Abstract
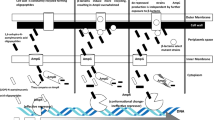
Hospital-acquired pneumonia caused by Acinetobacter baumannii is a major healthcare burden. Type VI Secretion System (T6SS) contributes to both virulence and drug resistance in this bacteria. This study aims to investigate the diagnostic value of hemolysin co-regulated protein (Hcp) gene in A. baumannii pneumonia and further explore the effect of hcp on clinical, pathogenicity and drug resistance. 53 clinical A. baumannii strains from patients’ respiratory tract at a teaching hospital were included in this study. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was carried out to examine the expression of hcp. Recombinant Hcp expression plasmids (pET-28a(+)-hcp) were constructed and his-tagged Hcp were purified to stimulate Tohoku Hospital Pediatrics-1 (THP-1) macrophages. Nuclear Factor Kappa B p65 (NF-κBp65) and Interleukin 8 (IL-8) were detected by qRT-PCR. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) were examined by an automated instrument system. Hcp gene had 92.6% sensitivity and 75% specificity for distinguishing invasive or colonizing A. baumannii from the respiratory tract. His-tagged Hcp induced NF-κBp65 and IL-8 at gene level in THP-1 macrophages. Additional, high hcp expression isolates showed higher rate of antimicrobial agent exposure (< 30 days) of carbapenems, antibiotic combination therapy and multiple or extensive drug-resistant (MDR/XDR) and exhibited higher resistance rate to clinical commonly-used antimicrobial agents. Hcp gene could serve as a novel diagnostic biomarker to distinguish A. baumannii respiratory tract infection from colonization and participate in eliciting inflammatory responses in vitro. T6SS/hcp may play a role in the development of carbapenem-resistant A. baumannii (CRAB), multiple or extensive drug-resistant A. baumannii (MDRAB/XDRAB).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Repizo G, Gagné S, Foucault-Grunenwald M, Borges V, Charpentier X, Limansky A et al (2015) Differential role of the T6SS in acinetobacter baumannii virulence. PLoS ONE 10:e0138265. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138265
Liao W, Huang HH, Huang QS, Fang-Ling D, Dan Wei D, La-Gen W et al (2022) Distribution of type VI secretion system (T6SS) in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae strains from a Chinese hospital and its potential relationship with virulence and drug resistance. Microb Pathog 162:105085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105085
Le N, Peters K, Espaillat A, Sheldon J, Gray J, Di Venanzio G et al (2020) Acinetobacter baumanniiPeptidoglycan editing provides immunity to during bacterial warfare. Sci Adv 6:eabb5614. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abb5614
Pan P, Wang X, Chen Y, Chen Q, Yang Y, Wei C et al (2022) Acinetobacter baumanniiEffect of Hcp iron ion regulation on the interaction between with human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells and biofilm formation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:761604. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.761604
Basler M, Pilhofer M, Henderson G, Jensen G, Mekalanos J (2012) Type VI secretion requires a dynamic contractile phage tail-like structure. Nature 483:182–186. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10846
Pukatzki S, Ma AT, Sturtevant D, Krastins B, Sarracino D, Nelson WC et al (2006) Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1528. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510322103
Pukatzki S, McAuley S, Miyata S (2009) The type VI secretion system: translocation of effectors and effector-domains. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2008.11.010
Burtnick MN, Brett PJ, Harding SV, Ngugi SA, Ribot WJ, Chantratita N et al (2011) The cluster 1 type VI secretion system is a major virulence determinant in Burkholderia pseudomallei. Infect Immun 79:1512–1525. https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.01218-10
Zhou Y, Tao J, Yu H, Ni J, Zeng L, Teng Q et al (2012) Hcp family proteins secreted via the type VI secretion system coordinately regulate Escherichia coli K1 interaction with human brain microvascular endothelial cells. Infect Immun 80:1243–1251. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.05994-11
Hu Y, Liu C, Liu P, Wu Z, Zhang Y, Xiong X et al (2018) hcpRegulation of gene expression of, a core gene of the type VI secretion system in causing respiratory tract infection. J Med Microbiol 67:945–951. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.000753
Magiorakos A, Srinivasan A, Carey R, Carmeli Y, Falagas M, Giske C et al (2012) Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 18:268–281. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03570.x
Huang Y, Liu A, Liang L, Jiang J, Luo H, Deng W et al (2018) Diagnostic value of blood parameters for community-acquired pneumonia. Int Immunopharmacol 64:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.08.022
Martín-Aspas A, Guerrero-Sánchez FM, García-Colchero F, Rodríguez-Roca S, Girón-González JA (2018) Differential characteristics of Acinetobacter baumannii colonization and infection: risk factors, clinical picture, and mortality. Infect Drug Resist 11:861–872. https://doi.org/10.2147/idr.s163944
Kim J, Lee JY, Lee H, Choi JY, Kim DH, Wi YM et al (2017) Microbiological features and clinical impact of the type VI secretion system (T6SS) in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates causing bacteremia. Virulence 8:1378–1389. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2017.1323164
Fernández-Bravo A, Kilgore P, Andersson J, Blears E, Figueras M, Hasan N et al (2019) Aeromonas hydrophilaT6SS and ExoA of flesh-eating in peritonitis and necrotizing fasciitis during mono- and polymicrobial infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:24084–24092. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1914395116
Basler M, Ho B, Mekalanos J (2013) Tit-for-tat: type VI secretion system counterattack during bacterial cell-cell interactions. Cell 152:884–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.01.042
Jani AJ, Cotter PA (2010) Type VI secretion: not just for pathogenesis anymore. Cell Host Microbe 8:2–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2010.06.012
Borgeaud S, Metzger LC, Scrignari T, Blokesch M (2015) The type VI secretion system of Vibrio cholerae fosters horizontal gene transfer. Science 347:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260064
Chen H, Yang D, Han F, Tan J, Zhang L, Xiao J et al (2017) The bacterial T6SS effector EvpP prevents NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting the Ca-dependent MAPK-Jnk pathway. Cell Host Microbe 21:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2016.12.004
Yen H, Sugimoto N, Tobe T (2015) Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli uses NleA to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation. PLoS Pathog 11:e1005121. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005121
Aubert D, Xu H, Yang J, Shi X, Gao W, Li L et al (2016) A burkholderia type VI effector deamidates Rho GTPases to activate the pyrin inflammasome and trigger inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 19:664–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2016.04.004
Dikshit N, Kale S, Khameneh H, Balamuralidhar V, Tang C, Kumar P et al (2018) NLRP3 inflammasome pathway has a critical role in the host immunity against clinically relevant Acinetobacter baumannii pulmonary infection. Mucosal Immunol 11:257–272. https://doi.org/10.1038/mi.2017.50
Bennett J, Capece D, Begalli F, Verzella D, D’Andrea D, Tornatore L et al (2018) NF-κB in the crosshairs: rethinking an old riddle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 95:108–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2017.12.020
Acknowledgements
All colleagues collaborated in the collection and interpretation of the data and contributed to the manuscript. We are grateful to Professor Yunsong Yu of the Infectious Diseases Department at Yifu Shao Hospital, which is affiliated with Zhejiang University, for providing the ATCC 17978 strain.
Funding
This study was supported by a Grant from the Nanyang Science and Technology Bureau (KJGG088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YH, SC, YZ, FW and AR. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YH and SC. QL and CL revised the manuscript and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. YH and SC contribute to this work equally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This is an retrospective study, so no ethical approval is required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Yy., Chen, S., Zhang, Yd. et al. Value of T6SS Core Gene hcp in Acinetobacter baumannii Respiratory Tract Infection. Indian J Microbiol 63, 291–298 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-023-01083-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-023-01083-8