Abstract
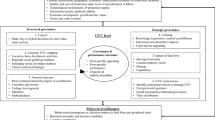
Supplier relationship management and supplier development initiatives assume a fundamental role in enterprise supply chain management. An important aspect of effective supplier relationship management is the role of trust. This paper seeks to understand whether supplier relationship management or supplier development initiative should be emphasized as a firm strives to achieve superior supplier performance. The analysis and discussion draws upon sourcing strategy literature and is based on empirical survey-data of mid to upper level managers with responsibility for supply management initiatives in their respective organizations in Denmark and in the USA. It examines the interrelationships among “relational norms”, “trust”, “supplier development initiatives” and ensuing “supplier performance”. The data analysis shows that firms must emphasize relation and trust building activities before investing in supplier development initiative. Supplier perception audits must be routinely performed to gauge the level of trust and strength of relational norms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson E, Weitz B (1992) The use of pledges to build and sustain commitment in distribution channels. J Mark Res 29:18–34
Apel H (1977) Simulation sozio-okonomischer Zusammenhange-Kritik und modification von systems analysis. Doctoral dissertation, J. von Goether University, Frankfurt am Main
Chaudry OB, Schnieper C (1999) Towards enterprise supply chain management. Supply Chain Manag Rev 3:72–82
Das A, Narasimhan R (2000) An examination of purchasing competence and its relationship with manufacturing performance. J Supply Chain Manag 36:17–28
Dwyer JH (1997) Effective inter-firm collaboration: how firms minimize transaction costs and maximize transaction value. Strateg Manage J 18:535–556
Ellram LM (1990) The supplier selection decision in strategic partnerships. J Purch Mater Manage 26:8–14
Fink RC, Edelman LF, Hatten KJ (2006) Relational exchange strategies, performance, uncertainty and knowledge. J Mark Theory Pract 14:139–153
Griffith DA, Harvey MG, Lusch RF (2006) Social exchange in inter-organizational relationships: the resulting benefits of procedural and distributive justice. J Oper Manag 24:85–98
Gulati R (1998) Alliances and networks. Strateg Manage J 19:293–317
Hair JF, Black WC, Babin B, Anderson RE, Tatham RL (2006) Multivariate data analysis. Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA
Handfield RB, Bechtel C (2002) The role of trust and relationship structure in improving supply chain responsiveness. Ind Mark Manage 31:367–82
Handfield RB, Bechtel C (2004) Trust, power, dependence, and economics: can SCM research borrow paradigms. International Journal of Integrated Supply Management 1:3–32
Handfield RB, Krause DR, Scannell TV, Monczka RM (2002) Avoid the pitfalls in supplier development. Sloan Manage Rev 41:37–52
Handfield RB, Nichols EL Jr (2002) Supply chain redesign. Financial Times Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA
Heide JB, John G (1992) Do norms matter in marketing relationships? J Mark 56:32–44
Heide JB, Miner AS (1992) The shadow of the future: effects of anticipated interaction and frequency of contact on buyer–seller cooperation. Acad Manage J 35:265–291
Jap SD (2001) ‘Pie-sharing’ in complex collaboration contexts. J Mark Res 38:86–99
Jap SD, Anderson E (2003) Safeguarding inter-organizational performance and continuity under ex post opportunism. Manage Sci 49:1684–1701
Krause DR (1999) The antecedents of buying firms’ efforts to improve suppliers. J Oper Manag 17:205–224
Liker JK, Choi TY (2004) Building deep supplier relationships. Harvard Bus Rev 82:104–113
Lusch F, Brown JR (1996) Interdependency, contracting, and relational behavior in marketing channels. International Journal of Marketing 60:19–38
Martin X, Swaminathan A, Mitchell W (1998) Organizational evolution in the inter-organizational environment: incentives and constraints on international expansion strategy. Adm Sci Q 43:566–601
Monczka RM, Petersen KJ, Handfield RB, Ragatz GL (1998) Success factors in strategic supplier alliances: the buying company perspective. Decision Sciences Journal 29:553–577
Mudambi R, Helper S (1998) The “close but adversarial” model of supplier relations in the U.S. auto industry. Strateg Manage J 1:775–792
Narasimhan R, Jayaram J, Carter JR (2001) An empirical examination of underlying dimensions of purchasing competence. Production Operations Management Journal 10:1–15
Nishiguchi T (1994) Strategic industrial sourcing. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, USA
Ring P, Van de Ven A (1994) Developmental processes of cooperative inter-organisational relationships. Acad Manage Rev 19:90–119
Rindfleisch A, Moorman C (2001) The acquisition and utilization of information in new product alliances: a strength-to-ties perspective. J Mark 65:1–18
Rindfleisch A, Moorman C (2003) Inter-firm cooperation and customer orientation. J Mark Res 40:421–436
Sako M (1997) Does trust improve business performance? In: Lane C, Backmann R (eds) Trust within and between organizations. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Shelanski H, Klein P (1995) Empirical research in transaction cost economics: a review and assessment. J Law Econ Organ 11:335–361
Zinkhan G, Joachimsthaler E, Kinnear T (1987) Individual differences and marketing decision support systems usage and satisfaction. J Mark Res 24:208–214
Zsidisin GA, Ellram LM (2003) An agency theory investigation of supply risk management. J Supply Chain Manag 39:15–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Sourcing strategy questionnaire
Please answer the following brief questionnaire on the souring strategy for a major item and the key supplier of the item in your firm.
Evaluate the following measures with respect to the item using the seven-point scale given below:

Buying firm’s investment in the major supplier | Level |
Transaction specific investment (in machine, training etc.) | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Financial assistance to supplier | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Technical assistance to supplier | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Training in quality/other operational aspects to supplier | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Incentives/awards to supplier | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Relational norms | |
Transaction specific investment by the supplier | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Usage of long-term contractual arrangement | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Top management’s commitment to relationship development | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Procurement manager’s concern for supplier earning a fair profit | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Joint problem solving with the supplier | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Formal procedures for supplier evaluation and feedback | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Cost/demand information sharing with the supplier | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Supplier performance | |
Degree of trust between the major supplier and buyer organization | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Cost reduction performance without compromising on quality or service | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Responsiveness to schedule changes without cost or time penalties | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Responsiveness to volume changes without cost or time penalties | 0 1–2–3–4–5–6–7 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narasimhan, R., Mahapatra, S. & Arlbjørn, J.S. Impact of relational norms, supplier development and trust on supplier performance. Oper Manag Res 1, 24–30 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-008-0004-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-008-0004-0