Abstract
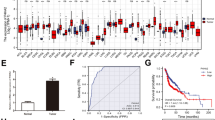
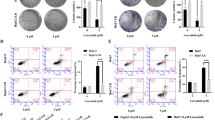
Erlotinib is an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) pathway. Although our previous study has proved the efficacy of Erlotinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), it has also demonstrated poor clinical response rates and disappointing results in clinical trials for HNSCC to date. In this study, we discovered elevated cell proliferation and invasion ability in erlotinib-resistant HNSCC cells. The contributions of miRNAs within extracellular vesicles (EVs) during the formation of chemoresistance were investigated in this study. Among up-regulated miRNAs in EVs derived from resistant cells, miR-7704, miR-21-5p and miR-3960 showed the most pro-tumorigenic alterations after transfection. Conversely, let-7i-5p, miR-619-5p and miR-30e-3p demonstrated tumor suppressive effects. By performing qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis, we found Vimentin played a pivotal role in modulating erlotinib resistance. Additionally, immune system was highlighted in the GO and KEGG analyses. Transfection of miR-7704, miR-21-5p significantly elevated CTLA-4 and LAG3 mRNA levels. Meanwhile, miR-3960 increased the relative mRNA expression of TIM3 in HNSCC cells. Transfection of let-7i-5p, miR-619-5p and miR-30e-3p decreased these checkpoint factors. To conclude, the present study described the roles of EVs-transmitted miRNAs on erlotinib resistance. Targeting the disregulated immune system could be the effective method to overcome erlotinib-resistance in HNSCC cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Nedawi K, Meehan B, Micallef J, Lhotak V, May L, Guha A, Rak J (2008) Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 10(5):619–624
Bach DH, Hong JY, Park HJ, Lee SK (2017) The role of exosomes and miRNAs in drug-resistance of cancer cells. Int J Cancer 141(2):220–230
Baron VT, Pio R, Jia Z, Mercola D (2015) Early growth response 3 regulates genes of inflammation and directly activates IL6 and IL8 expression in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 112(4):755–764
Bauman JE, Duvvuri U, Gooding WE, Rath TJ, Gross ND, Song J, Jimeno A, Yarbrough WG, Johnson FM, Wang L, Chiosea S, Sen M, Kass J, Johnson JT, Ferris RL, Kim S, Hirsch FR, Ellison K, Flaherty JT, Mills GB, Grandis JR (2017) Randomized, placebo-controlled window trial of EGFR, Src, or combined blockade in head and neck cancer. JCI Insight 2(6):e90449
Boelens MC, Wu TJ, Nabet BY, Xu B, Qiu Y, Yoon T, Azzam DJ, Twyman-Saint Victor C, Wiemann BZ, Ishwaran H, Ter Brugge PJ, Jonkers J, Slingerland J, Minn AJ (2014) Exosome transfer from stromal to breast cancer cells regulates therapy resistance pathways. Cell. 159(3):499–513
Casimiro MC, Velasco-Velazquez M, Aguirre-Alvarado C, Pestell RG (2014) Overview of cyclins D1 function in cancer and the CDK inhibitor landscape: past and present. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 23(3):295–304
Cassell A, Grandis JR (2010) Investigational EGFR-targeted therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19(6):709–722
Chen Y, Gao DY, Huang L (2015) In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: challenges and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 81:128–141
Chhabra R (2018) Let-7i-5p, miR-181a-2-3p and EGF/PI3K/SOX2 axis coordinate to maintain cancer stem cell population in cervical cancer. Sci Rep 8(1):7840
Cohen EE, Halpern AB, Kasza K, Kocherginsky M, Williams R, Vokes EE (2009) Factors associated with clinical benefit from epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in recurrent and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol 45(10):e155–e160
Cufi S, Bonavia R, Vazquez-Martin A, Oliveras-Ferraros C, Corominas-Faja B, Cuyas E, Martin-Castillo B, Barrajon-Catalan E, Visa J, Segura-Carretero A, Joven J, Bosch-Barrera J, Micol V, Menendez JA (2013) Silibinin suppresses EMT-driven erlotinib resistance by reversing the high miR-21/low miR-200c signature in vivo. Sci Rep 3:2459
Du B, Shim JS (2016) Targeting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to overcome drug resistance in cancer. Molecules 21(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21070965
Ehrengruber MU, Muhlebach SG, Sohrman S, Leutenegger CM, Lester HA, Davidson N (2000) Modulation of early growth response (EGR) transcription factor-dependent gene expression by using recombinant adenovirus. Gene. 258(1–2):63–69
Falzone L, Lupo G, La Rosa GRM, Crimi S, Anfuso CD, Salemi R, Rapisarda E, Libra M, Candido S (2019) Identification of novel MicroRNAs and their diagnostic and prognostic significance in oral cancer. Cancers (Basel) 11(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11050610
Goossens S, Vandamme N, Van Vlierberghe P, Berx G (2017) EMT transcription factors in cancer development re-evaluated: beyond EMT and MET. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1868(2):584–591
Gross ND, Bauman JE, Gooding WE, Denq W, Thomas SM, Wang L, Chiosea S, Hood BL, Flint MS, Sun M, Conrads TP, Ferris RL, Johnson JT, Kim S, Argiris A, Wirth L, Nikiforova MN, Siegfried JM, Grandis JR (2014) Erlotinib, erlotinib-sulindac versus placebo: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled window trial in operable head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20(12):3289–3298
Hahn AW, Gill DM, Pal SK, Agarwal N (2017) The future of immune checkpoint cancer therapy after PD-1 and CTLA-4. Immunotherapy. 9(8):681–692
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Bady P, Kamoshima Y, Kouwenhoven MC, Delorenzi M, Lambiv WL, Hamou MF, Matter MS, Koch A, Heppner FL, Yonekawa Y, Merlo A, Frei K, Mariani L, Hofer S (2011) Pathway analysis of glioblastoma tissue after preoperative treatment with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib--a phase II trial. Mol Cancer Ther 10(6):1102–1112
Huang D, Huang Y, Huang Z, Weng J, Zhang S, Gu W (2019) Relation of AURKB over-expression to low survival rate in BCRA and reversine-modulated aurora B kinase in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int 19:166
Keklikoglou I, Cianciaruso C, Guc E, Squadrito ML, Spring LM, Tazzyman S, Lambein L, Poissonnier A, Ferraro GB, Baer C, Cassara A, Guichard A, Iruela-Arispe ML, Lewis CE, Coussens LM, Bardia A, Jain RK, Pollard JW, De Palma M (2019) Chemotherapy elicits pro-metastatic extracellular vesicles in breast cancer models. Nat Cell Biol 21(2):190–202
Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH (2011) The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 11(1):9–22
Li S, Miao T, Sebastian M, Bhullar P, Ghaffari E, Liu M, Symonds AL, Wang P (2012) The transcription factors Egr2 and Egr3 are essential for the control of inflammation and antigen-induced proliferation of B and T cells. Immunity. 37(4):685–696
Liu B, Li J, Cairns MJ (2014) Identifying miRNAs, targets and functions. Brief Bioinform 15(1):1–19
Mahlab-Aviv S, Boulos A, Peretz AR, Eliyahu T, Carmel L, Sperling R, Linial M (2018) Small RNA sequences derived from pre-microRNAs in the supraspliceosome. Nucleic Acids Res 46(20):11014–11029
Martins RG, Parvathaneni U, Bauman JE, Sharma AK, Raez LE, Papagikos MA, Yunus F, Kurland BF, Eaton KD, Liao JJ, Mendez E, Futran N, Wang DX, Chai X, Wallace SG, Austin M, Schmidt R, Hayes DN (2013) Cisplatin and radiotherapy with or without erlotinib in locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a randomized phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 31(11):1415–1421
McNiel EA, Tsichlis PN (2017) Analyses of publicly available genomics resources define FGF-2-expressing bladder carcinomas as EMT-prone, proliferative tumors with low mutation rates and high expression of CTLA-4, PD-1 and PD-L1. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2016.45
Montermini L, Meehan B, Garnier D, Lee WJ, Lee TH, Guha A, Al-Nedawi K, Rak J (2015) Inhibition of oncogenic epidermal growth factor receptor kinase triggers release of exosome-like extracellular vesicles and impacts their phosphoprotein and DNA content. J Biol Chem 290(40):24534–24546
Morita K, Okamura T, Inoue M, Komai T, Teruya S, Iwasaki Y, Sumitomo S, Shoda H, Yamamoto K, Fujio K (2016) Egr2 and Egr3 in regulatory T cells cooperatively control systemic autoimmunity through Ltbp3-mediated TGF-beta3 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(50):E8131–E8140
Noman MZ, Janji B, Abdou A, Hasmim M, Terry S, Tan TZ, Mami-Chouaib F, Thiery JP, Chouaib S (2017) The immune checkpoint ligand PD-L1 is upregulated in EMT-activated human breast cancer cells by a mechanism involving ZEB-1 and miR-200. Oncoimmunology. 6(1):e1263412
Pilborough AE, Lambert DW, Khurram SA (2019) Extranodal extension in oral cancer: a role for the nodal microenvironment? Oral Pathol Med 48(10):863–870. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12870
Sesumi Y, Suda K, Mizuuchi H, Kobayashi Y, Sato K, Chiba M, Shimoji M, Tomizawa K, Takemoto T, Mitsudomi T (2017) Effect of dasatinib on EMT-mediated-mechanism of resistance against EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer 104:85–90
Shibue T, Weinberg RA (2017) EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(10):611–629
Suh Y, Amelio I, Guerrero Urbano T, Tavassoli M (2014) Clinical update on cancer: molecular oncology of head and neck cancer. Cell Death Dis 5:e1018
Takahashi RU, Prieto-Vila M, Hironaka A, Ochiya T (2017) The role of extracellular vesicle microRNAs in cancer biology. Clin Chem Lab Med 55(5):648–656
Tauro BJ, Mathias RA, Greening DW, Gopal SK, Ji H, Kapp EA, Coleman BM, Hill AF, Kusebauch U, Hallows JL, Shteynberg D, Moritz RL, Zhu HJ, Simpson RJ (2013) Oncogenic H-ras reprograms Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell-derived exosomal proteins following epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell Proteomics 12(8):2148–2159
Usuba W, Urabe F, Yamamoto Y, Matsuzaki J, Sasaki H, Ichikawa M, Takizawa S, Aoki Y, Niida S, Kato K, Egawa S, Chikaraishi T, Fujimoto H, Ochiya T (2019) Circulating miRNA panels for specific and early detection in bladder cancer. Cancer Sci 110(1):408–419
Van Roosbroeck K, Calin GA (2017) Cancer hallmarks and MicroRNAs: the therapeutic connection. Adv Cancer Res 135:119–149
Volinia S, Galasso M, Sana ME, Wise TF, Palatini J, Huebner K, Croce CM (2012) Breast cancer signatures for invasiveness and prognosis defined by deep sequencing of microRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(8):3024–3029
Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X, Zhou BP (2013) The role of snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 13(9):963–972
William WN Jr, Tsao AS, Feng L, Ginsberg LE, Lee JJ, Kies MS, Glisson BS, Kim ES (2018) Single arm, phase II study of Cisplatin, Docetaxel, and Erlotinib in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncologist. 23(5):526–e549
Yao M, Woods C, Lavertu P, Fu P, Gibson M, Rezaee R, Zender C, Wasman J, Sharma N, Machtay M, Savvides P (2016) Phase II study of erlotinib and docetaxel with concurrent intensity-modulated radiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E1770–E1776
Zhang W, Cai X, Yu J, Lu X, Qian Q, Qian W (2018) Exosome-mediated transfer of lncRNA RP11838N2.4 promotes erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Oncol 53(2):527–538
Zhang J, Sun W, Ren C, Kong X, Yan W, Chen X (2019) A PolH transcript with a short 3'UTR enhances PolH expression and mediates Cisplatin resistance. Cancer Res 79(14):3714–3724
Zheng Y, Wang Z, Ding X, Dong Y, Zhang W, Zhang W, Zhong Y, Gu W, Wu Y, Song X (2018a) Combined Erlotinib and PF-03084014 treatment contributes to synthetic lethality in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif 51(3):e12424
Zheng Y, Wang Z, Ding X, Zhang W, Li G, Liu L, Wu H, Gu W, Wu Y, Song X (2018b) A novel Notch1 missense mutation (C1133Y) in the Abruptex domain exhibits enhanced proliferation and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int 18(1)
Zibelman M, Mehra R (2016) Overview of current treatment options and investigational targeted therapies for locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Am J Clin Oncol 39(4):396–406
Zwijsen RM, Wientjens E, Klompmaker R, van der Sman J, Bernards R, Michalides RJ (1997) CDK-independent activation of estrogen receptor by cyclin D1. Cell 88(3):405–415
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81402236), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81772887), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD, 2018–87), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Team (CXTDA2017036), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK20171488) and Jiangsu Provincial Medical Youth Talent (QNRC2016854).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 10101 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Song, A., Zhou, Y. et al. Identification of extracellular vesicles-transported miRNAs in Erlotinib-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 14, 389–402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-020-00546-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-020-00546-7