Abstract
Background
Brain metastases (BMs) represent an important cause of morbidity in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and are associated with a mean survival of <1 year. Thus, new regimens improving the outcome of these patients are urgently needed. We have evaluated the response to treatment, overall survival, disease progression, and adverse effects of a concomitant treatment with whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) followed by intensity-modulated boosting RT (IMBRT) and temozolomide (TMZ) in patients with BMs from NSCLC.
Methods
A total of 32 patients with no more than four BMs were enrolled in this retrospective study. Patients received 30 Gy of WBRT in 15 fractions and followed by 20 Gy of IMBRT in 10 fractions with concomitant TMZ of 75 mg/m2/day orally during RT and continued TMZ therapy (150–200 mg/m2/day for 5 days every 28 days for an additional 2–6 cycles after RT).
Results
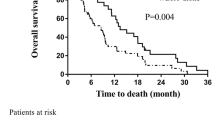
Three patients had a complete response, 9 patients had a partial response, while 15 patients had stable disease; therefore, the objective responses achieved 37.5 %. Median overall survival was 8.0 months and median time to progression was 5.5 months. Common treatment-related adverse effects (Grade ≤2) included nausea, vomiting, and asthenia. Grade 3 or worse hematologic toxicities were rare. No patient presented with gross neurocognitive dysfunction.
Conclusion
WBRT followed by IMBRT combined with concomitant TMZ is well tolerated, yielding an encouraging objective response rate; however, overall survival improves slightly comparing with RTOG 9508 randomized trial.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi A, Komaki R. Treatment of brain metastasis from lung cancer. Cancers. 2010;2:2100–37.
Ellis TL, Neal MT, Chan MD. The role of surgery, radiosurgery and whole brain radiation therapy in the management of patients with metastatic brain tumors. Int J Surg Oncol. 2012;2012:952345.
Rades D, Kieckebusch S, Haatanen T, Lohynska R, Dunst J, Schild SE. Surgical resection followed by whole brain radiotherapy versus whole brain radiotherapy alone for single brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;70:1319–24.
Murray KJ, Scott C, Greenberg HM, Emami B, Seider M, Vora NL, et al. A randomized phase III study of accelerated hyperfractionation versus standard in patients with unresected brain metastases: a report of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 9104. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;39:571–4.
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:2483–91.
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet. 2004;363:1665–72.
Tatar Z, Thivat E, Planchat E, Gimbergues P, Gadea E, Abrial C, et al. Temozolomide and unusual indications: review of literature. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013;39:125–35.
Gamboa-Vignolle C, Ferrari-Carballo T, Arrieta Ó, Mohar A. Whole-brain irradiation with concomitant daily fixed-dose temozolomide for brain metastases treatment: a randomised phase II trial. Radiother Oncol. 2012;102:187–91.
Liu R, Wang X, Ma B, Yang K, Zhang Q, Tian J. Concomitant or adjuvant temozolomide with whole-brain irradiation for brain metastases: a meta-analysis. Anticancer Drugs. 2010;21:120–8.
Faust D, Fogel BS. The development and initial validation of a sensitive bedside cognitive screening test. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1989;177:25–31.
Neuhaus T, Ko Y, Muller RP, Grabenbauer GG, Hedde JP, Schueller H, et al. A phase III trial of topotecan and whole brain radiation therapy for patients with CNS-metastases due to lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:291–7.
Antonadou D, Paraskevaidis M, Sarris G, Coliarakis N, Economou I, Karageorgis P, et al. Phase II randomized trial of temozolomide and concurrent radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:3644–50.
Verger E, Gil M, Yaya R, Viñolas N, Villà S, Pujol T, et al. Temozolomide and concomitant whole brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: a phase II randomized trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61:185–91.
Addeo R, Caraglia M, Faiola V, Capasso E, Vincenzi B, Montella L, et al. Concomitant treatment of brain metastasis with whole brain radiotherapy [WBRT] and temozolomide [TMZ] is active and improves quality of life. BMC Cancer. 2007;7:18.
Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC. Controversies in the management of multiple brain metastases: the roles of radiosurgery and radiation therapy. Forum (Genova). 2001;11:47–58.
Sankaranarayanan V, Ganesan S, Oommen S, Padmanaban TK, Stumpf J, Ayyangar KM. Study on dosimetric parameters for stereotactic radiosurgery and intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Med Dosim. 2003;28:85–90.
Roa DE, Schiffner DC, Zhang J, Dietrich SN, Kuo JV, Wong J. The use of RapidArc volumetric-modulated arc therapy to deliver stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy to intracranial and extracranial targets. Med Dosim. 2012;37:257–64.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Jiang, Z., Qi, X. et al. Whole brain radiation therapy followed by intensity-modulated boosting treatment combined with concomitant temozolomide for brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 16, 1000–1005 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1190-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1190-x