Abstract
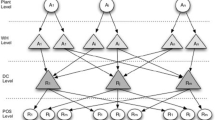
The primary purpose of this study is to empirically test the effects of trust, physical proximity, and network structure on the information-sharing ties across the Supply Chain Network (SCN) over time. Given a three-wave dataset, the Simulation Investigation for Empirical Network Analysis (SIENA) technique based on a Stochastic Actor-Oriented Model (SAOM) is employed to develop the research model. To do this, the two processes, including social selection (at the network level) and social influence (at the behavior level), are considered. The respondents of this study consisted of 91 chief executive officers from 32 Production Organizations (POs). The results revealed that information sharing was significantly the result of the social selection process. Physical proximity and network structure in the form of the social selection process affected information sharing. However, trust had no significant effect on information sharing. Indeed, trust may not directly predict information sharing rather indirectly explain it because of other phenomena such as physical proximity. Furthermore, the formation of information-sharing ties is not limited to the selection of a particular actor but is done with the aim of balancing the benefits and costs. The results provide managers with a set of useful mechanisms for enhancing information sharing across the supply chain.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Notes
The numbers 0 and 1 assigned to the two categories of actors towards the information-sharing process have no numerical value, meaning they are mere tags with no mathematical aspect. This scale simply divides actors into two distinct groups in terms of information sharing.
References
Abdeen F, Sandanayake Y (2018) Facilities Management Supply Chain: Functions, Flows and Relationships. Procedia Manuf 17:1104–1111
Ahn HJ, Lee H (2004) An agent-based dynamic information network for supply chain management. BT Technol J 22(2):18–27
Albino V, Fraccascia L, Giannoccaro I (2016) Exploring the role of contracts to support the emergence of self-organized industrial symbiosis networks: an agent-based simulation study. J Clean Prod 112:4353–4366
Amalou-Döpke L, Süß S (2014) HR measurement as an instrument of the HR department in its exchange relationship with top management: A qualitative study based on resource dependence theory. Scand J Manag 30(4):444–460
Banerjee M, Mishra M (2017) Retail supply chain management practices in India: A business intelligence perspective. J Retail Consum Serv 34:248–259
Benson T (2014) Building good management practices in Ethiopian agricultural cooperatives through regular financial audits. J Co-Operative Org Manag 2(2):72–82
Block P (2015) Reciprocity, transitivity, and the mysterious three-cycle. Soc Netw 40:163–173
Cai S, Jun M, Yang Z (2010) Implementing supply chain information integration in China: The role of institutional forces and trust. J Oper Manag 28(3):257–268
Caimo A, Friel N (2014) Actor-Based Models for Longitudinal Networks. In: Snijders TAB (ed) Encyclopedia of Social Network Analysis and Mining. Springer, pp 1–120
Çallı F, Sönmezer S (2018) A Model of Information Sharing Measurement in Integrated Supply Chain Networks. Paper presented at the Int Conf Eurasian Econ
Cao D, Li H, Wang G, Luo X, Yang X, Tan D (2017) Dynamics of project-based collaborative networks for BIM implementation: analysis based on stochastic actor-oriented models. J Manag Eng 33(3):04016055
Carnovale S, Rogers DS, Yeniyurt S (2016) Bridging structural holes in global manufacturing equity based partnerships: A network analysis of domestic vs. international joint venture formations. J Purchas Supply Manag 22(1):7–17
Carnovale S, Rogers DS, Yeniyurt S (2019) Broadening the perspective of supply chain finance: The performance impacts of network power and cohesion. J Purch Supply Manag 25(2):134–145
Chang C-W, Chiang DM, Pai F-Y (2012) Cooperative strategy in supply chain networks. Ind Mark Manage 41(7):1114–1124
Cheikhrouhou N, Pouly M, Madinabeitia G (2013) Trust categories and their impacts on information exchange processes in vertical collaborative networked organisations. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 26(1–2):87–100
Chen B (2008) Assesing interorganizational networks for public service delivery: A process-perceived effectiveness framework. Public Perform Manag Rev 31(3):348–363
Chen JV, Yen DC, Rajkumar T, Tomochko NA (2011) The antecedent factors on trust and commitment in supply chain relationships. Computer Standards & Interfaces 33(3):262–270
Cheng J-H (2011) Inter-organizational relationships and information sharing in supply chains. Int J Inf Manage 31(4):374–384
Cheng J-H, Chen S-W, Chen F-Y (2013) Exploring how inter-organizational relational benefits affect information sharing in supply chains. Inf Technol Manage 14(4):283–294
Cheng Y, Shen H (2020) United Airlines crisis from the stakeholder perspective: Exploring customers’ ethical judgment, trust and distrust, and behavioral intentions. Pub Relations Rev 101908
de la Haye K, Embree J, Punkay M, Espelage DL, Tucker JS, Green HD Jr (2017) Analytic strategies for longitudinal networks with missing data. Social Networks 50:17–25
Dou Y, Zhu Q, Sarkis J (2018) Green multi-tier supply chain management: An enabler investigation. J Purch Supply Manag 24(2):95–107
Ebrahim-Khanjari N, Hopp W, Iravani SM (2012) Trust and information sharing in supply chains. Prod Oper Manag 21(3):444–464
Feng Y (2012) System dynamics modeling for supply chain information sharing. Phys Procedia 25:1463–1469
Fu S, Han Z, Huo B (2017) Relational enablers of information sharing: evidence from Chinese food supply chains. Indust Manag Data Syst
Fu X, Han G (2017) Trust-embedded information sharing among one agent and two retailers in an order recommendation system. Sustainability 9(5):710
Galli F, Brunori G (2013) Short food supply chains as drivers of sustainable development. Evidence document
Gereffi G, Humphrey J, Sturgeon T (2005) The governance of global value chains. Rev Int Politic Econ 12(1):78–104
Gong Z, Wang H, Guo W, Gong Z, Wei G (2020) Measuring trust in social networks based on linear uncertainty theory. Inf Sci 508:154–172
Gremyr I, Birch-Jensen A, Kumar M, Löfberg N (2022) Quality functions’ use of customer feedback as activation triggers for absorptive capacity and value co-creation. Int J Oper Prod Manag 42(13):218–242
Ha AY, Tang CS (2017) Handbook of information exchange in supply chain management. Springer
Handfield RB, Bechtel C (2002) The role of trust and relationship structure in improving supply chain responsiveness. Ind Mark Manag 31(4):367–382
Hearnshaw EJ, Wilson MM (2013) A complex network approach to supply chain network theory. Int J Oper Prod Manag 33(4):442–469
Hill A, Doran D, Stratton R (2012) How should you stabilise your supply chains? Int J Prod Econ 135(2):870–881
Holland PW, Leinhardt S (1978) An omnibus test for social structure using triads. Sociol Methods Res 7(2):227–256
Hsu C-C, Kannan VR, Tan K-C, Keong Leong G (2008) Information sharing, buyer-supplier relationships, and firm performance: a multi-region analysis. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 38(4):296–310. https://doi.org/10.1108/09600030810875391
Huang Y-S, Hung J-S, Ho J-W (2017) A study on information sharing for supply chains with multiple suppliers. Comput Ind Eng 104:114–123
IMCLSW (2014) The cooperative sector law of the Islamic Republic of Iran's economy. http://coop.mcls.gov.ir/. Retrieved from http://coop.mcls.gov.ir/handler/dl_pubatt.aspx?a=1096
Kabelele DP (2019) The determinants of information sharing and the performance of supply chain: A case of beverage manufacturing companies in Dar es salaam. Mzumbe University, Tanzania
Kalantari K, Lavaei Adaryani R (2016) Identifying and explaining challenges faced by Iranian rural production cooperatives, based on a grounded theory paradigm. Coop Agric 17(5):33–51 (In Farsi)
Kang M, Park YE (2017) Exploring trust and distrust as conceptually and empirically distinct constructs: Association with symmetrical communication and public engagement across four pairings of trust and distrust. J Public Relations Res 29(2–3):114–135
Kao T-WD, Simpson N, Shao BB, Lin WT (2017) Relating supply network structure to productive efficiency: A multi-stage empirical investigation. Eur J Oper Res 259(2):469–485
Kärkkäinen M, Laukkanen S, Sarpola S, Kemppainen K (2007) Roles of interfirm information systems in supply chain management. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 37(4):264–286
Kechidi M, Talbot D (2010) Institutions and coordination: what is the contribution of a proximity-based analysis? The case of Airbus and its relations with the subcontracting network. Int J Technol Manage 50(3/4):285–299
Kembro J, Näslund D, Olhager J (2017) Information sharing across multiple supply chain tiers: A Delphi study on antecedents. Int J Prod Econ 193:77–86
Khan M, Hussain M, Papastathopoulos A, Manikas I (2018) Trust, information sharing and uncertainty: An empirical investigation into their impact on sustainability in service supply chains in the United Arab Emirates. Sustain Dev 26(6):870–878
Kim Y, Choi TY, Yan T, Dooley K (2011) Structural investigation of supply networks: A social network analysis approach. J Oper Manag 29(3):194–211
Kirezieva K, Bijman J, Jacxsens L, Luning PA (2016) The role of cooperatives in food safety management of fresh produce chains: Case studies in four strawberry cooperatives. Food Control 62:299–308
Knoben J, Oerlemans LA (2006) Proximity and inter-organizational collaboration: A literature review. Int J Manag Rev 8(2):71–89
Kulp SC, Lee HL, Ofek E (2004) Manufacturer benefits from information integration with retail customers. Manage Sci 50(4):431–444
Kumar N (1996) The power of trust in manufacturer-retailer relationships. Harv Bus Rev 74(6):92
Lage E, Alturas B (2012) Factors Influencing Information Sharing in Four SME Networks in Portugal-A Coordination Perspective. Paper presented at the KMIS
Lavaei Adaryani R, Kalantari K, Asadi A, Alambeigi A (2023) Surveying the institutional collaboration in the food supply chain: A qualitative study of livestock production cooperatives. Coop and Agr 11(2). https://doi.org/10.22034/AJCOOP.2022.345936.1783
Lee B-C, Kim P-S, Hong K-S, Lee I (2010) Evaluating antecedents and consequences of supply chain activities: an integrative perspective. Int J Prod Res 48(3):657–682
Lee C-H, Ha B-C (2018) The impact of buyer-supplier relationships’ social capital on bi-directional information sharing in the supply chain. J Bus Indust Market
Lee HK, Fernando Y (2015) The antecedents and outcomes of the medical tourism supply chain. Tour Manage 46:148–157
Lee HL, Padmanabhan V, Whang S (1997a) The bullwhip effect in supply chains. Sloan Manag Rev 38:93–102
Lee HL, Padmanabhan V, Whang S (1997b) Information distortion in a supply chain: The bullwhip effect. Manage Sci 43(4):546–558
Lee HL, So KC, Tang CS (2000) The value of information sharing in a two-level supply chain. Manage Sci 46(5):626–643
Leszczensky L, Pink S (2015) Ethnic segregation of friendship networks in school: Testing a rational-choice argument of differences in ethnic homophily between classroom-and grade-level networks. Soc Netw 42:18–26
Li T, Zhang H (2015) Information sharing in a supply chain with a make-to-stock manufacturer. Omega 50:115–125
Li Y, Ye F, Sheu C (2014) Social capital, information sharing and performance. Int J Opera Prod Manag
Luke DA (2015) A user's guide to network analysis in R. Springer
Madlberger M (2009) What drives firms to engage in interorganizational information sharing in supply chain management? Int J e-Collab (IJeC) 5(2):18–42
Malinowski B (1932) Crime and custom in savage society. Paul, Trench, Trubner, London
Maskey R, Fei J, Nguyen H-O (2017) Exploratory factor analysis-antecedents of information sharing in supply chains. Paper presented at the IAME2017
Maskey R, Fei J, Nguyen H-O (2020) Critical factors affecting information sharing in supply chains. Production Planning & Control 31(7):557–574
Mason‐Jones R, Towill DR (1997) Information enrichment: designing the supply chain for competitive advantage. Supply Chain Manag: An Int J
Mbhele TP (2014) Antecedents of Quality Information Sharing in the FMCG Industry. Journal of Economics and Behavioral Studies 6(12):986–1003
McKnight DH, Choudhury V, Kacmar C (2002) The impact of initial consumer trust on intentions to transact with a web site: a trust building model. J Strateg Inf Syst 11(3–4):297–323
Mena C, Humphries A, Choi TY (2013) Toward a theory of multi-tier supply chain management. J Supply Chain Manag 49(2):58–77
Mercken L, Snijders TA, Steglich C, Vartiainen E, De Vries H (2010) Dynamics of adolescent friendship networks and smoking behavior. Social Networks 32(1):72–81
Moberg CR, Cutler BD, Gross A, Speh TW (2002) Identifying antecedents of information exchange within supply chains. Int J Phys Distribut Logist Manag
Morgan RM, Hunt SD (1994) The commitment-trust theory of relationship marketing. J Market 20–38
Narang R, Sarin S, Singh P, Goyal R (2018) Impact of Reciprocity in Information Spreading Using Epidemic Model Variants. Information 9(6):136
Narasimhan R, Nair A (2005) The antecedent role of quality, information sharing and supply chain proximity on strategic alliance formation and performance. Int J Prod Econ 96(3):301–313
Nienhüser W (2008) Resource dependence theory-How well does it explain behavior of organizations? Manag Revue 9–32
Özer Ö, Zheng Y, Chen K-Y (2011) Trust in forecast information sharing. Manage Sci 57(6):1111–1137
Pai P, Tsai H-T (2016) Reciprocity norms and information-sharing behavior in online consumption communities: An empirical investigation of antecedents and moderators. Information & Management 53(1):38–52
Palouj M, Lavaei Adaryani R, Alambeigi A, Movarej M, Safi Sis Y (2021) Surveying the impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) on the poultry supply chain: A mixed methods study. Food Control 126:808410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108084
Patnayakuni R, Rai A, Seth N (2006) Relational antecedents of information flow integration for supply chain coordination. J Manag Inf Syst 23(1):13–49
Paulraj A, Lado AA, Chen IJ (2008) Inter-organizational communication as a relational competency: Antecedents and performance outcomes in collaborative buyer–supplier relationships. J Oper Manag 26(1):45–64
Pavlou PA (2002) Institution-based trust in interorganizational exchange relationships: the role of online B2B marketplaces on trust formation. J Strateg Inf Syst 11(3–4):215–243
Rached M, Bahroun Z, Campagne J-P (2015) Assessing the value of information sharing and its impact on the performance of the various partners in supply chains. Comput Ind Eng 88:237–253
Ramayah T, Omar R (2010) Information exchange and supply chain performance. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 9(01):35–52
Ripley RM, Snijders TA, Boda Z, Vörös A, Preciado P (2019) Manual for RSIENA. University of Oxford, Department of Statistics, Nuffield College, p 1
Ripley RM, Snijders TA, Boda Z, Vörös A, Preciado P (2020) Manual for RSIENA. University of Oxford, Department of Statistics, Nuffield College, p 1
Seiler A, Papanagnou C, Scarf P (2020) On the relationship between financial performance and position of businesses in supply chain networks. Int J Prod Econ 227:107690
Shaw AT, Gilly J-P (2000) On the analytical dimension of proximity dynamics. Reg Stud 34(2):169–180
Shen J (2020) An environmental supply chain network under uncertainty. Physica A 542:123478
Sherchan W, Nepal S, Paris C (2013) A survey of trust in social networks. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 45(4):1–33
Sirilertsuwan P, Ekwall D, Hjelmgren D (2018) Proximity manufacturing for enhancing clothing supply chain sustainability. Int J Logist Manag
Skilton PF, Bernardes E (2015) Competition network structure and product market entry. Strateg Manag J 36(11):1688–1696
Snijders TA, Steglich CE, Schweinberger M, Huisman M (2007) Manual for SIENA version 3.1. University of Groningen: ICS/Department of Sociology
Snijders TA, Van de Bunt GG, Steglich CE (2010) Introduction to stochastic actor-based models for network dynamics. Social Networks 32(1):44–60
Song H, Lu Q, Yu K, Qian C (2019) How do knowledge spillover and access in supply chain network enhance SMEs’ credit quality? Ind Manag Data Syst
Song H, Yu K, Ganguly A, Turson R (2016) Supply chain network, information sharing and SME credit quality. Ind Manag Data Syst 116(4):740–758
Teo LKY, Dang-Pham D, Nkhoma M (2016) Social Network Analysis Approach to Manage Information Risks and Sharing For Supply Chain Performance. Paper presented at the Intl Conf Opera Supply Chain Manag
Tichy NM, Tushman ML, Fombrun C (1979) Social network analysis for organizations. Acad Manag Rev 4(4):507–519
Todo Y, Matous P, Inoue H (2016) The strength of long ties and the weakness of strong ties: Knowledge diffusion through supply chain networks. Res Policy 45(9):1890–1906
Torre A (2008) On the role played by temporary geographical proximity in knowledge transmission. Reg Stud 42(6):869–889
Wang J-C, Wang Y-Y, Che T (2018) Information sharing and the impact of shutdown policy in a supply chain with market disruption risk in the social media era. In press, Inform Manag
Wang Q, Liu X, Liu Z, Xiang Q (2020) Option-based supply contracts with dynamic information sharing mechanism under the background of smart factory. Int J Prod Econ 220:107458
Wang Z, Ye F, Tan KH (2014) Effects of managerial ties and trust on supply chain information sharing and supplier opportunism. Int J Prod Res 52(23):7046–7061
Wei H-L, Wong CW, Lai K-H (2012) Linking inter-organizational trust with logistics information integration and partner cooperation under environmental uncertainty. Int J Prod Econ 139(2):642–653
Wu L, Chuang C-H, Hsu C-H (2014) Information sharing and collaborative behaviors in enabling supply chain performance: A social exchange perspective. Int J Prod Econ 148:122–132
Yam RC, Chan C (2015) Knowledge sharing, commitment and opportunism in new product development. Int J Opera Prod Manag
Yang Z, Zhang H, Xie E (2017) Relative buyer-supplier relational strength and supplier’s information sharing with the buyer. J Bus Res 78:303–313
Zhang M, Huo B (2013) The impact of dependence and trust on supply chain integration. Int J Phys Distribut Logist Manag
Acknowledgements
Firstly, the authors would like to thank Mohammad Javad Parvazi Shandi and Parham Jannati for helping with the data collection. Secondly, we are immensely grateful to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the earlier drafts of this paper. Finally, our special thanks go to Fatemeh Rezaei Adaryani for her continued support and patience.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Adaryani, R.L., Kalantari, K., Asadi, A. et al. Information sharing antecedents in the supply chain: a dynamic network perspective. Oper Manag Res 16, 887–903 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-022-00337-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-022-00337-w