Abstract
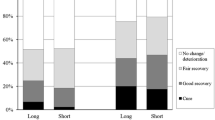
Sudden Sensory-Neural Hearing Loss (SSNHL) is one of the most important otologic emergency. Although adding intratympanic (IT) steroids to systematic steroid may be beneficial, the exact timing of the IT injections to provide the best response needs further investigations. To compare different protocols in treting sudden sensorineural hearing loss. We performed a clinical trial study on 120 patients from October 2021 to February 2022. All patients were prescribed 1 mg/Kg daily oral prednisolone. After randomization to three groups, the control group received standard twice a week IT steroid injections in 12 days (four total injections) while intervention groups 1 and 2 received once and twice a day IT injections for ten days. Audiometric study repeated 10–14 days after the last injection and assessed based on the Siegel criteria. We used the Chi-Square, Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), Kruskal–Wallis’s tests where appropriate. The most clinical improvement was found in the standard treatment group, and group-2 had the greatest number of patients with no improvement; however, no overall significant difference was observed among the three groups (p-value: 0.066; Pearson Chi-Square). Less frequent IT injections in patients already on systemic steroids provide similar results to more frequent injections.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article. Further enquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
References
Shewel Y, Asal SI (2020) Intratympanic injection of dexamethasone 4 mg/mL versus 10 mg/mL for management of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Egypt J Otolaryngol 36(1):1–6
Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, Schwartz SR et al (2019) Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 161:S1-45
Berjis N, Soheilipour S, Musavi A et al (2016) Intratympanic dexamethasone injection vs methylprednisolone for the treatment of refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Adv Biomed Res 5:111
Jung DJ, Park JH, Jang JH et al (2016) The efficacy of combination therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 126(8):1871–1876
Shirwany NA, Seidman MD, Tang W (1998) Effect of transtympanic injection of steroids on cochlear blood flow, auditory sensitivity, and histology in the guinea pig. Am J Otol 19(2):230–235
Lee JJ, Jang JH, Choo OS et al (2018) Steroid intracochlear distribution differs by administration method: systemic versus intratympanic injection. Laryngoscope 128(1):189–194
Hargunani CA, Kempton JB, DeGagne JM et al (2006) Intratympanic injection of dexamethasone: time course of inner ear distribution and conversion to its active form. Otol Neurotol 27(4):564–569
Suzuki H, Koizumi H, Ohkubo J-i et al (2016) Hearing outcome does not depend on the interval of intratympanic steroid administration in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Archiv Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 273(10):3101–7
Shewel Y, Asal S (2020) Intratympanic injection of dexamethasone 4 mg/mL versus 10 mg/mL for management of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Egypt J Otolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43163-020-00003-7
Chou YF, Chen PR, Kuo IJ et al (2013) Comparison of intermittent intratympanic steroid injection and near-continual transtympanic steroid perfusion as salvage treatments for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 123(9):2264–2269
Topf M, Hsu D, Adams D et al (2017) Rate of tympanic membrane perforation after intratympanic steroid injection. Am J Otolaryngol 38(1):21–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical Approval
This study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee of Approval Number: REC.1399.232. Written informed consent was obtained for participation in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nourizadeh, N., Rezaiee, N., Rajati, M. et al. Evaluation of Sudden Sensory-Neural Hearing Loss Patients Treated with Systemic Steroids with Additional Intratympanic Dexamethasone Injection in Different Intervals; a Clinical Trial Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75 (Suppl 1), 568–573 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03641-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03641-4