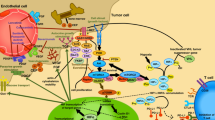
Abstract
Antiangiogenic therapy is currently considered as the cornerstone of treatment in metastatic kidney cancer. A monoclonal antibody against the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and several tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting the VEGF receptors demonstrated, 7 years ago, to deeply impact the outcome of this tumor and became a model of integration of molecular knowledge into clinical practice. Unfortunately, no further improvement in survival has been made and 20–25 % of cases remain primary refractory to these drugs, with an overall dismal prognosis. Since biomarker predictors of activity are lacking, their development could highly help in the process of making clinical decisions when choosing the best option for every patient or prompting the inclusion in clinical trials. This unmet medical need could become even more relevant if new immunotherapy confirms its initial promising results in this pathology. In this article, we provide an insight of current state of the art regarding the prediction of antiangiogenic efficacy in kidney cancer and propose new strategies for the implementation of such markers in clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9–29.
de Vivar Chevez AR, Finke J, Bukowski R. The role of inflammation in kidney cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;816:197–234.
Nosov DA, Esteves B, Lipatov ON, Lyulko AA, Anischenko AA, Chacko RT, et al. Antitumor activity and safety of tivozanib (AV-951) in a phase II randomized discontinuation trial in patients with renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(14):1678–85.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(2):115–24.
Gore ME, Szczylik C, Porta C, Bracarda S, Bjarnason GA, Oudard S, et al. Safety and efficacy of sunitinib for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: an expanded-access trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(8):757–63.
Escudier B, Pluzanska A, Koralewski P, Ravaud A, Bracarda S, Szczylik C, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9605):2103–11.
Rini BI, Halabi S, Rosenberg JE, Stadler WM, Vaena DA, Ou SS, et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa compared with interferon alfa monotherapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: CALGB 90206. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(33):5422–8.
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(6):1061–8.
Porta C, Paglino C, Grunwald V. Sunitinib re-challenge in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(6):1047–53.
Heng DY, Mackenzie MJ, Vaishampayan UN, Bjarnason GA, Knox JJ, Tan MH, et al. Primary anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma: clinical characteristics, risk factors, and subsequent therapy. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(6):1549–55.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J, Hawkins R, Guo J, et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(8):722–31.
Porta C, Levy A, Hawkins R, Castellano D, Bellmunt J, Nathan P, et al. Impact of adverse events, treatment modifications, and dose intensity on survival among patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with first-line sunitinib: a medical chart review across ten centers in five European countries. Cancer Med. 2014;3:1517–26.
Garcia-Donas J, Rodriguez-Antona C, Jonasch E. Molecular markers to predict response to therapy. Semin Oncol. 2013;40(4):444–58.
Evans WE, Relling MV. Moving towards individualized medicine with pharmacogenomics. Nature. 2004;429(6990):464–8.
Ingelman-Sundberg M. Pharmacogenomic biomarkers for prediction of severe adverse drug reactions. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(6):637–9.
Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Bennouna J, Formento JL, Douillard JY, Francoual M, Hennebelle I, et al. Multifactorial pharmacogenetic analysis in colorectal cancer patients receiving 5-fluorouracil-based therapy together with cetuximab-irinotecan. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;73(5):776–85.
Schultheis AM, Lurje G, Rhodes KE, Zhang W, Yang D, Garcia AA, et al. Polymorphisms and clinical outcome in recurrent ovarian cancer treated with cyclophosphamide and bevacizumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(22):7554–63.
Schneider BP, Wang M, Radovich M, Sledge GW, Badve S, Thor A, et al. Association of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 genetic polymorphisms with outcome in a trial of paclitaxel compared with paclitaxel plus bevacizumab in advanced breast cancer: ECOG 2100. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(28):4672–8.
Peer CJ, Sissung TM, Kim A, Jain L, Woo S, Gardner ER, et al. Sorafenib is an inhibitor of UGT1A1 but is metabolized by UGT1A9: implications of genetic variants on pharmacokinetics and hyperbilirubinemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(7):2099–107.
de Haas S, Delmar P, Bansal AT, Moisse M, Miles DW, Leighl N, et al. Genetic variability of VEGF pathway genes in six randomized phase III trials assessing the addition of bevacizumab to standard therapy. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(4):909–20.
van der Veldt AA, Eechoute K, Gelderblom H, Gietema J, Guchelaar HJ, van Erp NP, et al. Genetic polymorphisms associated with a prolonged progression-free survival in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with sunitinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(3):620–9.
Garcia-Donas J, Esteban E, Leandro-Garcia LJ, Castellano DE, del Alba AG, Climent MA, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphism associations with response and toxic effects in patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma treated with first-line sunitinib: a multicentre, observational, prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(12):1143–50.
Beuselinck B, Karadimou A, Lambrechts D, Claes B, Wolter P, Couchy G, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with outcome in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(4):887–900.
Kim JJ, Vaziri SA, Rini BI, Elson P, Garcia JA, Wirka R, et al. Association of VEGF and VEGFR2 single nucleotide polymorphisms with hypertension and clinical outcome in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients treated with sunitinib. Cancer. 2012;118(7):1946–54.
Xu CF, Bing NX, Ball HA, Rajagopalan D, Sternberg CN, Hutson TE, et al. Pazopanib efficacy in renal cell carcinoma: evidence for predictive genetic markers in angiogenesis-related and exposure-related genes. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(18):2557–64.
Xu CF, Johnson T, Garcia-Donas J, Choueiri TK, Sternberg CN, Davis ID, et al. IL8 polymorphisms and overall survival in pazopanib- or sunitinib-treated patients with renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(7):1190–8.
Escudier B, Loomis A, Kaprin A, Motzer R, Tomczak P, Tarazi J, et al. 7103 ORAL association of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in VEGF pathway genes with progression-free survival (PFS) and blood pressure (BP) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) in the phase 3 trial of axitinib versus sorafenib (AXIS Trial). Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:S505.
Choueiri TK, Vaziri SA, Jaeger E, Elson P, Wood L, Bhalla IP, et al. von Hippel-Lindau gene status and response to vascular endothelial growth factor targeted therapy for metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2008;180(3):860–5; discussion 5–6.
Pena C, Lathia C, Shan M, Escudier B, Bukowski RM. Biomarkers predicting outcome in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: results from sorafenib phase III treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(19):4853–63.
Hutson T, Davis I, Machiels J, De Souza P, Baker K, Bordogna W, et al. Biomarker analysis and final efficacy and safety results of a phase II renal cell carcinoma trial with pazopanib (GW786034), a multi-kinase angiogenesis inhibitor. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(15S):5046.
Kapur P, Pena-Llopis S, Christie A, Zhrebker L, Pavia-Jimenez A, Rathmell WK, et al. Effects on survival of BAP1 and PBRM1 mutations in sporadic clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma: a retrospective analysis with independent validation. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(2):159–67.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature. 2013;499(7456):43–9.
Kapur P, Christie A, Raman JD, Then MT, Nuhn P, Buchner A, et al. BAP1 immunohistochemistry predicts outcomes in a multi-institutional cohort with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2014;191(3):603–10.
Gordan JD, Bertout JA, Hu CJ, Diehl JA, Simon MC. HIF-2alpha promotes hypoxic cell proliferation by enhancing c-myc transcriptional activity. Cancer Cell. 2007;11(4):335–47.
Gordan JD, Lal P, Dondeti VR, Letrero R, Parekh KN, Oquendo CE, et al. HIF-alpha effects on c-Myc distinguish two subtypes of sporadic VHL-deficient clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2008;14(6):435–46.
Maroto P, Esteban E, Fernández-Parra E, Méndez-Vidal M, Domenech M, León L, et al. C-myc as a new predictive biomarker for sunitinib in metastatic renal clear cell carcinoma. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2012.
Mikami S, Mizuno R, Kosaka T, Saya H, Oya M, Okada Y. Expression of TNF-alpha and CD44 is implicated in poor prognosis, cancer cell invasion, metastasis and resistance to the sunitinib treatment in clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 2014;136:1504–14.
Jonasch E, Corn P, Pagliaro LC, Warneke CL, Johnson MM, Tamboli P, et al. Upfront, randomized, phase 2 trial of sorafenib versus sorafenib and low-dose interferon alfa in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: clinical and biomarker analysis. Cancer. 2010;116(1):57–65.
Jonasch E, Wood CG, Matin SF, Tu SM, Pagliaro LC, Corn PG, et al. Phase II presurgical feasibility study of bevacizumab in untreated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(25):4076–81.
Choueiri TK, Regan MM, Rosenberg JE, Oh WK, Clement J, Amato AM, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX and pathological features as predictors of outcome in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma receiving vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. BJU Int. 2010;106(6):772–8.
Choueiri TK, Cheng S, Qu AQ, Pastorek J, Atkins MB, Signoretti S. Carbonic anhydrase IX as a potential biomarker of efficacy in metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma patients receiving sorafenib or placebo: analysis from the treatment approaches in renal cancer global evaluation trial (TARGET). Urol Oncol. 2013;31(8):1788–93.
Prior C, Perez-Gracia JL, Garcia-Donas J, Rodriguez-Antona C, Guruceaga E, Esteban E, et al. Identification of tissue microRNAs predictive of sunitinib activity in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(1):e86263.
Tugues S, Koch S, Gualandi L, Li X, Claesson-Welsh L. Vascular endothelial growth factors and receptors: anti-angiogenic therapy in the treatment of cancer. Mol Aspects Med. 2011;32(2):88–111.
Jacobsen J, Grankvist K, Rasmuson T, Bergh A, Landberg G, Ljungberg B. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor protein in human renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2004;93(3):297–302.
Hegde PS, Jubb AM, Chen D, Li NF, Meng YG, Bernaards C, et al. Predictive impact of circulating vascular endothelial growth factor in four phase III trials evaluating bevacizumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(4):929–37.
Harmon C, Figlin R, Hutson T. Circulating protein biomarkers of sunitinib (SU) and interferon-α (IFN-α) efficacy in treatment (Tx)-naive patients (pts) with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(suppl; abstr 10525).
Rini BI, Michaelson MD, Rosenberg JE, Bukowski RM, Sosman JA, Stadler WM, et al. Antitumor activity and biomarker analysis of sunitinib in patients with bevacizumab-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(22):3743–8.
Deprimo SE, Bello CL, Smeraglia J, Baum CM, Spinella D, Rini BI, et al. Circulating protein biomarkers of pharmacodynamic activity of sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: modulation of VEGF and VEGF-related proteins. J Transl Med. 2007;5:32.
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Christensen JG, Mutsaers AJ, Kerbel RS. Multiple circulating proangiogenic factors induced by sunitinib malate are tumor-independent and correlate with antitumor efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(43):17069–74.
Lindauer A, Di Gion P, Kanefendt F, Tomalik-Scharte D, Kinzig M, Rodamer M, et al. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling of biomarker response to sunitinib in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;87(5):601–8.
Maroto P, Rini B. Molecular biomarkers in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(8):2060–71.
Gordon MS, Margolin K, Talpaz M, Sledge GW Jr, Holmgren E, Benjamin R, et al. Phase I safety and pharmacokinetic study of recombinant human anti-vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(3):843–50.
Loupakis F, Falcone A, Masi G, Fioravanti A, Kerbel RS, Del Tacca M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in immunodepleted plasma of cancer patients as a possible pharmacodynamic marker for bevacizumab activity. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(13):1816–8.
Maitland ML, Xu CF, Cheng YC, Kistner-Griffin E, Ryan KA, Karrison TG, et al. Identification of a variant in KDR associated with serum VEGFR2 and pharmacodynamics of pazopanib. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;21:365–72.
Zurita AJ, Jonasch E, Wang X, Khajavi M, Yan S, Du DZ, et al. A cytokine and angiogenic factor (CAF) analysis in plasma for selection of sorafenib therapy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(1):46–52.
Tran HT, Liu Y, Zurita AJ, Lin Y, Baker-Neblett KL, Martin AM, et al. Prognostic or predictive plasma cytokines and angiogenic factors for patients treated with pazopanib for metastatic renal-cell cancer: a retrospective analysis of phase 2 and phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(8):827–37.
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Hudes GR, Figlin RA, Martini JF, English PA, et al. Investigation of novel circulating proteins, germ line single-nucleotide polymorphisms, and molecular tumor markers as potential efficacy biomarkers of first-line sunitinib therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;74(4):739–50.
Miyake H, Nishikawa M, Tei H, Furukawa J, Harada K, Fujisawa M. Significance of circulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 ratio as a predictor of disease progression in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib. Urol Oncol. 2014;32(5):584–8.
Zurita-Saavedra A, Liu Y, Lin Y, Tran H, Pandite L, Heymach J. Multivariate analysis of cytokines and angiogenic factors (cafs) and established prognostic parameters in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mrcc) patients (pts) receiving pazopanib or placebo. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2012.
Woywodt A, Schroeder M, Gwinner W, Mengel M, Jaeger M, Schwarz A, et al. Elevated numbers of circulating endothelial cells in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2003;76(1):1–4.
Mutin M, Canavy I, Blann A, Bory M, Sampol J, Dignat-George F. Direct evidence of endothelial injury in acute myocardial infarction and unstable angina by demonstration of circulating endothelial cells. Blood. 1999;93(9):2951–8.
Sakamori Y, Masago K, Ohmori K, Togashi Y, Nagai H, Okuda C, et al. Increase in circulating endothelial progenitor cells predicts response in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2012;103(6):1065–70.
Jain S, Ward MM, O’Loughlin J, Boeck M, Wiener N, Chuang E, et al. Incremental increase in VEGFR1(+) hematopoietic progenitor cells and VEGFR2(+) endothelial progenitor cells predicts relapse and lack of tumor response in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;132(1):235–42.
Manzoni M, Mariucci S, Delfanti S, Rovati B, Ronzoni M, Loupakis F, et al. Circulating endothelial cells and their apoptotic fraction are mutually independent predictive biomarkers in Bevacizumab-based treatment for advanced colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138(7):1187–96.
Vroling L, van der Veldt AA, de Haas RR, Haanen JB, Schuurhuis GJ, Kuik DJ, et al. Increased numbers of small circulating endothelial cells in renal cell cancer patients treated with sunitinib. Angiogenesis. 2009;12(1):69–79.
Farace F, Gross-Goupil M, Tournay E, Taylor M, Vimond N, Jacques N, et al. Levels of circulating CD45(dim)CD34(+)VEGFR2(+) progenitor cells correlate with outcome in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Br J Cancer. 2011;104(7):1144–50.
Gruenwald V, Beutel G, Schuch-Jantsch S, Reuter C, Ivanyi P, Ganser A, et al. Circulating endothelial cells are an early predictor in renal cell carcinoma for tumor response to sunitinib. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:695.
Castellano DE, Esteban E, Leon L, Basterretxea L, Jose Mendez M, et al. Prospective assessment of circulating endothelial cells (CECs) as early markers of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (CCRCC) progression in first line setting: the circles study (SOGUG 2011-01). Alexandria: American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2012.
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ, Stopeck A, Matera J, Miller MC, et al. Circulating tumor cells, disease progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(8):781–91.
de Bono JS, Scher HI, Montgomery RB, Parker C, Miller MC, Tissing H, et al. Circulating tumor cells predict survival benefit from treatment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(19):6302–9.
Rahbari NN, Aigner M, Thorlund K, Mollberg N, Motschall E, Jensen K, et al. Meta-analysis shows that detection of circulating tumor cells indicates poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(5):1714–26.
Joosse SA, Pantel K. Biologic challenges in the detection of circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2013;73(1):8–11.
Gamez-Pozo A, Anton-Aparicio LM, Bayona C, Borrega P, Gallegos Sancho MI, Garcia-Dominguez R, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of peripheral blood samples predicts resistance to first-line sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients. Neoplasia. 2012;14(12):1144–52.
Motzer RJ, Mazumdar M, Bacik J, Berg W, Amsterdam A, Ferrara J. Survival and prognostic stratification of 670 patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(8):2530–40.
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, Warren MA, Golshayan AR, Sahi C, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(34):5794–9.
Hamnvik OP, Choueiri TK, Turchin A, McKay RR, Goyal L, Davis M, et al. Clinical risk factors for the development of hypertension in patients treated with inhibitors of the VEGF signaling pathway. Cancer. 2014;121:311–9.
Ammari S, Thiam R, Cuenod CA, Oudard S, Hernigou A, Grataloup C, et al. Radiological evaluation of response to treatment: application to metastatic renal cancers receiving anti-angiogenic treatment. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2014;95(6):527–39.
Iacovelli R, Massari F, Albiges L, Loriot Y, Massard C, Fizazi K, et al. Evidence and clinical relevance of tumor flare in patients who discontinue tyrosine kinase inhibitors for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2014;68:154–60.
Breen EC, Reynolds SM, Cox C, Jacobson LP, Magpantay L, Mulder CB, et al. Multisite comparison of high-sensitivity multiplex cytokine assays. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011;18(8):1229–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romero-Laorden, N., Doger, B., Hernandez, M. et al. Predictive biomarker candidates to delineate efficacy of antiangiogenic treatment in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 18, 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1332-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1332-9