Abstract
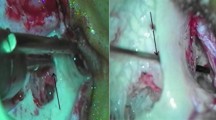
Facial recess approach through posterior tympanotomy is the most common & best appraoch for facilitating Cochlear Implant surgery through the round window. Sacrificing Chorda tympani nerve can be avoided by proper understanding of the anatomy of the Facial Recess & Chorda-Facial angles. Hence it is important to know the Chorda-Facial angle to prevent injury in Facial recess approach during Cochlear Implant surgery. Objective This study is done to know the Chorda-Facial angle variation with Round Window visibility during the Facial recess approach which is of relevance in Cochlear Implant surgery. Methods Thirty adult normal wet human cadaveric temporal bones were studied by performing by Posterior Tympanotomy & Facial Recess approach by using ZEISS microscope. Photographs were taken by digital camera of 26 megapixel, imported into computer, then Chorda-Facial angle were measured by Digimizer software & mean angle was calculated. Results The mean angle between the facial nerve & chorda tympani nerve was 20.232°. Bifurcation of chorda tympani nerve at the level of origin itself from the vertical segment of facial nerve was found in 6 Temporal bones out of 30. Round window visibility was noted in all 30 temporal bone specimens (100%). Conclusion The wide Chorda-Facial angle variations, especially the narrowest angle should be known to the otologist in particular to the Cochlear Implant surgeon, which may help avoid inadvertent damage to the CTN in facial recess approach during Cochlear Implant surgery & use diamond burr size of 0.6 mm or 0.8 mm.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No data support taken for this study.
References
Franz BK, Clark GM, Bloom DM (1987) Surgical anatomy of the round window with special reference to cochlear implantation. J Laryngol Otol 101(2):97–102. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022215100101343
McManus LJ, Dawes PJ, Stringer MD (2011) Clinical anatomy of the chorda tympani: a systematic review. J Laryngol Otol 125(11):1101–1108
Haynes DR (1955) The relations of the facial nerve in the temporal bone. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 16(3):175–185
Nager GT, Proctor B (1991) Anatomic variations and anomalies involving the facial canal. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 24(3):531–553
Măru N, Cheiţă AC, Mogoantă CA, Prejoianu B (2010) Intratemporal course of the facial nerve: morphological, topographic and morphometric features. Rom J Morphol Embryol 51(2):243–248
Durcan DJ, Shea JJ, Sleeckx JP (1967) Bifurcation of the facial nerve. Arch Otolaryngol 86(6):619–631. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1967.00760050621005
Zhu Y, Tong B, Xu S, Liu Y, Duan M, Lin C, Bi Y, Hou T, Wai J, Ke Za Z (2008) 22(19): 867–870
Calli C, Pinar E, Oncel S, Tatar B, Tuncbilek MA (2010) Measurements of the facial recess anatomy: implications for sparing the facial nerve and chorda tympani during posterior tympanotomy. Ear Nose Throat J 89(10):490–494
Öztürk K, Göde S, Çelik S et al (2016) Revisiting the anatomy of the facial recess: the boundaries of the round window exposure. Balkan Med J 33(5):552–555. https://doi.org/10.5152/balkanmedj.2016.150864
Hamamoto M, Murakami G, Kataura A (2000) Topographical relationships among the facial nerve, chorda tympani nerve and round window with special reference to the approach route for cochlear implant surgery. Clin Anat 13(4):251–256. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-2353(2000)13:4%3c251::AID-CA4%3e3.0.CO;2-E
Leong AC, Jiang D, Agger A, Fitzgerald-O’Connor A (2013) Evaluation of round window accessibility to cochlear implant insertion. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270(4):1237–1242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2106-4
Kalcıoğlu MT, Köse E, Bayındır T, Duman S (2011) A rare anatomic variation of the chorda tympani. Kulak BurunBogazIhtisDerg 21(3):171–172
Bhise SV, Patil NP, Hippergekar PM (2014) A very rare anatomical variation of chorda tympani nerve. IOSR J Dental Med Sci 13(7):117–119
Acknowledgements
We thank the Department of Anatomy for providing temporal bones & Department of ENT for constant support & guidance.
Funding
No funding taken for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Nil.
Ethical Approval
Under the valuable guidance of my teacher Dr. A.S. Harugop sir.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Damam, S.K., Harugop, A.K.S. Excursus in Chorda-Facial Angle Variation in Cochlear Implant Surgery: Cadaveric Temporal Bone Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75 (Suppl 1), 261–268 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-022-03415-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-022-03415-4