Abstract
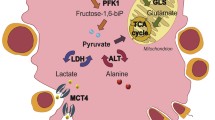
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-D3) is critical for the maintenance of normal male reproduction since reduced fertility is observed in vitamin D-deficient rats. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) is a membrane-bound enzyme that is localized on Sertoli cells and catalyses the transfer of the gamma-glutamyl residues to an amino acid or peptide acceptor. Sertoli cells are also responsible for providing nutrients, as lactate, to the development of germ cells. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect and the mechanism of action of 1,25-D3 on GGT on Sertoli cell functions from 30-day-old immature rat testis. Results demonstrated that 1,25-D3 stimulates GGT activity at Sertoli cells plasma membrane through a PKA-dependent mechanism of action, which was not dependent of active de novo protein synthesis. The hormone increases glucose uptake, as well as lactate production and release by Sertoli cells without altering the reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. In addition, 1,25-D3 did not change reduced glutathione (GSH) amount or oxygen consumption, and diminished Sertoli cell death. These findings demonstrate that 1,25-D3 stimulatory effect on GGT activity, glucose uptake, LDH activity and lactate production seem to be an important contribution of Sertoli cells for germ cells nutrition and for a full and active ongoing spermatogenesis.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BDC:
-
Bisdemethoxycurcumin
- CM:
-
Curcumin
- 1,25-D3 :
-
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
- 14C–DG:
-
[U-14C]-2-deoxy-D-glucose
- GGT:
-
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
- KRb:
-
Krebs Ringer-bicarbonate buffer
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- GSH:
-
Reduced gluthatione
- VDR:
-
Vitamin D receptor
- VDR-AP:
-
Vitamin D alternative pocket
- VDRnuc:
-
Vitamin D nuclear receptor
- VDRmem:
-
Vitamin D membrane receptor
- CH:
-
Cycloheximide
- ST:
-
Stearoylcarnitine chloride
References
Aly HAA, Khafagy RM (2011) 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-induced cytotoxicity accompanied by oxidative stress in rat Sertoli cells: possible role of mitochondrial fractions of Sertoli cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 252:273–280. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2011.02.019
Aprioku JS (2013) Pharmacology of free radicals and the impact of reactive oxygen species on the testis. J Reprod Infertil 14:158
Bajpai M, Gupta G, Setty BS (1998) Changes in carbohydrate metabolism of testicular germ cells during meiosis in the rat. Eur J Endocrinol 138:322–327
Berger AL, Randak CO, Ostedgaard LS et al (2005) Curcumin stimulates cystic fibrosis Transmembrane conductance regulator Cl- Channel activity. J Biol Chem 280:5221–5226. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412972200
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Blomberg Jensen M, Nielsen JE, Jorgensen A et al (2010) Vitamin D receptor and vitamin D metabolizing enzymes are expressed in the human male reproductive tract. Hum Reprod 25:1303–1311. doi:10.1093/humrep/deq024
Bouillon R, Okamura WH, Norman AW (1995) Structure-function relationships in the vitamin D endocrine system. Endocr Rev 16:200–257
Cardoso SM, Pereira C, Oliveira R (1999) Mitochondrial function is differentially affected upon oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 26:3–13
Caston LA, Sanborn BM (1988) Regulation of testicular and Sertoli cell gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase by follicle-stimulating hormone. Biol Reprod 38:109–113
Cazarolli LH, Folador P, Moresco HH et al (2009) Mechanism of action of the stimulatory effect of apigenin-6-C-(2″-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-l-fucopyranoside on 14C-glucose uptake. Chem Biol Interact 179:407–412. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.11.012
de Liz Oliveira Cavalli VL, Cattani D, Heinz Rieg CE et al (2013) Roundup disrupts male reproductive functions by triggering calcium-mediated cell death in rat testis and Sertoli cells. Free Radic Biol Med 65:335–346. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.043
de Paula Martins R, Glaser V, da Luz SD et al (2013) Platelet oxygen consumption as a peripheral blood marker of brain energetics in a mouse model of severe neurotoxicity. J Bioenerg Biomembr 45:449–457. doi:10.1007/s10863-013-9499-7
Dorrington JH, Roller NF, Fritz IB (1975) Effects of follicle-stimulating hormone on cultures of Sertoli cell preparations. Mol Cell Endocrinol 3:57–70
Galardo MN, Riera MF, Pellizzari EH et al (2008) Regulation of expression of Sertoli cell glucose transporters 1 and 3 by FSH, IL1β, and bFGF at two different time-points in pubertal development. Cell Tissue Res 334:295–304. doi:10.1007/s00441-008-0656-y
Galdieri M, Ziparo E, Palombi F et al (1981) Pure Sertoli cell cultures: a new model for the study of somatic-germ cell interactions. J Androl 2:249–254. doi:10.1002/j.1939-4640.1981.tb00625.x
Grootegoed JA, Oonk RB, Jansen R, Van der Molen HJ (1986) Metabolism of radiolabelled energy-yielding substrates by rat Sertoli cells. J Reprod Fertil 77:109–118
Habib FK, Maddy SQ, Gelly KJ (1990) Characterisation of receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in the human testis. J Steroid Biochem 35:195–199
Harding CO, Williams P, Wagner E et al (1997) Mice with genetic γ-glutamyl transpeptidase deficiency exhibit glutathionuria, severe growth failure, reduced life spans, and infertility. J Biol Chem 272:12560–12567
Hatefi Y, Haavik AG, Griffiths DE (1962) Studies on the electron transfer system XL. Preparation and properties of mitochondrial DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase. J Biol Chem 237:1676–1680
Hayes JD, Pulford DJ (1995) The glutathione S-transferase supergene family: regulation of GST and the contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 30:445–600. doi:10.3109/10409239509083491
Hodgen GD, Sherins RJ (1973) Enzymes as markers of testicular growth and development in the rat. Endocrinology 93:985–989. doi:10.1210/endo-93-4-985
Hutchesson A, Preece MA, Gray G, Green A (1997) Measurement of lactate in cerebrospinal fluid in investigation of inherited metabolic disease. Clin Chem 43:158–161
Ito R, Ihara H, Okada T, Ikeda Y (2014) 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances γ-glutamyl transpeptidase activity in LLC-PK1 porcine kidney epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2436
Jain SK, Micinski D (2013) Vitamin D upregulates glutamate cysteine ligase and glutathione reductase, and GSH formation, and decreases ROS and MCP-1 and IL-8 secretion in high-glucose exposed U937 monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 437:7–11. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.06.004
Jensen MB (2014) Vitamin D and male reproduction. Nat Rev Endocrinol 10:175–186. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2013.262
Johnson JA, Grande JP, Roche PC, Kumar R (1996) Immunohistochemical detection and distribution of the 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptor in rat reproductive tissues. Histochem Cell Biol 105:7–15
Jurutka PW, Bartik L, Whitfield GK et al (2007) Vitamin D receptor: key roles in bone mineral pathophysiology, molecular mechanism of action, and novel nutritional ligands. J Bone Miner Res 22:V2–V10. doi:10.1359/jbmr.07s216
Kinuta K, Tanaka H, Moriwake T et al (2000) Vitamin D is an important factor in estrogen biosynthesis of both female and male gonads. Endocrinology 141:1317–1324
Kowaltowski AJ, Vercesi AE (1999) Mitochondrial damage induced by conditions of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 26:463–471
Kumar TR, Wiseman AL, Kala G et al (2000) Reproductive defects in γ-glutamyl transpeptidase-deficient mice 1. Endocrinology 141:4270–4277
Kwiecinski GG, Petrie GI, DeLuca HF (1989) Vitamin D is necessary for reproductive functions of the male rat. J Nutr 119:741–744
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lu C, Steinberger A (1977) Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity in the developing rat testis. Enzyme localization in isolated cell types. Biol Reprod 17:84–88
Marchionatti AM, Picotto G, Narvaez CJ et al (2009) Antiproliferative action of menadione and 1,25(OH)2D3 on breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 113:227–232. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2009.01.004
Mareš V, Malík R, Lisá V, Šedo A (2005) Up-regulation of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) activity in growth perturbed C6 astrocytes. Mol Brain Res 136:75–80. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.01.007
Masoumi A, Goldenson B, Ghirmai S et al (2009) 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 interacts with curcuminoids to stimulate amyloid-beta clearance by macrophages of Alzheimer’s disease patients. J Alzheimers Dis JAD 17:703–717. doi:10.3233/JAD-2009-1080
Meister A (1988) Glutathione metabolism and its selective modification. J Biol Chem 263:17205–17208
Menegaz D, Rosso A, Royer C et al (2009) Role of 1α,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 on α-[1-14C]MeAIB accumulation in immature rat testis. Steroids 74:264–269. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2008.11.015
Menegaz D, Barrientos-Duran A, Kline A et al (2010) 1α,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 stimulation of secretion via chloride channel activation in Sertoli cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 119:127–134. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.01.011
Menegaz D, Mizwicki MT, Barrientos-Duran A et al (2011) Vitamin D receptor (VDR) regulation of voltage-gated chloride channels by ligands preferring a VDR-alternative pocket (VDR-AP). Mol Endocrinol 25:1289–1300. doi:10.1210/me.2010-0442
Meroni S, Cánepa D, Pellizzari E et al (1997) Regulation of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase activity by Ca2 + −and protein kinase C-dependent pathways in Sertoli cells. Int J Androl 20:189–194
Mizwicki MT, Norman AW (2009) The vitamin D sterol-vitamin D receptor ensemble model offers unique insights into both genomic and rapid-response signaling. Sci Signal 2:re4. doi:10.1126/scisignal.275re4
Nehar D, Mauduit C, Boussouar F, Benahmed M (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated lactate production is linked to lactate dehydrogenase a expression and activity increase in porcine cultured Sertoli cells 1. Endocrinology 138:1964–1971
Norman AW (2008) From vitamin D to hormone D: fundamentals of the vitamin D endocrine system essential for good health. Am J Clin Nutr 88:491S–499S
Norman AW, Roberts PA (1980) Steroid competition assay for determination of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Methods Enzymol 67:473–478
Norman AW, Ishizuka S, Okamura WH (2001a) Ligands for the vitamin D endocrine system: different shapes function as agonists and antagonists for genomic and rapid response receptors or as a ligand for the plasma vitamin D binding protein. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 76:49–59
Norman AW, Mena FR, Silva B (2001b) Structure function studies: identification of vitamin D analogs for the ligand-binding domains of important proteins in the vitamin D-endocrine system. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2:229–238
Norman AW, Bishop JE, Bula CM et al (2002) Molecular tools for study of genomic and rapid signal transduction responses initiated by 1α, 25 (OH) 2-vitamin D 3. Steroids 67:457–466
Orlowski M, Meister A (1963) Gamma-GLUTAMYL-P-NITROANILIDE: A New Convenient Substrate for determination and study of L- and D-gamma-GLUTAMYLTRANSPEPTIDASE Activities. Biochim Biophys Acta 73:679–681
Pandur S, Ravuri C, Moens U, Huseby N-E (2014) Combined incubation of colon carcinoma cells with phorbol ester and mitochondrial uncoupling agents results in synergic elevated reactive oxygen species levels and increased γ-glutamyltransferase expression. Mol Cell Biochem 388:149–156. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1906-1
Prelot M, Do TX, Planchenault P, Girault A (1990) In vitro effects of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol on alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyltransferase activity in hypophysectomized rats. Arch Int Physiol Biochim 98:59–66
Prelot M, Do TX, Giraul A, Thuillier A (1991) In vitro effects of 24R,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyltransferase in the kidney of hypophysectomized rats. Arch Int Physiol Biochim Biophys 99:269–273
Rato L, Alves MG, Socorro S et al (2012) Metabolic regulation is important for spermatogenesis. Nat Rev Urol 9:330–338. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2012.77
Ravuri C, Svineng G, Pankiv S, Huseby N-E (2011) Endogenous production of reactive oxygen species by the NADPH oxidase complexes is a determinant of γ-glutamyltransferase expression. Free Radic Res 45:600–610. doi:10.3109/10715762.2011.564164
Remor AP, de Matos FJ, Ghisoni K et al (2011) Differential effects of insulin on peripheral diabetes-related changes in mitochondrial bioenergetics: involvement of advanced glycosylated end products. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis 1812:1460–1471. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.06.017
Riera MF, Meroni SB, Gómez GE et al (2001) Regulation of lactate production by FSH, IL1β, and TNFα in rat Sertoli cells. Gen Comp Endocrinol 122:88–97. doi:10.1006/gcen.2001.7619
Robinson R, Fritz IB (1981) Metabolism of glucose by Sertoli cells in culture. Biol Reprod 24:1032–1041
Rosso A, Pansera M, Zamoner A et al (2012) 1α,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 stimulates rapid plasma membrane calcium influx via MAPK activation in immature rat Sertoli cells. Biochimie 94:146–154. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2011.10.001
Schteingart HF, Cigorraga S, León M et al (1988) Hormonal regulation of rat testicular γ-glutamyl-transpeptidase “in vivo” and “in vitro”/die hormonelle regulation von testikulärer γ-glutamyl-transpeptidase bei Ratten “in vivo” und “in vitro”. Andrologia 20:351–359
Sharpe RM, McKinnell C, Kivlin C, Fisher JS (2003) Proliferation and functional maturation of Sertoli cells, and their relevance to disorders of testis function in adulthood. Reproduction 125:769–784
Silva FRMB (2014) Functional importance of 1α,25(OH)2-vitamin D3 and the identification of its nongenomic and genomic signaling pathways in the testis. Adv Androl 2014:1–10. doi:10.1155/2014/808906
Tate SS, Meister A (1981) Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: catalytic, structural and functional aspects. Mol Cell Biochem 39:357–368
Tindall DJ, Rowley DR, Murthy L et al (1985) Structure and biochemistry of the Sertoli cell. Int Rev Cytol 94:127–149
Verkman AS, Galietta LJV (2009) Chloride channels as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:153–171. doi:10.1038/nrd2780
Wang W, Bernard K, Li G, Kirk KL (2007) Curcumin opens cystic fibrosis Transmembrane conductance regulator channels by a novel mechanism that requires neither ATP binding nor dimerization of the nucleotide-binding domains. J Biol Chem 282:4533–4544. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609942200
Zamoner A, Barreto KP, Filho DW et al (2007) Hyperthyroidism in the developing rat testis is associated with oxidative stress and hyperphosphorylated vimentin accumulation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 267:116–126. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2007.01.005
Zamoner A, Barreto KP, Filho DW et al (2008) Propylthiouracil-induced congenital hypothyroidism upregulates vimentin phosphorylation and depletes antioxidant defenses in immature rat testis. J Mol Endocrinol 40:125–135. doi:10.1677/JME-07-0089
Zanatta L, Zamoner A, Gonçalves R et al (2011a) Effect of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in plasma membrane targets in immature rat testis: ionic channels and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 515:46–53. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2011.09.001
Zanatta L, Zamoner A, Gonçalves R et al (2011b) 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 signaling pathways on calcium uptake in 30-day-old rat Sertoli cells. Biochemistry (Mosc) 50:10284–10292. doi:10.1021/bi201113n
Zanatta AP, Zanatta L, Gonçalves R et al (2013) Rapid responses to reverse T3 hormone in immature rat Sertoli cells: calcium uptake and exocytosis mediated by integrin. PLoS One 8:e77176. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077176
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico-Brasil (CNPq n° 472071/2013-0) and Coordenação de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Santa Catarina (FAPESC). RG, AR and DLS are registered on the PPG-Biochemistry/UFSC. APZ is registered on the PGFAR/UFSC. FRMBS, AZ and AL are recipient of CNPq productivity fellowship. We thank LAMEB I-CCB/UFSC technicians for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, R., Zamoner, A., Zanatta, L. et al. 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 signalling on immature rat Sertoli cells: gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and glucose metabolism. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 11, 233–243 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0367-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0367-1