Abstract
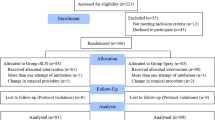
This study aimed at comparing the anesthetic efficacy of lidocaine injection versus pledgets soaked in lidocaine and epinephrine during radiosurgery of inferior turbinates. The study prospectively enrolled 120 outbound patients, who were randomly assigned to group 1 -anaesthesia with tampon soaked in lidocaine and adrenaline- or group 2 -anesthesia with tampon followed by lidocaine and adrenaline injection. The following parameters were evaluated by a visual analogue scale 1 h after surgery: pain, anxiety, chocking sensation and difficulty swallowing. Nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea, sneezing, headache and inferior turbinate size were evaluated preoperatively (T0), after 1 (T1), 2 (T2) and 3 months (T3) to surgery. The data collected were analyzed by statistic tests. Group 1 showed lesser pain than group 2 during the procedure (p < 0.01); no statistically significant differences were observed for anxiety, chocking sensation and difficulty swallowing. All patients, independently from the belonging group, significantly improved the nasal symptoms comparing T0 and T1 (p < 0.01), T2 (p < 0.01) and T3 (p < 0.01), without statistically significant differences among the groups. Radiofrequency turbinoplasty allowed to all patients to reduce the turbinates hypertrophy. Local anaesthesia with tampon allowed to obtain the same results the injective anaesthesia in term of surgical outcomes; the use of tampon allowed patients did not experience pain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Villwock JA, Kuppersmith RB (2018) Diagnostic algorithm for evaluating nasal airway obstruction. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 51(5):867–872
Ciprandi G, Tosca MA, Gallo F, Passali GC, Ameli F (2020) Turbinate hypertrophy in children with allergic rhinitis: clinical relevance. Acta bio-medica: Atenei Parmensis 91:43–47
Cox DR, Wise SK (2018) Medical treatment of nasal airway obstruction. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 51(5):897–908
Heppt W, Kertzscher U, Goubergrits L, Hildebrandt T (2013) The Concept of Rhinorespiratory Homeostasis—A New Approach to nasal breathing. Facial Plast Surg 29(02):085–92
Harju T, Numminen J, Kivekäs I, Rautiainen M (2018) A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study of inferior turbinate surgery. Laryngoscope 128(9):1997–2003
Unsal AA, Gregory N, Rosenstein K (2018) Current opinions in office-based rhinology. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 26(1):8–12
Armstrong M (2005) Office-based procedures in Rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 38(6):1327–1338
Safiruddin F, Vroegop AVMT, Ravesloot MJL, De Vries N (2012) Long-term self-reported treatment effects and experience of radiofrequency-induced thermotherapy of the inferior turbinates performed under local anesthesia: a retrospective analysis. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology. 270(6):1849–1853
Erol O, Buyuklu F (2020) Comparison of the efficacy of two different local anesthetics in inferior turbinate reduction. Am J Otolaryngol 41(6):102712
Camacho M, Zaghi S, Certal V, Abdullatif J, Means C, Acevedo J et al (2014) Inferior turbinate classification system, grades 1 to 4: development and validation study. Laryngoscope 125(2):296–302
Leong SC, Eccles R (2010) Inferior turbinate surgery and nasal airflow: evidence-based management. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 18(1):54–59
Acevedo JL, Camacho M, Brietzke SE (2015) Radiofrequency ablation Turbinoplasty versus Microdebrider-assisted Turbinoplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 153(6):951–956
Bakshi SS, Manoharan KS, Gopalakrishnan S (2017) Comparison of the long term efficacy of radiofrequency ablation and surgical turbinoplasty in inferior turbinate hypertrophy: a randomized clinical study. Acta Otolaryngol 137(8):856–861
Gunhan K, Unlu H, Yuceturk AV, Songu M (2010) Intranasal steroids or radiofrequency turbinoplasty in persistent allergic rhinitis: effects on quality of life and objective parameters. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268(6):845–850
Yan Y, Gordon WM, Wang DY (2013) Nasal epithelial repair and remodeling in physical injury, infection, and inflammatory diseases. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21(3):263–270
Leng T, Moshfeghi DM (2010) Branch Retinal artery occlusion after Septoplasty. Ophthalmic surgery. Lasers Imaging. 1–2
Chang MT, Jitaroon K, Nguyen T, Yan CH, Overdevest JB, Nayak JV et al (2019) Hemodynamic changes in patients undergoing office-based sinus procedures under local anesthesia. Int Forum Allergy Rhinology (Print) 10(1):114–120
Mundiya J, Woodbine E (2022) Updates on topical and local Anesthesia agents. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 34:147–155
Joki-Erkkilä VP, Kääriäinen J, Penttilä M, Rautiainen M (2002) Local Anesthesia with Emla Cream for Maxillary Sinus Puncture. Annals of Otology, Rhinology & Laryngology. 111(1):80–2
Mertes PM, Tajima K, Regnier-Kimmoun MA, Lambert M, Iohom G, Guéant-Rodriguez RM et al (2010) Perioperative Anaphylaxis Med Clin North Am 94(4):761–789
Martellucci S, Pagliuca G, de Vincentiis M, Greco A, Fusconi M, De Virgilio A et al (2014) EMLA® cream as local anesthetic for radiofrequency turbinate tissue reduction. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(10):2717–2722
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Giunta, A., Cianchetta, F., Liberati, L. et al. Topical Anesthesia Versus Submucosal Injection for Radiofrequency Turbinoplasty: Same Benefit but without Patient’s Pain. A Comparative Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04716-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04716-6