Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the association of hemodialysis duration with the recurrence of urothelial carcinoma (UC) of the bladder and overall survival in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis (MHD).
Patients and methods
52 bladder cancer patients who underwent MHD at the Xiangya Hospital of The Central South University between 2001 and 2011 were enrolled in the study. The patients were divided into three groups according to hemodialysis duration, and patient mortality and tumor recurrence rates were analyzed. The association of hemodialysis duration with occurrence and recurrence of UC of the bladder was analyzed by Cox regression analysis. Survival was evaluated by the Kaplan–Meier method.
Results
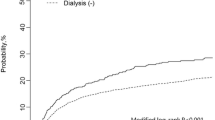
Out of 6266 chronic hemodialysis patients, 52 patients had UC of the bladder after the initiation of hemodialysis for 6 months. The mean age at hemodialysis onset was 55 years (IQR 36, 71). The major complaints were painless gross hematuria and urethral bloody discharge. Tumors were generally large and multifocal. The standardized incidence ratio of UC of the bladder was 43.9 compared with general population, and it was higher in women (76.7) and in the age group 61–65 years (186.6). The mean hemodialysis duration before the diagnosis of bladder cancer was 32 months. 30 (57.7 %) patients received hemodialysis no more than 3 years, 10 (19.2 %) patients received hemodialysis between 3 and 6 years, and 12 (23.1 %) patients received hemodialysis for more than 6 years.
Conclusion
Preoperative shorter hemodialysis duration is a risk factor for the occurrence and recurrence of UC of the bladder in patients undergoing MHD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maisonneuve P, Agodoa L, Gellert R, Stewart JH, Buccianti G, Lowenfels AB et al. Cancer in patients on dialysis for end-stage renal disease: an international collaborative study. Lancet. 1999;354(9173):93–9. doi:S0140673699061541.
Lin HF, Li YH, Wang CH, Chou CL, Kuo DJ, Fang TC. Increased risk of cancer in chronic dialysis patients: a population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(4):1585–90. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfr464.
Wu CF, Shee JJ, Ho DR, Chen WC, Chen CS. Different treatment strategies for end stage renal disease in patients with transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2004;171(1):126–9. doi:10.1097/01.ju.0000101758.41635.28.
Ou JH, Pan CC, Lin JS, Tzai TS, Yang WH, Chang CC et al. Transitional cell carcinoma in dialysis patients. Eur Urol. 2000;37(1):90–4. doi:20106.
Lin MY, Kuo MC, Hung CC, Wu WJ, Chen LT, Yu ML, et al. Association of dialysis with the risks of cancers. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0122856. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122856PONE-D-14-49516.
Mandayam S, Shahinian VB. Are chronic dialysis patients at increased risk for cancer? J Nephrol. 2008;21(2):166–74.
Stewart JH, Buccianti G, Agodoa L, Gellert R, McCredie MR, Lowenfels AB, et al. Cancers of the kidney and urinary tract in patients on dialysis for end-stage renal disease: analysis of data from the United States, Europe, and Australia and New Zealand. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(1):197–207.
Wang TY, Hu CJ, Kuo CW, Chen Y, Lin JL, Yang CW, et al. High incidence and recurrence of transitional cell carcinoma in Taiwanese patients with end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Carlton. 2011;16(2):225–31. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1797.2010.01366.x.
Yossepowitch O, Sagy I, Margel D, Baniel J. Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder in patients on hemodialysis: clinical characteristics and oncological outcomes. J Urol. 2012;. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2011.11.098.
Kang CH, Chen CH, Chiang PH. Primary urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract in dialysis patients with 5-year follow-up. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2010;40(3):241–6. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyp143.
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A, et al. AJCC cancer staging man. 7th ed. New York: Springer; 2009.
Wu CF, Chang PL, Chen CS, Chuang CK, Weng HH, Pang ST. The outcome of patients on dialysis with upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2006;176(2):477–81. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2006.03.099.
Yen TH, Lin JL, Lin-Tan DT, Hsu KH. Cardiothoracic ratio, inflammation, malnutrition, and mortality in diabetes patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Am J Med Sci. 2009;337(6):421–8. doi:10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31819bbec1.
Chung SD, Huang KH, Lai MK, Huang CY, Chen CH, Pu YS, et al. CKD as a risk factor for bladder recurrence after nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007;50(5):743–53. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.08.007.
Wu CF, Pang ST, Shee JJ, Chang PL, Chuang CK, Chen CS, et al. Identification of genetic alterations in upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma in end-stage renal disease patients. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2010;49(10):928–34. doi:10.1002/gcc.20803.
Tseng SF, Chuang YC, Yang WC. Long-term outcome of radical cystectomy in ESDR patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 2011;43(4):1067–71. doi:10.1007/s11255-011-9960-7.
Chen KS, Lai MK, Huang CC, Chu SH, Leu ML. Urologic cancers in uremic patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995;25(5):694–700. doi:0272-6386(95)90544-8.
Kang CH, Yu TJ, Hsieh HH, Yang JW, Shu K, Huang CC, et al. The development of bladder tumors and contralateral upper urinary tract tumors after primary transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Cancer. 2003;98(8):1620–6. doi:10.1002/cncr.11691.
Chen CH, Shun CT, Huang KH, Huang CY, Yu HJ, Pu YS. Characteristics of female non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer in Taiwan: association with upper tract urothelial carcinoma and end-stage renal disease. Urology. 2008;71(6):1155–60. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2007.11.140.
Heidland A, Bahner U, Vamvakas S. Incidence and spectrum of dialysis-associated cancer in three continents. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35(2):347–51; discussion 52–3. doi:S0272-6386(00)70349-0.
Chung CJ, Huang CY, Tsai HB, Muo CH, Chung MC, Chang CH, et al. Sex differences in the development of malignancies among end-stage renal disease patients: a nationwide population-based follow-up study in Taiwan. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44675. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044675PONE-D-12-16564.
Liang JA, Sun LM, Yeh JJ, Sung FC, Chang SN, Kao CH. The association between malignancy and end-stage renal disease in Taiwan. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011;41(6):752–7. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyr051hyr051.
Yang HY, Wang JD, Lo TC, Chen PC. Increased mortality risk for cancers of the kidney and other urinary organs among Chinese herbalists. J Epidemiol. 2009;19(1):17–23. doi:JST.JSTAGE/jea/JE20080035.
Cosyns JP, Dehoux JP, Guiot Y, Goebbels RM, Robert A, Bernard AM, et al. Chronic aristolochic acid toxicity in rabbits: a model of Chinese herbs nephropathy? Kidney Int. 2001;59(6):2164–73. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00731.x.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (No. 217772150050582.2014zzts079) and the Medjaden Academy & Research Foundation for Young Scientists (Grant No. MJR20150025).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SL., Qi, L., Han, WQ. et al. Shorter hemodialysis duration is a risk factor for the recurrence of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Clin Transl Oncol 18, 304–309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1368-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1368-x