inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of thyroid papillary carcinoma cells by negatively regulating YAP1 expression. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:4711–21. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S164052.
Chen M, Wu L, Tu J, Zhao Z, Fan X, Mao J, Weng Q, Wu X, Huang L, Xu M, Ji J. miR-590-5p suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma chemoresistance by targeting YAP1 expression. EBioMedicine. 2018;35:142–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.08.010.
Yu M, Luo Y, Cong Z, Mu Y, Qiu Y, Zhong M. MicroRNA-590-5p inhibits intestinal inflammation by targeting YAP. J Crohns Colitis. 2018;12:993–1004. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy046.
Wei J, Jia A, Ma L, Wang Y, Qiu L, Xiao B. MicroRNA-16 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of human lung cancer cells by modulating the expression of YAP1. J BUON. 2020;25:862–8.
Ou C, Sun Z, Li X, Li X, Ren W, Qin Z, Zhang X, Yuan W, Wang J, Yu W, Zhang S, Peng Q, Yan Q, Xiong W, Li G, Ma J. MiR-590-5p, a density-sensitive microRNA, inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting YAP1 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;399:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.04.011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XH conceived and designed the study, and drafted the manuscript. AS collected, analyzed and interpreted the experimental data. XH and AS revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by Ethical Committee of Weifang Cancer Hospital and conducted in accordance with the ethical standards.
Informed consent
Subjects signed the informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, X., Su, A. MiR-590 suppresses the progression of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating YAP1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Clin Transl Oncol 24, 546–555 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02713-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02713-7