Abstract
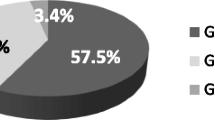
Mutations in the genes, GJB2 and GJB6 play an important role in autosomal recessive, non-syndromic hearing loss. This study is aimed to detect the association of mutations in GJB2 and GJB6 genes in familial autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment cases. We included 26 families with at least two affected individuals having congenital bilateral, non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Blood samples were drawn, DNA was extracted, and sent for multiplex PCR and Sanger sequencing. Of the 26 families analyzed, GJB2 mutations were detected in 9(34.6%) and GJB6 mutations were not detected in any of the families. GJB2 mutations are a major cause of congenital, non-syndromic hearing loss in this study population. This study also suggests that GJB6 mutations do not contribute to autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss in the Indian population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kral A, O’Donoghue GM (2010) Profound deafness in childhood. N Engl J Med 363:1438–1450
Wu X, Wang S et al (2018) Autosomal recessive congenital sensorineural hearing loss due to a novel compound heterozygous PTPRQ mutation in a Chinese Family. Neural Plast 2018:9425725
Adhikary B, Ghosh S et al (2015) Spectrum and frequency of GJB2, GJB6 and SLC26A4 gene mutations among non-syndromic hearing loss patients in eastern part of India. Gene 573:239–245
Kelsell DP, Dunlop J, Stevens HP et al (1997) Connexin 26 mutations in hereditary non-syndromic sensorineural deafness. Nature 387:80–83 (This was the first paper to describe mutations in the GJB2 genes)
Kelley PM, Harris DJ, Comer BC et al (1998) Novel mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) that cause autosomal recessive (DFNB1) hearing loss. Am J Hum Genet 62:792–799
Snoeckx RL, Huygen PL, Feldmann D et al (2005) GJB2 mutations and degree of hearing loss: a multicenter study. Am J Human Genet 77:945–957
Castillo I, Villamar M et al (2002) A deletion involving the connexin 30 gene in non-syndromic hearing impairment. N Engl J Med 346:243–249
Castillo I, Moreno-Pelayo MA et al (2003) Prevalence and evolutionary origins of the del(GJB6-D13S1830) mutation in the DFNB1 locus in hearing impaired subjects: a multicenter study. Am J Hum Genet 73:1452–1458
Maeda S, Nakagawa S, Suga M, Yamashita E, Oshima A, Fujiyoshi Y, Tsukihara T (2009) Structure of the connexin 26 gap junction channel at 35Å resolution. Nature 458(7238):597–602
Year (2007) Position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics 120(4):898–921
Ghosh M, Vijaya R, Kabra M (2004) Genetics of deafness in India. Indian J Pediatr 71(6):531–533
Yum SW, Zhang J, Valiunas V, Kanaporis G, Brink PR, White TW, Scherer SS (2007) Human connexin26 and connexin30 form functional heteromeric and heterotypic channels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293(3):C1032–C1048
Godbole K, Hemavathi J, Vaid N et al (2010) Low prevalence of GJB2 mutations in non-syndromic hearing loss in Western India. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 62:60–63
Bhalla S, Sharma R, Khandelwal G, Panda NK, Khullar M (2009) Low incidence of GJB2, GJB6 and mitochondrial DNA mutations in North Indian patients with non-syndromic hearing impairment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385(3):445–448
Santos RL, Wajid M, Pham TL, Hussan J, Ali G, Ahmad W, Leal SM (2005) Low prevalence of Connexin 26 (GJB2) variants in Pakistani families with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment. Clin Genet 67(1):61–68
Funding
This research received 6,00,000/- funds from RAJASTHAN UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH AND SCIENCES(RUHS), JAIPUR, RAJASTHAN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dadhich, A., Bhargava, S., Samdhani, S. et al. A Descriptive Observational Study of GJB2 and GJB6 Mutations in Familial Autosomal Recessive Non-syndromic Hearing Impairment. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 3575–3580 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03948-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03948-2