Abstract
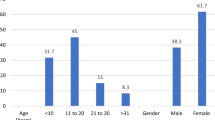
The usual indication for surgical resection of tonsils is chronic recurrent tonsillitis. Literature also does not indicate the reason behind the fact that only part of the population suffers from recurrent chronic tonsillitis in spite being exposed to similar conditions. This was a prospective study, in which 50 tonsil biopsy samples obtained from chronic tonsillitis patients. Specimens were analysed with rapid urease broth test, HelicotecUT PLUS assay and Toluidine blue staining for presence of Helicobacter pylori. The age ranged from 4 to 34 years. The median age for patients with chronic recurrent tonsillitis was 9.5, 23 (46%) patients were male while 27 (54%) were female, presence of H. pylori by rapid urease broth test, HelicotecUT PLUS assay and Histopathology was 4%. Our analysis revealed that H. pylori did not significantly colonize the tonsils and does not play a role in the pathogenesis or development of chronic tonsillitis. The heterogeneity in study population and methodology may have contributed to the non significant results.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- H. pylori :
-
Helicobacter pylori
- h:
-
Hours
- MALT:
-
Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue
- mm:
-
Millimetre
- min:
-
Minutes
- Ltd:
-
Limited
- GABHS:
-
Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus
References
Arora S, Agrawal M, Nazmi M, Kapoor NK (2008) Histological study of routine tonsillectomy specimen. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 60:309–313
Cammarota GA, Tursi L, Marinis De, Papa A, Valle D, Cuoco L et al (1997) Gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Scand J Gastroenterol 32(9):869–872
Pytko-Polonczyk J, Konturek SJ, Karczewska E, Bielański W, Kaczmarczyk-Stachowska A (1996) Oral cavity as permanent reservoir of Helicobacter pylori and potential source of re infection. J Physiol Pharmacol 47(1):121–129
Kim N, Lim SH, Lee KH, You JY, Kim JM, Lee NR et al (2000) Helicobacter pylori in dental plaque and saliva. Korean J Intern Med 15(3):187–194
Paradise JL, Bluestone CD, Bachman RZ et al (1984) Efficacy of tonsillectomy for recurrent throat infection in severely affected children. Results of parallel randomized and nonrandomized clinical trials. N Engl J Med 310:674–683
Khademi B, Imanieh MH, Gandomi B, Yeganeh F, Niknejad N (2005) Investigation of H. pylori colonization in adenotonsillectomy specimens by means of rapid urease (CLO) test. Iran J Med Sci 30(3):54–65
Peter Ochung O, Mugwe P, Masinde P, Waweru W (2015) The prevalence of H. pylori in tonsillar tissue of patients with adenotonsillar hypertrophy using Rapid Urease Test in a tertiary hospital in a sub Saharan country. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 67(3):223–226
Woolford TJ, Hanif J, Washband S, Hari CK, Ganguli LA (1999) The effect of previous antibiotic therapy on the bacteriology of the tonsils in children. Int J Clin Pract 53(2):96–98
Stoodley P, Debeer D, Longwell M, Nistico L, Hall-Stoodley L, Wenig B (2009) Tonsillolith: not just a stone but a living biofilm. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141:316–321
Ramírez A, Peidrola D, López A, Martínez MD, Ros MJ, Corral JL, Arteaga E (1997) Beta-hemolytic streptococci in tonsil hypertrophy and recurrent tonsillitis. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin 15(6):315–318
Zahedi MJ, Moghadam SD, Mosavi MA, Mirshekari T, Hayatbakhsh M (2009) Helicobacter pylori colonization in biopsies of the adenotonsillectomy specimens. Am J Appl Sci 6(12):2050–2053
Kariya Shin, Okano Mitsuhiro, Nishizaki Kazunori (2014) An association between Helicobacter pylori and upper respiratory tract disease: fact or fiction? World J Gastroenterol 20(6):1470–1484
Hwang MS, Forman SN, Kanter JA, Friedman M (2015) Tonsillar Helicobacter pylori colonization in chronic tonsillitis systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 141(3):245–249
Sakonlaya D, Apisarnthanarak A, Yamada N, Tomtitchong P (2014) Modified toluidine blue: an alternative stain for Helicobacter pylori detection in routine diagnostic use and post-eradication confirmation for gastric cancer prevention. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15(16):6983–6987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
No funding was received for this study
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical Approval
We have received ethical clearance from our institute ethical committee before starting the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mani, S., Rekha, A., Srinivasan, M.K.R. et al. To Evaluate the Role of H. pylori in Patients with Chronic Recurrent Tonsillitis. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71, 254–258 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1313-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1313-8