Abstract
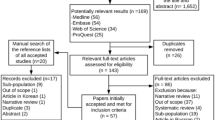
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease which affects the joints and bones of individuals diagnosed with this condition. Little remains known about the possible impact of this disease on hearing function, particularly the possibilities of preventive audiology in low-and-middle-income countries (LMICs). The study aimed to review published evidence on hearing function in adults with RA. A scoping review of literature from January 2010 to August 2020 was conducted using Sage, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Scopus, Medline, ProQuest and Google Scholar. Studies published in English which reported on the audiological function in adult individuals with RA were included in the review. From 832 initial title records, 18 articles were included into the final scoping review. A qualitative analysis of the reviewed evidence revealed four themes: (1) hearing loss occurs—causality still unclear; (2) nature, degree and configuration of the hearing loss varies; (3) systematic and standardized assessment battery required; and (4) sensitive and specific measures for early detection needed. The occurrence of hearing loss in this population ranges between 21.3 and 66.6%, and this increased where advanced sensitive measures such as ultrahigh frequency and otoacoustic emission (OAEs) measures were included in the test battery. Many audiological tests were used in the studies in order to identify the presence and type of hearing loss in these individuals, with basic audiometry testing being the most commonly used. The most prevalent type of hearing loss was found to be a high frequency sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), with mixed (MHL) and conductive hearing losses (CHL) being present in some of the individuals. Causal links between RA and hearing loss remains unclear. Although there are limited studies which have reported on the audiological function in the population with RA, the studies which have been reviewed seem to establish an association between RA and the presence of hearing loss. The published high prevalence of hearing loss in this population, when compared to healthy control groups raises implications for well-designed studies that utilize sensitive audiologic diagnostic measures, with clear inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure more accurate causal links establishment between RA and hearing loss in this population.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- SNHL:
-
Sensorineural hearing loss
- MHL:
-
Mixed hearing loss
- CHL:
-
Conductive hearing loss
- NSAIDS:
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- DMARDS:
-
Disease modifying anti rheumatic drugs
- LMIC:
-
Low- and middle-income country
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem response
- OAEs:
-
Otoacoustic emissions
- DPOAEs:
-
Distortion product OAEs
- TEOAEs:
-
Transient evoked OAEs
- VEMPS:
-
Vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials
- VNG:
-
Videonystagmography
- DPOAEs:
-
Distortion product otoacoustic emissions
- TEOAEs:
-
Transient evoked otoacoustic emissions
References
Guo Q, Wang Y, Xu D et al (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res 6(15). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-018-0016-9
Emamifer A, Hansen IMJ (2018) An update on hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Otol 13(1): 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joto.2017.10.002.
Heidari B (2011) Rheumatoid arthritis: early diagnosis and treatment outcomes. Caspian J Intern Med 2(1):161–170
Yildirim A, Surucu G, Dogan S, Karabiber M (2016) Relationship between disease activity and hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with controls. Clin Rheumatol 35(2):309–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3129-1
Lobo FS, Dossi MO, Batista L, Shinzato MM (2016) Hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: association with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. Clin Rheumatol 35(9):2327–2332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3278-x
Nasution MES, Haryuna TSH (2019) Elevated matrix metalloproteinase-3 level may affect hearing function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Chin Med Assoc 82(4):272–276. https://doi.org/10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000036
Pascual-Ramos V, Contreras-Yáñez I, Enríquez L, Valdés S, Ramírez-Anguiano J (2012) Hearing impairment in a tertiary-care-level population of Mexican rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Clin Rheumatol 18(8):393–398. https://doi.org/10.1097/RHU.0b013e31827732d3
Alonso L, Gutierrez-Farfan I, Peña-Ayala et al (2011) Clinical significance of auditive involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. Hindawi.Com. ISRN Rheumatol (3):208627. https://doi.org/10.5402/2011/208627
Selim ZI, Hamed SA, Elattar AM (2015) Peripheral and central auditory pathways function with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Clin Rheumatol 10(2):85–96. https://doi.org/10.2217/ijr.15.7
Pascual-Ramos V, Contreras-Yáñez I, Rivera-Hoyos P, Enríquez L, Ramírez-Anguiano J (2014) Cumulative disease activity predicts incidental hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clin Rheumatol 33(3):315–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2485-6
Jeong H, Chang YS, Baek SY et al (2016) Evaluation of audiometric test results to determine hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: analysis of data from the Korean national health and nutrition examination survey. PLoS One 11(10):e0164591. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164591. Published 2016 Oct 13
Tsirves GK, Voulgari PV, Pelechas E, Asimakopoulos AD, Drosos AA (2019) Cochlear involvement in patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases: a clinical and laboratory comparative study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 276(9):2419–2426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-019-05487-5
De la Vega M, Villarreal IM, Lopez-Moya J, Garcia-Berrocal JR (2016) Examination of hearing in a rheumatoid arthritis population: role of extended-high-frequency audiometry in the diagnosis of subclinical involvement. Scientifica (1). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5713283
Özcan M, Karakus MF, Gündüz OH, Tuncel Ü, Sahin H (2002) Hearing loss and middle ear involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol Int 22:16–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-002-0185-z
Ahmadzadeh A, Daraei M, Jalessi M et al (2017) Hearing status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Laryngol Otol 131(10):895–899. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215117001670
Galarza-Delgado DA, Villegas Gonzalez MJ, Riega Torres J, Soto-Galindo GA, Mendoza Flores L, Treviño González JL (2018) Early hearing loss detection in rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjögren syndrome using extended high frequency audiometry. Clin Rheumatol 37(2):367–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3959-0
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C et al (2018) Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMW Med Res Methodol 18:143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x
Spike J (2018) Principles for public health ethics. Ethics Med Public Health 4:13–20
Thompson M, Tiwari A, Fu R et al (2012) A framework to facilitate the use of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in the design of primary research studies. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2012 Jan. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83621/
Elbeltagy R, Galhom D, Hammad M, Dawa GA (2018) Audio-vestibular dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: an undervalued extra-articular feature. Indian J Otol 24:47–52
Rahne T, Clauß F, Plontke SK, Keyßer G (2017) Prevalence of hearing impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA, Wegener’s granulomatosis), or systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 36(7):1501–1510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3651-4
Huang CM, Chen HJ, Huang PH, Tsay GJ, Lan JL, Sung FC (2018) Retrospective cohort study on risk of hearing loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using claims data. BMJ Open 8(1):e018134. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018134
Baradaranfar MH, Doosti A (2010) A survey of relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and hearing disorders. Acta Med Iran 48(6):371–373
Özkırış M, Kapusuz Z, Günaydın İ, Kubilay U, Pırtı İ, Saydam L (2014) Does rheumatoid arthritis have an effect on audiovestibular tests? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271(6):1383–1387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2551-8
Lee SY, Kong IG, Oh DJ, Choi HG (2019) Increased risk of sudden sensory neural hearing loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort. Clin Rheumatol 38(3):683–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4333-6
Lee LY, Akhtar MM, Kirresh O, Gibson T (2012) Interstitial keratitis and sensorineural hearing loss as a manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis: clinical lessons from a rare complication. BMJ Case Rep 2012:bcr2012007324. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2012-007324
Kanji A, Khoza-Shangase K (2018) Objective hearing screening measures: an exploration of a suitable combination for risk-based newborn hearing screening. J Am Acad Audiol 29(6):495–502. https://doi.org/10.3766/jaaa.16155
Khoza-Shangase K, Masondo N (2020) In Pursuit of preventive audiology in South Africa: scoping the context for ototoxicity assessment and management. J Pharm Bioall Sci. https://doi.org/10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_334_19
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Institute for the Humanities and Social Sciences (NIHSS) for publication costs and funding towards time out for writing fees.
Funding
The authors thank the National Institute for the Humanities and Social Sciences (NIHSS) for providing financial assistance for the publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, RR and KKS; Methodology, RR and KKS; data collection, RR; Formal Analysis, RR and KKS; Investigation, RR and KKS; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, RR and KKS; Writing—Review & Editing, KKS; Supervision, KKS. Revisions, KKS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional ethics committee (University of the Witwatersrand’s Medical Human Research Ethics Committee: Ethical clearance waiver number: M200377).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoza-Shangase, K., Riva, R. Hearing Function in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Scoping Review for Preventive Audiology Planning. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 3), 3965–3976 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02747-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02747-x