Abstract
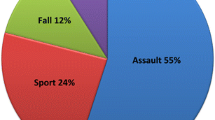
This study was conducted to evaluate the outcomes of closed reduction of different types of nasal bone fractures depending on time between onset of injury and reduction and comparing the outcomes of early closed reduction (within 6 h) of nasal bone fracture with late closed reduction (after 2 weeks). A hospital based Prospective cohort type of study was conducted among cases of nasal bone fracture attending the outpatient department of Otorhinolaryngology at Chettinad Hospital and Research Institute, Chennai during the months of August 2021 to January 2022. A total of 54 participants were included in the study. Primary outcome was to assess the effectiveness of closed reduction of different types of nasal bone fractures postoperatively. The second objective was to compare the outcomes of early closed reduction (within 6 h) of nasal bone fracture with late closed reduction (after 2 weeks). Using chi square test, the association of factors such as age, sex, mode of injury, external framework deformity, type of fracture and treatment was analyzed with outcome measures such as post op degree of deviation, arch irregularity, malalignment, bony irregularity, bony displacement, olfactory disturbances and result. We analyzed the sample data statistically and measured the outcomes which showed that post operatively after undergoing closed reduction, some degree of deviation was present in 17(31.48./.), arch irregularity present in 12(22.2./.), malalignment in 11(20.37./.), bony irregularity in 24(44.44./.), bony displacement in 19(35.19./.), olfactory disturbances in 2(3.70./.). Comparing the outcome factors between early and late reduction, we found that the outcome was better in early closed reduction when compared with late closed reduction. Among the 54 patients studied, the results of closed reduction were found to be excellent in 27(50./.), Fair in 16(29.63./.), Good in 10(18.52./.) and poor in 1(1.85./.) We could thus conclude from this study that early closed reduction of nasal bone fracture gave better results than a late closed reduction in terms of post operative deformity, arch irregularity, malalignment, bony irregularity, bony displacement and olfactory disturbances.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvi S, Patel BC. Nasal fracture reduction. StatPearls [Internet]. 2021
McQuillan KA, Makic MB (2019) Trauma nursing E-Book: from resuscitation through rehabilitation. Elsevier Health Sciences, New York
Flint PW, Haughey BH, Robbins KT, Thomas JR, Niparko JK, Lund VJ, Lesperance MM. Cummings otolaryngology-head and neck surgery e-book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2014 Nov 28.
Kang BH, Kang HS, Han JJ, Jung S, Park HJ, Oh HK, Kook MS (2019) A retrospective clinical investigation for the effectiveness of closed reduction on nasal bone fracture. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 41(1):1–6
Hwang K, You SH, Kim SG, Lee SI (2006) Analysis of nasal bone fractures; a six-year study of 503 patients. J Craniofac Surg 17(2):261–264
Kang CM, Han DG (2017) Objective outcomes of closed reduction according to the type of nasal bone fracture. Arch Craniofac Surg 18(1):30
Fertuzinhos A, Teixeira MA, Ferreira MG, Fernandes R, Correia R, Malheiro AR, Flores P, Zille A, Dourado N (2020) Thermo-mechanical behaviour of human nasal cartilage. Polymers 12(1):177
Das TA, Aslam AS, Mangalath U, Abida R, Nair RB, Soman S (2018) Evaluation of treatment outcome following closed reduction of nasal bone fractures. J Contemp Dent Pract 19(10):1174–1180
Han DG (2020) Considerations for nasal bone fractures: preoperative, perioperative, and postoperative. Arch Craniofac Surg 21(1):3
Klinginsmith M, Katrib Z. Nasal septal fracture. StatPearls [Internet]. 2020
Gupta A, Mahajan V, Jamwal PS. A Clinical Study of Nasal Bone Fractures: A Retrospective Study.
Kim L, Huddle MG, Smith RM, Byrne P. 2020 Nasal Fractures. In: Facial Trauma Surgery, (pp 122–128). Elsevier
Hwang K, Yeom SH, Hwang SH (2017) Complications of nasal bone fractures. J Craniofac Surg 28(3):803–805
Kang CM, Han DG (2017) Correlation between operation result and patient satisfaction of nasal bone fracture. Arch Craniofac Surg 18(1):25
Atighechi S, Karimi G (2009) Serial nasal bone reduction: a new approach to the management of nasal bone fracture. J Craniofac Surg 20(1):49–52
Sadhoo A, Sharma M, Singh P. Nasal bone fracture management-our experience
Han DS, Han YS, Park JH (2011) A new approach to the treatment of nasal bone fracture: the clinical usefulness of closed reduction using a C-arm. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64(7):937–943
Nishioka H, Kondoh S, Yuzuriha S (2018) Convex bone deformity after closed reduction of nasal bone fracture. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 71(1):85–89
Lee K, Yoo BH, Yon JH, Kim KM, Kim MC, Lee WY, Lee S, Lim YH, Nam SH, Choi YW, Kim H (2013) General anesthesia versus monitored anesthetic care with dexmedetomidine for closed reduction of nasal bone fracture. Korean J Anesthesiol 65(3):209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Raghvi, A., Priya, K., Rajasekaran, S. et al. Evaluating the Outcomes of Closed Reduction of Different Types of Nasal Bone Fractures. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 2998–3006 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03894-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03894-z